Assessing in silico the recruitment and functional spectrum of
... diversity. For a high-level classification, metabolism is subdivided into primary (PM) and secondary (SM) metabolism. SM products are often not essential for survival of the organism and it is generally assumed that SM enzymes stem from PM homologs. Results: We wanted to assess evolutionary relation ...
... diversity. For a high-level classification, metabolism is subdivided into primary (PM) and secondary (SM) metabolism. SM products are often not essential for survival of the organism and it is generally assumed that SM enzymes stem from PM homologs. Results: We wanted to assess evolutionary relation ...
- BioMed Central
... in the generation of a massive amount of expression data. One of the greatest challenge we are faced with is to then analyse the data as a whole and extract the meaningful relationships among specific genes. Standard methods such as SAM [6] or machine learning algorithms [7] are able to detect patte ...
... in the generation of a massive amount of expression data. One of the greatest challenge we are faced with is to then analyse the data as a whole and extract the meaningful relationships among specific genes. Standard methods such as SAM [6] or machine learning algorithms [7] are able to detect patte ...
Microbiology bio 123
... How organisms capture, manufacture, and store energy Most animals are limited to aerobic metabolism. Bacteria are not limited to aerobic metabolism. Enzymes process energy, and are manufactured by the DNA. Enzymes: Enzymes are organic catalysts, and therefore determine everything that a cell does. O ...
... How organisms capture, manufacture, and store energy Most animals are limited to aerobic metabolism. Bacteria are not limited to aerobic metabolism. Enzymes process energy, and are manufactured by the DNA. Enzymes: Enzymes are organic catalysts, and therefore determine everything that a cell does. O ...
008 Chapter 08 Metabolism: Energy Enzymes and Regulation 1
... 26. Which of the following can be used as electron acceptors during anaerobic respiration? A. nitrate B. sulfate C. carbon dioxide D. all of the choices 27. Fatty acids are metabolized by the __________ pathway. A. alpha-oxidation B. beta-oxidation C. gamma-oxidation D. delta-oxidation 28. During b ...
... 26. Which of the following can be used as electron acceptors during anaerobic respiration? A. nitrate B. sulfate C. carbon dioxide D. all of the choices 27. Fatty acids are metabolized by the __________ pathway. A. alpha-oxidation B. beta-oxidation C. gamma-oxidation D. delta-oxidation 28. During b ...
Co-enzyme
... results from the shape of the enzyme –due to a compatible fit between the active site and the substrate • The substrate binds to the “active site” of the ...
... results from the shape of the enzyme –due to a compatible fit between the active site and the substrate • The substrate binds to the “active site” of the ...
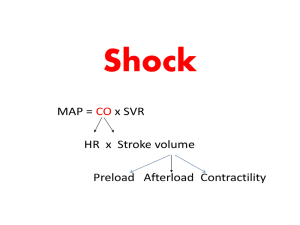
Shock - HIMSK
... Anne, who is drinking beer at a party, falls and hits her head on the ground. Her friend Liza dials “911” because Anne is unconscious, depressed ventilation (shallow and slow ...
... Anne, who is drinking beer at a party, falls and hits her head on the ground. Her friend Liza dials “911” because Anne is unconscious, depressed ventilation (shallow and slow ...
Toxicology I
... Organisms capture and store the energy they need in the form of... Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) ...
... Organisms capture and store the energy they need in the form of... Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) ...
PBHS AP Biology
... important as the AP Test will have least one essay question and several multiple choice questions based on these labs. ...
... important as the AP Test will have least one essay question and several multiple choice questions based on these labs. ...
Learning Objectives
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where substrate-level phosphor ...
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where substrate-level phosphor ...
Enzymes Problem Set 1 A) What concentration of the substrate
... phosphate (DHAP) using ATP as a co-substrate. The enzyme assay relies on a coupled reaction in which the reaction product, DHAP, is subsequently converted into glycerol 3phosphate by the presence of the enzyme glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, which uses NADH as a co-substrate. Glycerol is added t ...
... phosphate (DHAP) using ATP as a co-substrate. The enzyme assay relies on a coupled reaction in which the reaction product, DHAP, is subsequently converted into glycerol 3phosphate by the presence of the enzyme glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, which uses NADH as a co-substrate. Glycerol is added t ...
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is
... Some enzymes or enzyme complexes require several cofactors. For example, the multienzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase at the junction of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle requires five organic cofactors and one metal ion: loosely bound thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), covalently bound lipoamide a ...
... Some enzymes or enzyme complexes require several cofactors. For example, the multienzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase at the junction of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle requires five organic cofactors and one metal ion: loosely bound thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), covalently bound lipoamide a ...
Presentation
... • Experiments examine the amount of product (P) formed per unit of time (D[P] / Dt) • Velocity (v) - the rate of a reaction (varies with reactant concentration) • Rate constant (k) - indicates the speed or efficiency of a reaction ...
... • Experiments examine the amount of product (P) formed per unit of time (D[P] / Dt) • Velocity (v) - the rate of a reaction (varies with reactant concentration) • Rate constant (k) - indicates the speed or efficiency of a reaction ...
source file
... Provides information about the class to which an enzyme belongs: oxidoreductases transferases hydrolases lysases isomerases ligases ...
