It Could Just Be Stress: The Teens of LeRoy and Conversion Disorder
... Roy, first settled way back in the 18th century, was best known as the birthplace of Jell-O. More unsettling than the tics and twitches themselves is the fact that nobody seems to know what is causing them. There are a couple of theories, though, the most prominent of which is that a 41-year-old tox ...
... Roy, first settled way back in the 18th century, was best known as the birthplace of Jell-O. More unsettling than the tics and twitches themselves is the fact that nobody seems to know what is causing them. There are a couple of theories, though, the most prominent of which is that a 41-year-old tox ...
here! - Eichlin`s AP psychology
... Severity to Justify Diagnosis of a Major Depressive Episode. c. Bi-Polar Disorder (Maniac Depressive Disorder) – Characterized by the Experience of 1 or More Manic Episodes as Well as Periods of Depression. i. Cyclothymic Disorder – When they Exhibit Chronic but Relatively Mild Symptoms of Bi-Polar ...
... Severity to Justify Diagnosis of a Major Depressive Episode. c. Bi-Polar Disorder (Maniac Depressive Disorder) – Characterized by the Experience of 1 or More Manic Episodes as Well as Periods of Depression. i. Cyclothymic Disorder – When they Exhibit Chronic but Relatively Mild Symptoms of Bi-Polar ...
Interpersonal Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT) for Bipolar Disorder
... In particular, IPSRT focuses on (1) the reciprocal relationships between life stress and the onset of mood disorder symptoms, (2) the importance of maintaining regular daily rhythms and sleep–wake cycles, and (3) the identification and management of potential precipitants of rhythm dysregulation, wi ...
... In particular, IPSRT focuses on (1) the reciprocal relationships between life stress and the onset of mood disorder symptoms, (2) the importance of maintaining regular daily rhythms and sleep–wake cycles, and (3) the identification and management of potential precipitants of rhythm dysregulation, wi ...
NHS Symptoms of Depression - the Central London CBT Training
... Mild depression has some impact on your daily life. Moderate depression has a significant impact on your daily life. Severe depression makes the activities of daily life nearly impossible. A small proportion of people with severe depression may have psychotic symptoms. ...
... Mild depression has some impact on your daily life. Moderate depression has a significant impact on your daily life. Severe depression makes the activities of daily life nearly impossible. A small proportion of people with severe depression may have psychotic symptoms. ...
Training - Illinois Co-Occurring Center for Excellence
... Marked and persistent fear of social or performance situations, possible scrutiny by others or may act in a way that will be embarrassing or humiliating Exposure to feared social situation provokes anxiety (or may have panic attack) Person recognizes that the fear is excessive Feared situations are ...
... Marked and persistent fear of social or performance situations, possible scrutiny by others or may act in a way that will be embarrassing or humiliating Exposure to feared social situation provokes anxiety (or may have panic attack) Person recognizes that the fear is excessive Feared situations are ...
Is it an Anxiety Disorder?
... • DSM believes (‘based on studies’) that 75% of those previously diagnosed with hypochondriasis will be diagnosed CSSD, and the remaining 25% who have high levels of anxiety but minimal somatic symptoms will be diagnosed Illness Anxiety Disorder ...
... • DSM believes (‘based on studies’) that 75% of those previously diagnosed with hypochondriasis will be diagnosed CSSD, and the remaining 25% who have high levels of anxiety but minimal somatic symptoms will be diagnosed Illness Anxiety Disorder ...
Ch. 18: Psychological Disorders Sec. 1: Understanding
... Two neurotransmitters in the brain—serotonin and noradrenaline—may partly explain the connection between genes and mood. ...
... Two neurotransmitters in the brain—serotonin and noradrenaline—may partly explain the connection between genes and mood. ...
