Introduction - The University of Michigan Press
... tense Corinthian hatred (µι σος) of the Athenians. In 457 B .C., the Athenians won the battle of Oenophyta and conquered their northern neighbors Boeotia and Phocis. Next, the island of Aegina was added to the Athenian Empire (457–456 B .C.), as was Achaea, the territory flanking the south shore of ...
... tense Corinthian hatred (µι σος) of the Athenians. In 457 B .C., the Athenians won the battle of Oenophyta and conquered their northern neighbors Boeotia and Phocis. Next, the island of Aegina was added to the Athenian Empire (457–456 B .C.), as was Achaea, the territory flanking the south shore of ...
Day 4 Notes Ancient Greece (Persian Wars)
... i. Pericles – leader that brought Athens into its “Golden Age” 1. Parthenon – built to honor Athena 3. Athens created the “DELIAN LEAGUE” a. Alliance to stop further Persian attacks b. Athens used it to create the Athenian Empire c. Sparta was not a member 4. Greek culture would become the basis of ...
... i. Pericles – leader that brought Athens into its “Golden Age” 1. Parthenon – built to honor Athena 3. Athens created the “DELIAN LEAGUE” a. Alliance to stop further Persian attacks b. Athens used it to create the Athenian Empire c. Sparta was not a member 4. Greek culture would become the basis of ...
Sparta and the Persian Wars
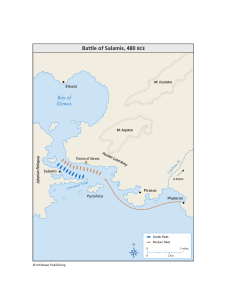
... • In the narrow waters of Salamis the Athenian-led Greek fleet destroys the Persian navy. • Xerxes, for fear of being cut off, leaves for Asia • His general Mardonius is left behind with much of the land army ...
... • In the narrow waters of Salamis the Athenian-led Greek fleet destroys the Persian navy. • Xerxes, for fear of being cut off, leaves for Asia • His general Mardonius is left behind with much of the land army ...
File
... Council of Elders – 2 Kings and 28 Citizens over the age of 60 Made decisions about the laws that would be voted on by the male assembly. The assembly would vote, not discuss or debate an issue. ...
... Council of Elders – 2 Kings and 28 Citizens over the age of 60 Made decisions about the laws that would be voted on by the male assembly. The assembly would vote, not discuss or debate an issue. ...
Ancient Greece - Harrison High School
... Philip II of Macedonia, Alexander’s father, had conquered most of Greece by the time of his death 336 BC-Alexander from Macedonia (north of Greece) becomes King (age 20) 334 BC-Alexander invades Persian empire & wins major victory in Asia Minor ...
... Philip II of Macedonia, Alexander’s father, had conquered most of Greece by the time of his death 336 BC-Alexander from Macedonia (north of Greece) becomes King (age 20) 334 BC-Alexander invades Persian empire & wins major victory in Asia Minor ...
The Persian Wars
... • The Greeks ships first sailed from shore like they were fleeing the island • They then turned quickly around and began ramming the Persian ships • Before the Persians knew what had happened half of their fleet was on the ocean floor • The Persians once again retreated back to Persia ...
... • The Greeks ships first sailed from shore like they were fleeing the island • They then turned quickly around and began ramming the Persian ships • Before the Persians knew what had happened half of their fleet was on the ocean floor • The Persians once again retreated back to Persia ...
Ancient Greece
... – The city-states of Greece united against the Persians during the Persian Wars – The Greek victory in the war and the leadership of Pericles contributed to a golden age in Athens ...
... – The city-states of Greece united against the Persians during the Persian Wars – The Greek victory in the war and the leadership of Pericles contributed to a golden age in Athens ...
The Persian Wars - Doral Academy Preparatory
... The Battle of Salamis • As their city-state burned the Athenian people and the army escaped to the island of Salamis • The Persians were quick to follow the retreating Greeks to Salamis ...
... The Battle of Salamis • As their city-state burned the Athenian people and the army escaped to the island of Salamis • The Persians were quick to follow the retreating Greeks to Salamis ...
What do you already know about ancient Greece?
... origin of the marathon ◦ “Rejoice! We conquer!” ...
... origin of the marathon ◦ “Rejoice! We conquer!” ...
File
... 6. City-state—A city with its own traditions and its own government and laws; both a city and a separate independent state. Early Greek societies were heavily influenced by the topography and available resources of the region leading to the development of city-states. Greek city-states developed rad ...
... 6. City-state—A city with its own traditions and its own government and laws; both a city and a separate independent state. Early Greek societies were heavily influenced by the topography and available resources of the region leading to the development of city-states. Greek city-states developed rad ...
document
... (immortals) and 200 ships. Pheidippides ran to Sparta for more troops meanwhile Miltiades led his army to Marathon where they met the Persians. On the 3rd day the Persian cavalry the Persian commander decided to sail to Athens to attack before the Spartans arrived. When Athenians saw that Persian ca ...
... (immortals) and 200 ships. Pheidippides ran to Sparta for more troops meanwhile Miltiades led his army to Marathon where they met the Persians. On the 3rd day the Persian cavalry the Persian commander decided to sail to Athens to attack before the Spartans arrived. When Athenians saw that Persian ca ...
CHAPTER 5
... 2. How did Greece's landforms influence the way of life of the people living there? ...
... 2. How did Greece's landforms influence the way of life of the people living there? ...
ATHENS vs SPARTA – THE PELOPONNESIAN WAR
... •Athens could not match Sparta’s Army, routinely invaded Attica ...
... •Athens could not match Sparta’s Army, routinely invaded Attica ...