... Provides information about the class to which an enzyme belongs: oxidoreductases transferases hydrolases lysases isomerases ligases ...
Chapter 4 Outline
... 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy, but we will only study the steps of CR for the breakdown of glucose (C6H12O6). 5. Oxygen is required to receive the maximum energy possible per molecule of glucose and products of the reactions include w ...
... 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy, but we will only study the steps of CR for the breakdown of glucose (C6H12O6). 5. Oxygen is required to receive the maximum energy possible per molecule of glucose and products of the reactions include w ...
Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways
... 1. Glycolysis: from glucose to pyruvate. 2. Krebs or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle for conversion of pyruvate to CO2. 3. Respiration or electron transport chain for formation of ATP by transferring electrons from NADH to an electron acceptor (O2 under aerobic conditions). ...
... 1. Glycolysis: from glucose to pyruvate. 2. Krebs or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle for conversion of pyruvate to CO2. 3. Respiration or electron transport chain for formation of ATP by transferring electrons from NADH to an electron acceptor (O2 under aerobic conditions). ...
CHAPTER 4: CELLULAR METABOLISM
... 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy, but we will only study the steps of CR for the breakdown of glucose (C6H12O6). 5. Oxygen is required to receive the maximum energy possible per molecule of glucose and products of the reactions include w ...
... 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy, but we will only study the steps of CR for the breakdown of glucose (C6H12O6). 5. Oxygen is required to receive the maximum energy possible per molecule of glucose and products of the reactions include w ...
Secondary metabolism is a term for pathways and products
... Organic natural products are constructed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; frequently nitrogen atoms are also involved, and less frequently sulphur, phosphorus, chlorine, bromine, and iodine atoms. Organometalic compounds, especially metal complexes, also occur. The ultimate sources of these el ...
... Organic natural products are constructed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; frequently nitrogen atoms are also involved, and less frequently sulphur, phosphorus, chlorine, bromine, and iodine atoms. Organometalic compounds, especially metal complexes, also occur. The ultimate sources of these el ...
Micro 260 Fall 2009 Name: ___ Allan Keys ____ Tools: You may
... 11) Draw a diagram for the exergonic energy of activation (Ea) type graph while on the same graph drawing a comparison with an un-catalyzed reaction. Label all parts of the graph. (10 pts) ...
... 11) Draw a diagram for the exergonic energy of activation (Ea) type graph while on the same graph drawing a comparison with an un-catalyzed reaction. Label all parts of the graph. (10 pts) ...
CHAPTER 4: CELLULAR METABOLISM
... 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy, but we will only study the steps of CR for the breakdown of glucose (C6H12O6). 5. Oxygen is required to receive the maximum energy possible per molecule of glucose and products of the reactions include w ...
... 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy, but we will only study the steps of CR for the breakdown of glucose (C6H12O6). 5. Oxygen is required to receive the maximum energy possible per molecule of glucose and products of the reactions include w ...
Document
... • Eukaryotic cells isolate enzymes of different metabolic pathways within membranebounded organelles • Cells use allosteric sites on enzymes to control activity of enzymes • Feedback inhibition slows/stops anabolic pathways when product is in abundance • Cells regulate amphibolic pathways by requiri ...
... • Eukaryotic cells isolate enzymes of different metabolic pathways within membranebounded organelles • Cells use allosteric sites on enzymes to control activity of enzymes • Feedback inhibition slows/stops anabolic pathways when product is in abundance • Cells regulate amphibolic pathways by requiri ...
ENZYME KINETICS - University of Pennsylvania
... extracted from some living material. It may then be assayed in the crude extract or after various degrees of purification, using standard methods for fractionating proteins. The processes of extraction and purification may vary from fairly simple to quite difficult, depending upon the particular enz ...
... extracted from some living material. It may then be assayed in the crude extract or after various degrees of purification, using standard methods for fractionating proteins. The processes of extraction and purification may vary from fairly simple to quite difficult, depending upon the particular enz ...
Higher Human Biology unit 1 section 5 ENZYMES
... • A 1 molar solution is produced when 138g are dissolved in 1 litre of water. • A 0.1 molar solution is produced when 13.8g are dissolved in 100ml of water • A 0.01 molar solution is produced when 1.38g are dissolved in 100ml of water Work out what weights of sodium phosphate need to be added to 100 ...
... • A 1 molar solution is produced when 138g are dissolved in 1 litre of water. • A 0.1 molar solution is produced when 13.8g are dissolved in 100ml of water • A 0.01 molar solution is produced when 1.38g are dissolved in 100ml of water Work out what weights of sodium phosphate need to be added to 100 ...
Metabolic network modelling

Metabolic network reconstruction and simulation allows for an in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism. In particular, these models correlate the genome with molecular physiology. A reconstruction breaks down metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and the Citric acid cycle) into their respective reactions and enzymes, and analyzes them within the perspective of the entire network. In simplified terms, a reconstruction collects all of the relevant metabolic information of an organism and compiles it in a mathematical model. Validation and analysis of reconstructions can allow identification of key features of metabolism such as growth yield, resource distribution, network robustness, and gene essentiality. This knowledge can then be applied to create novel biotechnology.In general, the process to build a reconstruction is as follows: Draft a reconstruction Refine the model Convert model into a mathematical/computational representation Evaluate and debug model through experimentation↑