REACH FOR THE STARS MLK 2009
... How many AU does light travel in one year? _____________ What are Hayashi tracks? ______________________________________________________________ What causes a sun like star to suddenly contract in diameter? ___________________________________ How many times will a blue giant orbit the center of the ...
... How many AU does light travel in one year? _____________ What are Hayashi tracks? ______________________________________________________________ What causes a sun like star to suddenly contract in diameter? ___________________________________ How many times will a blue giant orbit the center of the ...
Toys Watch the Sky - The Sun is a close star
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
Chapter 12
... 1. Binary stars are important because they allow us to measure stellar masses using Kepler’s third law as modified by Newton. 2. Knowledge of the size of one of the star’s ellipses, along with knowledge of the period of its motion, permits calculation of the total mass of the two stars. 3. To determ ...
... 1. Binary stars are important because they allow us to measure stellar masses using Kepler’s third law as modified by Newton. 2. Knowledge of the size of one of the star’s ellipses, along with knowledge of the period of its motion, permits calculation of the total mass of the two stars. 3. To determ ...
Physical Science Laboratory: Skyglobe
... given: First set the location then press F to find the star. Then F11 to show RA-Dec lines on lower left screen. Star Meaning of Name Features RA DEC Location Alpha Centauri ...
... given: First set the location then press F to find the star. Then F11 to show RA-Dec lines on lower left screen. Star Meaning of Name Features RA DEC Location Alpha Centauri ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III
... Example III–7. We measure the trigonometric parallax of a visual binary star as 0.20 arcsec and measure an angular separation between the pair of stars in this binary as 5 arcsec. Over a few years of observations, we determine the orbital period of this pair to be 30 years. What is the combined mass ...
... Example III–7. We measure the trigonometric parallax of a visual binary star as 0.20 arcsec and measure an angular separation between the pair of stars in this binary as 5 arcsec. Over a few years of observations, we determine the orbital period of this pair to be 30 years. What is the combined mass ...
Chandra Emission Line Diagnostics of Sco
... Dr. David Cohen, Swarthmore College With a new high-resolution spectrum from the Chandra x-ray telescope we investigated the properties of the wind of the hot main sequence star Sco. We were able to fit line profiles to many of the lines between 4 and 26 Å, and thus to measure their widths. The ma ...
... Dr. David Cohen, Swarthmore College With a new high-resolution spectrum from the Chandra x-ray telescope we investigated the properties of the wind of the hot main sequence star Sco. We were able to fit line profiles to many of the lines between 4 and 26 Å, and thus to measure their widths. The ma ...
Abs-Apar Mag
... – A ranking system – Brightest stars = 1st class, then 2nd, 3rd… – 6th magnitude are faintest stars seen at night – Result: lower number = brighter “There is no other rule for classing the stars but the estimation of the observer; and hence it is that some astronomers reckon those stars of the first ...
... – A ranking system – Brightest stars = 1st class, then 2nd, 3rd… – 6th magnitude are faintest stars seen at night – Result: lower number = brighter “There is no other rule for classing the stars but the estimation of the observer; and hence it is that some astronomers reckon those stars of the first ...
Slide 1
... closest to the Sun? Which of these stars is the brightest? Which of these stars has the largest diameter? Which of these stars has the lowest temperature? ...
... closest to the Sun? Which of these stars is the brightest? Which of these stars has the largest diameter? Which of these stars has the lowest temperature? ...
How Bright is that star?
... Relates luminosity, temperature and Radius of a star. The luminosity/meter² (l), is determined by the temperature (T) of that area ) l = σT⁴ (σ is a constant which if T is in °K, l comes out in Watts) Surface area is determined by radius(R): A = 4πR² So the total Lumnosity of star becomes L = 4πR²σT ...
... Relates luminosity, temperature and Radius of a star. The luminosity/meter² (l), is determined by the temperature (T) of that area ) l = σT⁴ (σ is a constant which if T is in °K, l comes out in Watts) Surface area is determined by radius(R): A = 4πR² So the total Lumnosity of star becomes L = 4πR²σT ...
THE CONSTELLATION OCTANS, THE OCTANT
... Nu Octantis is the brightest star in the constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.76 and is approximately 69 light years distant from the solar system. The star is an orange giant with the stellar classification K1III. It is one of the least luminous giant stars known, with a mass 1.4 ...
... Nu Octantis is the brightest star in the constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.76 and is approximately 69 light years distant from the solar system. The star is an orange giant with the stellar classification K1III. It is one of the least luminous giant stars known, with a mass 1.4 ...
constellations - Otterbein University
... - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. ...
... - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. ...
Chapter21
... close pair are close enough together to do so. 2. Binaries with periods less than a few years are usually only a few AU apart. This is too close together for their images to be separated so that they would be seen as a visual binary. 3. If the binary doesn’t appear to obey Kepler’s laws, the orbit m ...
