OS Virtualization
... Figure 8-26. When the operating system in a virtual machine executes a kernel-only instruction, it traps to the hypervisor if virtualization technology is present. cs431-cotter Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, (c) 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-6006639 ...
... Figure 8-26. When the operating system in a virtual machine executes a kernel-only instruction, it traps to the hypervisor if virtualization technology is present. cs431-cotter Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, (c) 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-6006639 ...
OS Virtualization
... Figure 8-26. When the operating system in a virtual machine executes a kernel-only instruction, it traps to the hypervisor if virtualization technology is present. cs431-cotter Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, (c) 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-6006639 ...
... Figure 8-26. When the operating system in a virtual machine executes a kernel-only instruction, it traps to the hypervisor if virtualization technology is present. cs431-cotter Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, (c) 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-6006639 ...
Module 3: Operating
... Operating System Services OS as a service provider via system calls & commands ...
... Operating System Services OS as a service provider via system calls & commands ...
第二章
... 每一设备控制器有一局部缓存 CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers .CPU 通过局部缓存与主存交换数据 I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller. I/O是从设备到设备控制器的局部缓存 Device controller informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt. 设备控制器通过引起中断通知CPU操作已完成 ...
... 每一设备控制器有一局部缓存 CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers .CPU 通过局部缓存与主存交换数据 I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller. I/O是从设备到设备控制器的局部缓存 Device controller informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt. 设备控制器通过引起中断通知CPU操作已完成 ...
Fundamental Concepts
... Interrupts are a mechanism for causing the CPU to suspend its current computation and take up some new task. Control may be returned to the original task at some time later. Reasons for interrupts (or traps): – control of asynchronous I/O devices – CPU scheduling – exceptional conditions (e.g., div. ...
... Interrupts are a mechanism for causing the CPU to suspend its current computation and take up some new task. Control may be returned to the original task at some time later. Reasons for interrupts (or traps): – control of asynchronous I/O devices – CPU scheduling – exceptional conditions (e.g., div. ...
Chapter 2: Computer Systems Structures ("Computer Architecture")
... Disk surface is logically divided into tracks, which are subdivided ...
... Disk surface is logically divided into tracks, which are subdivided ...
Operating system structures
... Debugging facilities can greatly enhance the user’s and programmer’s abilities to efficiently use the system ...
... Debugging facilities can greatly enhance the user’s and programmer’s abilities to efficiently use the system ...
Operating Systems
... Windows XP 40 million lines of code Vista released 2007 Windows 7 (now!) Lecture 14: Operating Systems ...
... Windows XP 40 million lines of code Vista released 2007 Windows 7 (now!) Lecture 14: Operating Systems ...
What is an Operating System?
... • Time-Sharing Systems provide the following: – On-Line file system, where the files are on a collection of disks. Therefore, disk management must be provided. – A mechanism for concurrent execution, which requires CPU scheduling schemes. – Mechanisms for job synchronization and communication to ens ...
... • Time-Sharing Systems provide the following: – On-Line file system, where the files are on a collection of disks. Therefore, disk management must be provided. – A mechanism for concurrent execution, which requires CPU scheduling schemes. – Mechanisms for job synchronization and communication to ens ...
Operating System
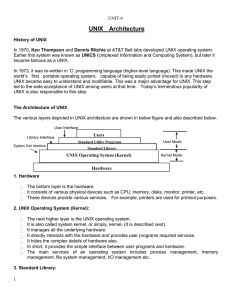
... Various flavors of UNIX have one thing in common. They all use the same set of system calls provided by POSIX standard. If any operating system is using other system calls, then it will not be a UNIX operating system. ...
... Various flavors of UNIX have one thing in common. They all use the same set of system calls provided by POSIX standard. If any operating system is using other system calls, then it will not be a UNIX operating system. ...
AppGuard - UTSA CS
... In our work, the OS is assumed to be untrustworthy since it is vulnerable to attacks due to its large code base, which consists of not only the kernel but also device drivers and system services. The large body of code exposes broad attack surfaces to attackers. The sensitive data of users' applicat ...
... In our work, the OS is assumed to be untrustworthy since it is vulnerable to attacks due to its large code base, which consists of not only the kernel but also device drivers and system services. The large body of code exposes broad attack surfaces to attackers. The sensitive data of users' applicat ...
D00_Files
... current Unix-like operating systems (OS) are POSIX compliant (or nearly so): Linux, BSD, Solaris, AIX, IRIX While an understanding of each operating system’s design is necessary to fully utilize its API, most functions work almost identically on any compliant operating system We will develop for ...
... current Unix-like operating systems (OS) are POSIX compliant (or nearly so): Linux, BSD, Solaris, AIX, IRIX While an understanding of each operating system’s design is necessary to fully utilize its API, most functions work almost identically on any compliant operating system We will develop for ...
