Document
... An amount of heat equal to 2500 J is added to a system, and 1800 J of work is done on the system. What is the change in internal energy of the system? A. ...
... An amount of heat equal to 2500 J is added to a system, and 1800 J of work is done on the system. What is the change in internal energy of the system? A. ...
temperature dependence of the speciation of copper and iron in
... values increase with increasing temperature for all species. The plots of log (K 0f) versus temperature all look linear, despite the fact that the A, B, C and D parameters in Table 2 are not zero. This due to a compensation effect between the various parameter values. Only one plot (the one correspo ...
... values increase with increasing temperature for all species. The plots of log (K 0f) versus temperature all look linear, despite the fact that the A, B, C and D parameters in Table 2 are not zero. This due to a compensation effect between the various parameter values. Only one plot (the one correspo ...
thermodynamics - La Salle High School
... where Stot is the total entropy of the isolated system ...
... where Stot is the total entropy of the isolated system ...
Document
... be said that all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates. Question 10: How important is the presence of air bladder in Pisces? Answer 10: Gas bladder or air bladder is a gas filled sac present in fishes. It helps in maintaining buoyancy. Thus, it helps fishes to ascend or des ...
... be said that all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates. Question 10: How important is the presence of air bladder in Pisces? Answer 10: Gas bladder or air bladder is a gas filled sac present in fishes. It helps in maintaining buoyancy. Thus, it helps fishes to ascend or des ...
The Correlation of Standard Entropy with Enthalpy
... for diamond. Furthermore, for temperatures near 300 K, Cp(T) has nearly reached its classical plateau of 3R + Δ, where Δ = Cp – Cv > 0 and Cv is the constant-volume molar heat capacity.7 This is consistent with the equipartition of energy, namely, each degree of freedom contributes ½R per mole to th ...
... for diamond. Furthermore, for temperatures near 300 K, Cp(T) has nearly reached its classical plateau of 3R + Δ, where Δ = Cp – Cv > 0 and Cv is the constant-volume molar heat capacity.7 This is consistent with the equipartition of energy, namely, each degree of freedom contributes ½R per mole to th ...
File
... ethanol. Given that the specific heat capacity of ethanol is 2.4 kJ/kg. oC, and that the temperature changed from 21.05oC to 19.39oC, what is the molar heat of fusion for the benzene? Note: Ethanol is the surroundings, not water and benzene dissolves in the ethanol. ...
... ethanol. Given that the specific heat capacity of ethanol is 2.4 kJ/kg. oC, and that the temperature changed from 21.05oC to 19.39oC, what is the molar heat of fusion for the benzene? Note: Ethanol is the surroundings, not water and benzene dissolves in the ethanol. ...
Bilateral Symmetry
... Comparative Anatomy – the study of structures and functions of various animal groups. Taxonomy – the science of finding, describing, and classifying animals. Entomology – the study of insects. Ichthyology – the study of fish Herpetology – the study of reptiles and amphibians. Ethology – the st ...
... Comparative Anatomy – the study of structures and functions of various animal groups. Taxonomy – the science of finding, describing, and classifying animals. Entomology – the study of insects. Ichthyology – the study of fish Herpetology – the study of reptiles and amphibians. Ethology – the st ...
Heat Capacity - Uplift North Hills Prep
... molecules are vibrating and their chemical bonds. Heat goes from objects with high temperature to low temperature, not high thermal energy to low thermal energy. For example, a massive glacier will have more total thermal energy than a small hot nail (simply because it has more molecules); however, ...
... molecules are vibrating and their chemical bonds. Heat goes from objects with high temperature to low temperature, not high thermal energy to low thermal energy. For example, a massive glacier will have more total thermal energy than a small hot nail (simply because it has more molecules); however, ...
Statistical Interpretation of Temperature and Entropy
... obtain the same result. We need only assume that E0 is not degenerate. Also, if the ground state had degeneracy g0 , S = k log g0 at T = 0, which is negligible compared to any finite T entropy. If S contained a constant as well as the two terms in eq. (9.10) this constant would be the same for all s ...
... obtain the same result. We need only assume that E0 is not degenerate. Also, if the ground state had degeneracy g0 , S = k log g0 at T = 0, which is negligible compared to any finite T entropy. If S contained a constant as well as the two terms in eq. (9.10) this constant would be the same for all s ...
Chapter 2-C
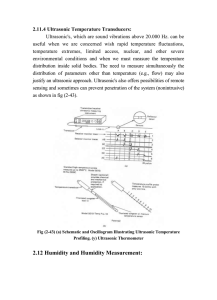
... The encoder consists of a cylindrical disc with the coding patterns (with conducting and insulating sections) arranged in concentric rings on one side of the disc. The black areas are made of conducting material while white areas are made of non-conducting materials. A thin layer of insulating mater ...
... The encoder consists of a cylindrical disc with the coding patterns (with conducting and insulating sections) arranged in concentric rings on one side of the disc. The black areas are made of conducting material while white areas are made of non-conducting materials. A thin layer of insulating mater ...