MDMV Visualization
... Functions, Data, and Distributions The problem: • Visualization and analysis of large dataset with multiple parameters or factors, and the key relationships among them • MDMV problem ...
... Functions, Data, and Distributions The problem: • Visualization and analysis of large dataset with multiple parameters or factors, and the key relationships among them • MDMV problem ...
Data Mining: My view - Department of Computer Science
... Main challenge: Complexity We are working with large datasets: Many attributes (p > 102 ) Many records (N > 106 ) Problems with computational complexity will dominate: The “classic” problems are N P hard We will typically not look at algorithms of complexity higher than O(N · p3 ) We need to make so ...
... Main challenge: Complexity We are working with large datasets: Many attributes (p > 102 ) Many records (N > 106 ) Problems with computational complexity will dominate: The “classic” problems are N P hard We will typically not look at algorithms of complexity higher than O(N · p3 ) We need to make so ...
(IT) has also generated a ... world is drowning in a ...
... (1) Most data will never be seen by humans. This is a novel experience for scientists, but the sheer volume of TBscale data sets (or larger) makes it impractical to do even a most cursory examination of all data. This implies a need for reliable data storage, networking, and database-related technol ...
... (1) Most data will never be seen by humans. This is a novel experience for scientists, but the sheer volume of TBscale data sets (or larger) makes it impractical to do even a most cursory examination of all data. This implies a need for reliable data storage, networking, and database-related technol ...
Data Preprocessing Motivation Data Records Attributes Attribute
... – Usually done when class label is missing (for classification tasks) ...
... – Usually done when class label is missing (for classification tasks) ...
Statistical Data Analysis - Faoza Hafiz Saragih, SP, M.Sc
... multilevel models that do not require a big size samples PLS regression is particularly useful when we need to predict a set of dependent variables from a (very) large set of independent variables (predictors) In addition there are also some advantages, namely PLS which will have implications fo ...
... multilevel models that do not require a big size samples PLS regression is particularly useful when we need to predict a set of dependent variables from a (very) large set of independent variables (predictors) In addition there are also some advantages, namely PLS which will have implications fo ...
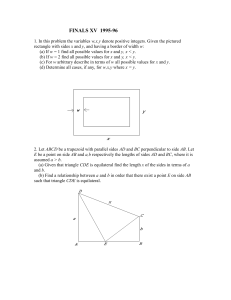
1996
... (c) For w arbitrary describe in terms of w all possible values for x and y. (d) Determine all cases, if any, for w,x,y where x = y. ...
... (c) For w arbitrary describe in terms of w all possible values for x and y. (d) Determine all cases, if any, for w,x,y where x = y. ...
PROYECTO FONDECYT N° 1020578
... the material specific parameters and model functions are given. The aim of this project is to provide the mathematical foundation of the identification of parameter from data measured by laboratory devices. We intend to treat the parameter identification problem by a Lagrangian formulation, and to d ...
... the material specific parameters and model functions are given. The aim of this project is to provide the mathematical foundation of the identification of parameter from data measured by laboratory devices. We intend to treat the parameter identification problem by a Lagrangian formulation, and to d ...
Pieces Of The Whole - Positive Communication Systems
... sense of their own value and strength and their own capacity to handle life's problems.“ - (Bush and Folger, 1994, p. 2) Occurs throughout the conversation/discussion/mediation Is internal not external Can only occur when parties are making their own decisions and developing their own understanding ...
... sense of their own value and strength and their own capacity to handle life's problems.“ - (Bush and Folger, 1994, p. 2) Occurs throughout the conversation/discussion/mediation Is internal not external Can only occur when parties are making their own decisions and developing their own understanding ...
Lakshmi Nannapaneni`s presentation on Patterns for Secure Boot
... The bootloader loads the operating system kernel, and the operating system kernel loads system services, device drivers, and other applications. At any stage of the bootstrap process, software components could have been exchanged or modified by another user or by malicious software that has been ...
... The bootloader loads the operating system kernel, and the operating system kernel loads system services, device drivers, and other applications. At any stage of the bootstrap process, software components could have been exchanged or modified by another user or by malicious software that has been ...
10.2 Worksheet Part 2
... In a telephone survey of 150 households, 75 people answered “yes” to a particular question, 50 answered “no,” and 25 were “not sure.” Find each experimental probability. 1. P(yes) ...
... In a telephone survey of 150 households, 75 people answered “yes” to a particular question, 50 answered “no,” and 25 were “not sure.” Find each experimental probability. 1. P(yes) ...
Generating Better Radial Basis Function Network for Large
... On the other hand, decision tree algorithms are also one of the representative data mining methods. There have been a lot of efforts to build better decision trees with respect to error rates. As a way to achieve this goal, many splitting criteria have been invented. For example, one of the represen ...
... On the other hand, decision tree algorithms are also one of the representative data mining methods. There have been a lot of efforts to build better decision trees with respect to error rates. As a way to achieve this goal, many splitting criteria have been invented. For example, one of the represen ...
Probability - New Mexico State University
... • Sought a mathematical model to describe abstractly outcome of a random event. • Formalized the classical definition of probability: If the total number of possible outcomes, all equally likely, associated with some actions is n and if m of those n result in the occurrence of some given event, then ...
... • Sought a mathematical model to describe abstractly outcome of a random event. • Formalized the classical definition of probability: If the total number of possible outcomes, all equally likely, associated with some actions is n and if m of those n result in the occurrence of some given event, then ...
Artificial Neural Networks - Introduction -
... problems. They have the ability to learn from experience in order to improve their performance and to adapt themselves to changes in the environment. In addition, they are able to deal with incomplete information or noisy data and can be very effective especially in situations where it is not possib ...
... problems. They have the ability to learn from experience in order to improve their performance and to adapt themselves to changes in the environment. In addition, they are able to deal with incomplete information or noisy data and can be very effective especially in situations where it is not possib ...
Survival and Event
... This chapter presents methods for analyzing event data. Survival analysis involves several related techniques that focus on times until the event of interest occurs. Although the event could be good or bad, by convention we refer to the event as a "failure." The time until failure is "survival time. ...
... This chapter presents methods for analyzing event data. Survival analysis involves several related techniques that focus on times until the event of interest occurs. Although the event could be good or bad, by convention we refer to the event as a "failure." The time until failure is "survival time. ...
Secondary data collection
... Secondary data can help us: 1. Diagnose(teşhis) the research problem 2. Develop an approach to the problem 3. Develop a sampling plan 4. Formulate an appropriate research design (for example, by identifying the key variables to measure or understand) 5. Answer certain research questions and test so ...
... Secondary data can help us: 1. Diagnose(teşhis) the research problem 2. Develop an approach to the problem 3. Develop a sampling plan 4. Formulate an appropriate research design (for example, by identifying the key variables to measure or understand) 5. Answer certain research questions and test so ...