Abstract View of System Components
... addresses of all the service routines. Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interrupted instruction. Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt. A trap is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user re ...
... addresses of all the service routines. Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interrupted instruction. Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt. A trap is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user re ...
What is an Operating System?
... by an error (ex: Division by zero or invalid memory access) Or by a request from a user program for operating system service System call Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system Dual-mode operation allows OS to protect itself and oth ...
... by an error (ex: Division by zero or invalid memory access) Or by a request from a user program for operating system service System call Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system Dual-mode operation allows OS to protect itself and oth ...
Chapter 1: OS overview
... by an error (ex: Division by zero or invalid memory access) Or by a request from a user program for operating system service System call Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system Dual-mode operation allows OS to protect itself and oth ...
... by an error (ex: Division by zero or invalid memory access) Or by a request from a user program for operating system service System call Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system Dual-mode operation allows OS to protect itself and oth ...
Layer 1 Process Management
... terminates. It is neither swapped out and also never moved to another place in memory. This strategy deserves some explanation. It derives from three factors: (1) the idea that MINIX is for personal computers, rather than for large time sharing systems. (2) the desire to have MINIX work on all IBM P ...
... terminates. It is neither swapped out and also never moved to another place in memory. This strategy deserves some explanation. It derives from three factors: (1) the idea that MINIX is for personal computers, rather than for large time sharing systems. (2) the desire to have MINIX work on all IBM P ...
Unix Commands
... computer, including memory, file storage, and CPU. • Multitasking (the ability for more than one application to “run” at once) is possible on new computers. ...
... computer, including memory, file storage, and CPU. • Multitasking (the ability for more than one application to “run” at once) is possible on new computers. ...
9781439079201_PPT_ch14
... – System begins interaction with user • List of system’s primary subdirectories and files • Any system-generated configuration files • Any user-generated booting instructions ...
... – System begins interaction with user • List of system’s primary subdirectories and files • Any system-generated configuration files • Any user-generated booting instructions ...
View
... I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently. Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type (Use CPU more and more). Each device controller has a local buffer. CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller. Device ...
... I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently. Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type (Use CPU more and more). Each device controller has a local buffer. CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller. Device ...
Four Components of a Computer System
... I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently" Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type" Each device controller has a local buffer" CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers" I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller" Device contr ...
... I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently" Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type" Each device controller has a local buffer" CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers" I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller" Device contr ...
Linux - Rock Fort Networks
... any other operating system.[citation needed] It is a leading operating system on servers and other big iron systems such as mainframe computers and supercomputers. Although not released until 1992 due to legal complications, development of 386BSD, from which NetBSD, OpenBSD and FreeBSD descended, ...
... any other operating system.[citation needed] It is a leading operating system on servers and other big iron systems such as mainframe computers and supercomputers. Although not released until 1992 due to legal complications, development of 386BSD, from which NetBSD, OpenBSD and FreeBSD descended, ...
Computer Science - Rainhill High School
... Be able to type at least one instruction at a command prompt Understand that there are two ways to manage files and folders Be able to move, copy, rename and delete files and folders at a command prompt Be able to identify advantages and disadvantages of both graphical and command line methods for m ...
... Be able to type at least one instruction at a command prompt Understand that there are two ways to manage files and folders Be able to move, copy, rename and delete files and folders at a command prompt Be able to identify advantages and disadvantages of both graphical and command line methods for m ...
Lecture #3: Operating
... Debugging facilities can greatly enhance the user’s and programmer’s abilities to efficiently use the system ...
... Debugging facilities can greatly enhance the user’s and programmer’s abilities to efficiently use the system ...
Acorn MOS

Acorn's Machine Operating System (MOS) or OS was a computer operating system used in the Acorn BBC computer range. It included support for four-channel sound and graphics, file system abstraction, and digital and analogue I/O including a daisy-chained fast expansion bus. The implementation was single-tasking, monolithic and non-reentrant.Versions 0.10 to 1.20 were used on the BBC Micro, version 1.00 on the Electron, version 2 was used on the B+, and versions 3 to 5 were used in the BBC Master Series range.The final BBC computer, the BBC A3000, was 32-bit and ran RISC OS. Its operating system used portions of the Acorn MOS architecture and shared a number of characteristics (commands, VDU system) with the earlier 8-bit MOS.Versions 0 and 1 of the MOS were 16KiB in size, written in 6502 machine code, and held in ROM on the motherboard. The upper quarter of the 16-bit address space (0xC000 to 0xFFFF) is reserved for its ROM code and I/O space.Versions 2 to 5 were still restricted to a 16KiB address space but managed to hold more code and hence more complex routines, partly because of the alternative 65C102 CPU with its denser instruction set plus the careful use of paging.