13A-Psychdisorder-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
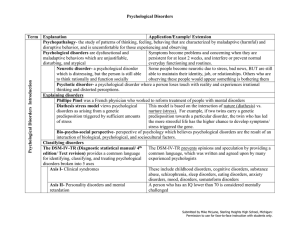
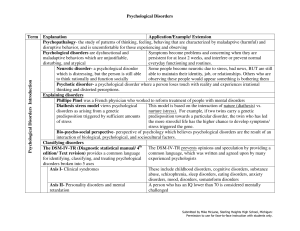
Psychological Disorders Term Explanation Application
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
Medicalizing Sadness - Student Pugwash USA
... obtained treatment in these settings only ten years earlier. The consumption of antidepressant medications has also dramatically expanded. At present, 3 of the 7 largest selling prescription drugs (Prozac, Paxil, and Xoloft) of any sort are anti-depressants. Persons treated for depression were four ...
... obtained treatment in these settings only ten years earlier. The consumption of antidepressant medications has also dramatically expanded. At present, 3 of the 7 largest selling prescription drugs (Prozac, Paxil, and Xoloft) of any sort are anti-depressants. Persons treated for depression were four ...
Comer, Abnormal Psychology, 5th edition
... hypomania and mild depressive symptoms, a diagnosis of cyclothymic disorder is appropriate • Mild symptoms for two or more years, interrupted by periods of normal mood • May blossom into bipolar I or II disorder • Affects 0.4% of the population ...
... hypomania and mild depressive symptoms, a diagnosis of cyclothymic disorder is appropriate • Mild symptoms for two or more years, interrupted by periods of normal mood • May blossom into bipolar I or II disorder • Affects 0.4% of the population ...
Slide 1
... disorders are at greater risk for developing depression when compared to children without an autism spectrum disorder (Barnhill, 2001; Ghaziuddin et al., 1998; Tantam, 1991). Research indicates as many as 38% of children with autism spectrum disorders also suffer from depression (Stewart et al., 200 ...
... disorders are at greater risk for developing depression when compared to children without an autism spectrum disorder (Barnhill, 2001; Ghaziuddin et al., 1998; Tantam, 1991). Research indicates as many as 38% of children with autism spectrum disorders also suffer from depression (Stewart et al., 200 ...
Practice Parameter for the Assessment and Treatment
... (Carlson, 2005). This atypical but common presentation of mania in children appears to be caused by developmental differences in manic symptom expression and the evolving picture of this disorder in children. Although current DSM-IV-TR nosology does not distinguish age-specific criteria for bipolar ...
... (Carlson, 2005). This atypical but common presentation of mania in children appears to be caused by developmental differences in manic symptom expression and the evolving picture of this disorder in children. Although current DSM-IV-TR nosology does not distinguish age-specific criteria for bipolar ...
NIMH Co-Occurring Disorders Curriculum
... • At risk for relapse • Criminality/criminal thinking • Housing needs • Transportation needs • Family reunification • Greater psychological impairment (e.g., trauma) ...
... • At risk for relapse • Criminality/criminal thinking • Housing needs • Transportation needs • Family reunification • Greater psychological impairment (e.g., trauma) ...
PROBLEM-SOLVING AND COGNITIVE SCARS IN MOOD AND ANXIETY DISORDERS:
... left by depression. Although it is clear that both children and adults exhibit a more pessimistic/hopeless explanatory style in the midst of a depressive episode (e.g., Nolen-Hoeksema, Girgus, & Seligman, 1986), there remains ambiguity as to whether people continue to possess a hopeless style after ...
... left by depression. Although it is clear that both children and adults exhibit a more pessimistic/hopeless explanatory style in the midst of a depressive episode (e.g., Nolen-Hoeksema, Girgus, & Seligman, 1986), there remains ambiguity as to whether people continue to possess a hopeless style after ...
Psych B – Module 28
... • Hereditary factors may result in a predisposition for developing anxiety disorders • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. ...
... • Hereditary factors may result in a predisposition for developing anxiety disorders • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. ...
Psychological Disorders
... Somatoform disorder is a condition in which the physical pain and symptoms a person feels are related to psychological factors. These symptoms can not be traced to a specific physical cause. Their symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other illnesses and may last for several years. People who have ...
... Somatoform disorder is a condition in which the physical pain and symptoms a person feels are related to psychological factors. These symptoms can not be traced to a specific physical cause. Their symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other illnesses and may last for several years. People who have ...
