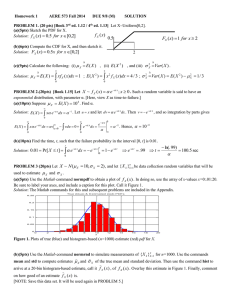
Data Mining in PHM
... interest, hard to annotate, or contain only aggregate data • noisy: contain errors or outliers • inconsistent: contain discrepancies in codes or names • Lack of quality data results generated: inconsistent, lack robustness, do not contribute to knowledge gain! • Quality decisions must be based on ...
... interest, hard to annotate, or contain only aggregate data • noisy: contain errors or outliers • inconsistent: contain discrepancies in codes or names • Lack of quality data results generated: inconsistent, lack robustness, do not contribute to knowledge gain! • Quality decisions must be based on ...
DSS Chapter 1
... Feedforward Recurrent Associative memory Probabilistic Self-organizing feature maps Hopfield networks … many more … ...
... Feedforward Recurrent Associative memory Probabilistic Self-organizing feature maps Hopfield networks … many more … ...
Document
... • m be the number of occurrences of x in A, and • k be the number of occurrences of x in B. It follows that the other values appear at least k times in B. Consequently, the other values appear in A: • at least 2k times: those pairs that are represented in B by a value different than x; plus • m-2k t ...
... • m be the number of occurrences of x in A, and • k be the number of occurrences of x in B. It follows that the other values appear at least k times in B. Consequently, the other values appear in A: • at least 2k times: those pairs that are represented in B by a value different than x; plus • m-2k t ...
Introduction to MIS
... University to develop software that is used to automatically drive vehicles. One system (Ranger) is used in an army ambulance that can drive itself over rough terrain for up to 16 km. ALVINN is a separate road-following system that has driven vehicles at ...
... University to develop software that is used to automatically drive vehicles. One system (Ranger) is used in an army ambulance that can drive itself over rough terrain for up to 16 km. ALVINN is a separate road-following system that has driven vehicles at ...
Summit Report
... “I think that it’s probably the way to go and I’m encouraged by, for example, the AI partnership where you have five big AI companies saying we recognize that AI is something that we need to think about self-regulating. That’s an important need. “But I want to come back to something we mentioned ear ...
... “I think that it’s probably the way to go and I’m encouraged by, for example, the AI partnership where you have five big AI companies saying we recognize that AI is something that we need to think about self-regulating. That’s an important need. “But I want to come back to something we mentioned ear ...
Factor of safety and probability of failure
... in a rock mass and the measured in situ stresses in the rock surrounding an opening do not have a single fixed value but may assume any number of values. There is no way of predicting exactly what the value of one of these parameters will be at any given location. Hence, these parameters are describ ...
... in a rock mass and the measured in situ stresses in the rock surrounding an opening do not have a single fixed value but may assume any number of values. There is no way of predicting exactly what the value of one of these parameters will be at any given location. Hence, these parameters are describ ...
A New Measure for the Accuracy of a Bayesian Network
... The range of values for the degree of accuracy of a Bayesian network, with respect to any data set, is (-∞,0]. Since the MDL formalism evaluates the likelihood of a Bayesian network given a particular data set, the specific range of values for the degree of accuracy of a Bayesian network, with respe ...
... The range of values for the degree of accuracy of a Bayesian network, with respect to any data set, is (-∞,0]. Since the MDL formalism evaluates the likelihood of a Bayesian network given a particular data set, the specific range of values for the degree of accuracy of a Bayesian network, with respe ...
Factor of safety and probability of failure
... in a rock mass and the measured in situ stresses in the rock surrounding an opening do not have a single fixed value but may assume any number of values. There is no way of predicting exactly what the value of one of these parameters will be at any given location. Hence, these parameters are describ ...
... in a rock mass and the measured in situ stresses in the rock surrounding an opening do not have a single fixed value but may assume any number of values. There is no way of predicting exactly what the value of one of these parameters will be at any given location. Hence, these parameters are describ ...
Scalable Methods for Estimating Document Frequencies
... Database of 2000 newsgroup articles Evaluated on a lexicon of 100 words Vary sample size s and number of queries q ...
... Database of 2000 newsgroup articles Evaluated on a lexicon of 100 words Vary sample size s and number of queries q ...