... close pair are close enough together to do so. 2. Binaries with periods less than a few years are usually only a few AU apart. This is too close together for their images to be separated so that they would be seen as a visual binary. 3. If the binary doesn’t appear to obey Kepler’s laws, the orbit m ...
1 How luminous are stars?
... middle, rA = rB. The more unequal the masses are, the more it shifts toward the more massive star. ...
... middle, rA = rB. The more unequal the masses are, the more it shifts toward the more massive star. ...
Bluffing your way in Astronomy: Taurus
... shine light into space, so it still ends up brighter than the Sun. It’s a old star too, being much further through its lifecycle than the Sun, having exhausted its supply of hydrogen it is now generating energy by fusing atoms of helium into carbon. In other words, it isn’t too well and is on the st ...
... shine light into space, so it still ends up brighter than the Sun. It’s a old star too, being much further through its lifecycle than the Sun, having exhausted its supply of hydrogen it is now generating energy by fusing atoms of helium into carbon. In other words, it isn’t too well and is on the st ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
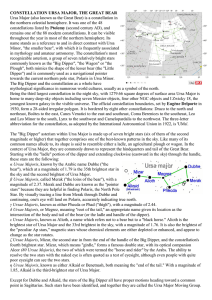
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
... Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its ...
... Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... • Stellar lifetimes depend on mass; the more the mass, the shorter the lifetime ...
... • Stellar lifetimes depend on mass; the more the mass, the shorter the lifetime ...
The Properties of Stars
... along their orbits. In the following figures, wavelength increases toward the right and only the hydrogen Balmer lines are shown. In each case, the Balmer lines observed in the laboratory are displayed on the bottom for comparison with the binary’s spectrum on the top. The first figure shows the spe ...
... along their orbits. In the following figures, wavelength increases toward the right and only the hydrogen Balmer lines are shown. In each case, the Balmer lines observed in the laboratory are displayed on the bottom for comparison with the binary’s spectrum on the top. The first figure shows the spe ...
elementary measuring stars
... Parsec. A measure of distance for an object that has a parallax of 1 arcsecond = 3.26 light years. Magnitude, m. A scale developed by Hipparchus to rank the naked-eye stars in terms of brightness. Luminosity. The rate at which a star emits light, often measured using absolute magnitude. Absolute Mag ...
... Parsec. A measure of distance for an object that has a parallax of 1 arcsecond = 3.26 light years. Magnitude, m. A scale developed by Hipparchus to rank the naked-eye stars in terms of brightness. Luminosity. The rate at which a star emits light, often measured using absolute magnitude. Absolute Mag ...
Chapter 11: Stars
... It would be only 1/3 as bright It would be only 1/6 as bright It would be only 1/9 as bright It would be three times brighter ...
... It would be only 1/3 as bright It would be only 1/6 as bright It would be only 1/9 as bright It would be three times brighter ...
Constellations, Star Names, and Magnitudes
... What brightness difference corresponds to 1 step in magnitude? Need to know what number you have to multiply by itself five times to get 100. That number is 2.5118864315095…. (usually rounded to 2.512 when used in calculations). So 1 step in magnitude corresponds to a 2.512× difference in brightness ...
... What brightness difference corresponds to 1 step in magnitude? Need to know what number you have to multiply by itself five times to get 100. That number is 2.5118864315095…. (usually rounded to 2.512 when used in calculations). So 1 step in magnitude corresponds to a 2.512× difference in brightness ...
Luminosity - UCF Physics
... Amount of power a star radiates (energy per second=Watts) Apparent brightness: Amount of starlight that reaches Earth (energy per second per square meter) ...
... Amount of power a star radiates (energy per second=Watts) Apparent brightness: Amount of starlight that reaches Earth (energy per second per square meter) ...
StarCharacteristics
... across the street, which light would appear brighter? You cannot tell by looking in the sky how bright a star truly is. The farther away the star is, the less bright it will appear. ...
... across the street, which light would appear brighter? You cannot tell by looking in the sky how bright a star truly is. The farther away the star is, the less bright it will appear. ...
Capella

Capella is the brightest star in the constellation Auriga, the sixth brightest in the night sky and the third brightest in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus and Vega. Its name is derived from the diminutive of the Latin capra ""goat"", hence ""little goat"". Capella also bears the Bayer designation Alpha Aurigae (often abbreviated to α Aurigae, α Aur or Alpha Aur). Although it appears to be a single star to the naked eye, it is actually a star system of four stars in two binary pairs. The first pair consists of two bright, large type-G giant stars, both with a radius around 10 times that of the Sun and two and a half times its mass, in close orbit around each other. Designated Capella Aa and Capella Ab, these two stars have both exhausted their core hydrogen fuel and become giant stars, though it is unclear exactly what stage they are on the stellar evolutionary pathway. The second pair, around 10,000 astronomical units from the first, consists of two faint, small and relatively cool red dwarfs. They are designated Capella H and Capella L. The stars labelled Capella C through to G and I through to K are actually unrelated stars in the same visual field. The Capella system is relatively close, at only 42.8 light-years (13.1 pc) from Earth.