Guidelines for the Pharmacological Treatment of Antisocial and
... “Additional points” section expands on flow charts and incorporates text from previous version, to improve clarity. ...
... “Additional points” section expands on flow charts and incorporates text from previous version, to improve clarity. ...
4468 ANXIETY DISORDERS - PANIC DISORDER
... b. asked to focus primarily on their thought processes. c. given increased levels of light exposure over a period of several weeks 9. The following is not one of the symptoms that defines a panic attack: a. increased heart rate b. chest pain c. amnesia d. feeling dizzy 10. A panic disorder is distin ...
... b. asked to focus primarily on their thought processes. c. given increased levels of light exposure over a period of several weeks 9. The following is not one of the symptoms that defines a panic attack: a. increased heart rate b. chest pain c. amnesia d. feeling dizzy 10. A panic disorder is distin ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 11. Which of the following is not an example of a person who is likely to be suffering from major depression? • A) Bob, who does not make eye contact and feels hopeless • B) Jamie, who is preoccupied with death and only sleeps three hours per day • C) Steve, who can’t sleep because his father died ...
... 11. Which of the following is not an example of a person who is likely to be suffering from major depression? • A) Bob, who does not make eye contact and feels hopeless • B) Jamie, who is preoccupied with death and only sleeps three hours per day • C) Steve, who can’t sleep because his father died ...
Ch. 16 Psychological Disorders
... › It is generally agreed that behavior must interfere with normal activities and cause distress to be abnormal; behavior must be “maladaptive,” not meeting demands of day to day life (e.g., danger to self and/or others) ...
... › It is generally agreed that behavior must interfere with normal activities and cause distress to be abnormal; behavior must be “maladaptive,” not meeting demands of day to day life (e.g., danger to self and/or others) ...
Mental Health: Types of Mental Illness
... Impulse control and addiction disorders: People with impulse control disorders are unable to resist urges, or impulses, to perform acts that could be harmful to themselves or others. Pyromania (starting fires), kleptomania (stealing) and compulsive gambling are examples of impulse control disorders. ...
... Impulse control and addiction disorders: People with impulse control disorders are unable to resist urges, or impulses, to perform acts that could be harmful to themselves or others. Pyromania (starting fires), kleptomania (stealing) and compulsive gambling are examples of impulse control disorders. ...
Depression in the Elderly: Risk Factors and Treatment
... Heun, R., & Hein, S. (2005). Risk factors of major depression in the elderly. European Psychiatry, 20(3), 199-204. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2004.09.036 Jensen, H. V., Munk, K. P., & Madsen, S. A. (2010). Gendering late-life depression? the coping process in a group of elderly men. Nordic Psychology, 62( ...
... Heun, R., & Hein, S. (2005). Risk factors of major depression in the elderly. European Psychiatry, 20(3), 199-204. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2004.09.036 Jensen, H. V., Munk, K. P., & Madsen, S. A. (2010). Gendering late-life depression? the coping process in a group of elderly men. Nordic Psychology, 62( ...
Chapter 6 - Forensic Consultation
... These people may suffer from chronic distress and cope with this distress by exaggerating physical symptoms Treatment Same as somatization disorder, involving helping people identify feelings and thoughts behind the symptoms and find more adaptive ways of coping Chapter 6 ...
... These people may suffer from chronic distress and cope with this distress by exaggerating physical symptoms Treatment Same as somatization disorder, involving helping people identify feelings and thoughts behind the symptoms and find more adaptive ways of coping Chapter 6 ...
Tripken Abnoraml 16 Review geuide and study guid [Type text
... 2. decreased need for sleep (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep) 3. more talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking 4. flight of ideas or subjective experience that thoughts are racing 5. distractibility (i.e., attention too easily drawn to unimportant or irrelevant external stimul ...
... 2. decreased need for sleep (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep) 3. more talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking 4. flight of ideas or subjective experience that thoughts are racing 5. distractibility (i.e., attention too easily drawn to unimportant or irrelevant external stimul ...