Egypt and Mesopotamia Answer Sheet
... Alexander’s most lasting achievement was the spread of Greek culture. Alexander encouraged a blending of Greek culture with the cultures of conquered lands. He adopted Persian customs and married a Persian woman. Greek soldiers, traders, and artisans settled in the new cities Alexander created in co ...
... Alexander’s most lasting achievement was the spread of Greek culture. Alexander encouraged a blending of Greek culture with the cultures of conquered lands. He adopted Persian customs and married a Persian woman. Greek soldiers, traders, and artisans settled in the new cities Alexander created in co ...
Ancient Greece - Harrison High School
... Peloponnesian War (431 BC-404 BC) Series of battles between Athens and Sparta Sparta eventually wins (military superiority) Greece weakened over next century by fighting Growing power to the North, Macedonia goes unnoticed End of classical Greece ...
... Peloponnesian War (431 BC-404 BC) Series of battles between Athens and Sparta Sparta eventually wins (military superiority) Greece weakened over next century by fighting Growing power to the North, Macedonia goes unnoticed End of classical Greece ...
Unit 2: Ancient Empires
... foreigners. After the guard killed Commudus, they sold power to the highest bidder. This led to chaos every time a leader died. All leaders became dictators, and almost all were killed by their guards. The Roman Empire had 26 leaders in the next 50 years. • A leader had to pay his army well to keep ...
... foreigners. After the guard killed Commudus, they sold power to the highest bidder. This led to chaos every time a leader died. All leaders became dictators, and almost all were killed by their guards. The Roman Empire had 26 leaders in the next 50 years. • A leader had to pay his army well to keep ...
The Persian Wars In 519 BC Darius I ascended the throne of
... . Athos peninsula (where they had been caught before). They also spanned the Hellespont with pontoo n bridges for their army to march over. Some 30 city-states of central and southern Greece met in Corinth to devise a common defense (others, including the oracle at Delphi, sided with the Persians ). ...
... . Athos peninsula (where they had been caught before). They also spanned the Hellespont with pontoo n bridges for their army to march over. Some 30 city-states of central and southern Greece met in Corinth to devise a common defense (others, including the oracle at Delphi, sided with the Persians ). ...
Document
... Exported wine, olive oil, pottery, and cloth. *A land of high mountain ranges enclosing fertile valleys which were isolated because transportation over the mountains was tough. This led the Greeks to organize my independent city-states. *City-state – a political unit that includes a town or a city a ...
... Exported wine, olive oil, pottery, and cloth. *A land of high mountain ranges enclosing fertile valleys which were isolated because transportation over the mountains was tough. This led the Greeks to organize my independent city-states. *City-state – a political unit that includes a town or a city a ...
The Greeks at War
... He encouraged the __________________________________ to build up their fleet and prepare for battle with the _____________________________. In 480 B.C. Darius’ son __________________________ sent a larger force to conquer Greece. He sent ______________________ soldiers and nearly 1,000 ships. By thi ...
... He encouraged the __________________________________ to build up their fleet and prepare for battle with the _____________________________. In 480 B.C. Darius’ son __________________________ sent a larger force to conquer Greece. He sent ______________________ soldiers and nearly 1,000 ships. By thi ...
Greeks and Romans
... Plato explained his views of government in The Republic. Plato established a school in Athens called the Academy. His most important pupil was Aristotle, who studied at the ...
... Plato explained his views of government in The Republic. Plato established a school in Athens called the Academy. His most important pupil was Aristotle, who studied at the ...
The Persian Wars - Mrs. Darling`s Digital Classroom.
... Darius could have both “earth and water” at the same time! This was also their way of showing Darius that the Spartans were not intimidated. Darius responded by sending his huge navy, carrying the massive Persian army, across the Aegean to have his troops start the land war. His goal was to ...
... Darius could have both “earth and water” at the same time! This was also their way of showing Darius that the Spartans were not intimidated. Darius responded by sending his huge navy, carrying the massive Persian army, across the Aegean to have his troops start the land war. His goal was to ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide Key Honors
... the largest empire in the world at that point. Never lost a battle. Died at age 32 from malaria. Philip of Macedonia – Father of Alexander the Great. Conquered the Greek city-states. ...
... the largest empire in the world at that point. Never lost a battle. Died at age 32 from malaria. Philip of Macedonia – Father of Alexander the Great. Conquered the Greek city-states. ...
First Peloponnesian War
The First Peloponnesian War (460–445 BC) was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War. There were several causes for the war including the building of the Athenian long walls, Megara's defection and the envy and concern felt by Sparta at the growth of the Athenian Empire.The war began in 460 BC (Battle of Oenoe). At first the Athenians had the better of the fighting, winning the naval engagements using their superior fleet. They also had the better of the fighting on land, until 457 BC when the Spartans and their allies defeated the Athenian army at Tanagra. The Athenians, however, counterattacked and scored a crushing victory over the Boeotians at the Battle of Oenophyta and followed this victory up by conquering all of Boeotia except for Thebes.Athens further consolidated their position by making Aegina a member of the Delian League and by ravaging the Peloponnese. The Athenians were defeated in 454 BC by the Macedonians which caused them to enter into a five years' truce with Sparta. However, the war flared up again in 448 BC with the start of the Second Sacred War. In 446 BC, Boeotia revolted and defeated the Athenians at Coronea and regained their independence.The First Peloponnesian War ended in an arrangement between Sparta and Athens, which was ratified by the Thirty Years' Peace (winter of 446–445 BC). According to the provisions of this peace treaty, both sides maintained the main parts of their empires. Athens continued its domination of the sea while Sparta dominated the land. Megara returned to the Peloponnesian League and Aegina becoming a tribute paying but autonomous member of the Delian League. The war between the two leagues restarted in 431 BC and in 404 BC, Athens was occupied by Sparta.