
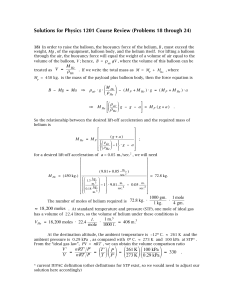
SOLUTIONS: HOMEWORK #6
... Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with time. 2 Air is an ideal gas with constant specific heats. 3 Potential energy changes are negligible. 4 The device is adiabatic and thus heat transfer is negligible. 5 There are no work interactions. Properties The gas constant ...
... Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with time. 2 Air is an ideal gas with constant specific heats. 3 Potential energy changes are negligible. 4 The device is adiabatic and thus heat transfer is negligible. 5 There are no work interactions. Properties The gas constant ...
The effect of heat on the metallurgical structure and B
... 10% addition of silicon to iron, the Curie temperature decreases from 770 ◦ C to 600 ◦ C [8]. In this study, the temperature applied to the silicon-iron alloy stator with 1.78% silicon is about 350-400 ◦ C. Thus, because this value is below the Curie temperature, the stator does not lose its ferroma ...
... 10% addition of silicon to iron, the Curie temperature decreases from 770 ◦ C to 600 ◦ C [8]. In this study, the temperature applied to the silicon-iron alloy stator with 1.78% silicon is about 350-400 ◦ C. Thus, because this value is below the Curie temperature, the stator does not lose its ferroma ...
Heat - Quia
... Theuse units for Q, t must in joules, calories, consistent and andm with mmust must those be bein based ingrams. kilograms. on the value of the constant c. ...
... Theuse units for Q, t must in joules, calories, consistent and andm with mmust must those be bein based ingrams. kilograms. on the value of the constant c. ...
Topic 3_2__Thermal properties of matter
... the temperature of the air in a 3 m by 4 m by 5 m room by 5°C? SOLUTION: From the previous table we see that c = 1050. The change in temperature is given: ∆T = 5°C. We get the mass from = m/V or m = V = (1.2)(3)(4)(5) = 72 kg. Q = mcT = (72)(1050)(5) = 378000 J or 378 kJ. ...
... the temperature of the air in a 3 m by 4 m by 5 m room by 5°C? SOLUTION: From the previous table we see that c = 1050. The change in temperature is given: ∆T = 5°C. We get the mass from = m/V or m = V = (1.2)(3)(4)(5) = 72 kg. Q = mcT = (72)(1050)(5) = 378000 J or 378 kJ. ...
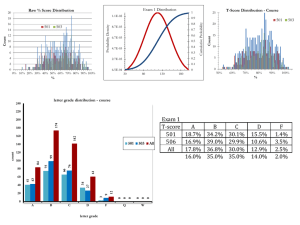
27 Oct. 2010 - PHA Science
... 3 November 2011 Objective: You will be able to: calculate the molar heat of crystallization for a chemical handwarmer Homework Quiz: A 10.0 gram piece of copper (specific heat = 0.385 J/g oC) has been heated to 100oC. It is then added to a sample of water at 22.0oC in a calorimeter. If the fina ...
... 3 November 2011 Objective: You will be able to: calculate the molar heat of crystallization for a chemical handwarmer Homework Quiz: A 10.0 gram piece of copper (specific heat = 0.385 J/g oC) has been heated to 100oC. It is then added to a sample of water at 22.0oC in a calorimeter. If the fina ...
Chapter 5
... 7. x + y = -2 x-y=0 Solve the first equation for y, y = -2 - x . Substitute -2 - x for y in the second equation. x - (-2 - x) = 0 x +2 + x = 0 2x = -2 x = -1 Substitute –1 for x in the equation y = -2 - x . y = -2 - (-1) y = -2 + 1 y = -1 The solution is (–1, –1). ...
... 7. x + y = -2 x-y=0 Solve the first equation for y, y = -2 - x . Substitute -2 - x for y in the second equation. x - (-2 - x) = 0 x +2 + x = 0 2x = -2 x = -1 Substitute –1 for x in the equation y = -2 - x . y = -2 - (-1) y = -2 + 1 y = -1 The solution is (–1, –1). ...
chapter 1
... manometer readings indicate the values of temperature. The sensitive element of the bimetallic thermometers comprises two plates made up of different metal alloys. The plates are both attached to each other using one of their ends; the other end is left free to expand in accordance to temperature. W ...
... manometer readings indicate the values of temperature. The sensitive element of the bimetallic thermometers comprises two plates made up of different metal alloys. The plates are both attached to each other using one of their ends; the other end is left free to expand in accordance to temperature. W ...
Chapter 9.doc
... Though an analogy cannot be made for the case of a constant surface temperature, resulting models approximately hold for this case as well ...
... Though an analogy cannot be made for the case of a constant surface temperature, resulting models approximately hold for this case as well ...
BTD QUESTION BANK[1].
... 2. The Temperature t on a certain Celsius thermometric scale is given by means of a property through a relation t = a ln p + b Where a and b are constants and p is the property of the fluid .If at the ice point and steam points the values of pare found to be 4 and 20 respectively, What will be tempe ...
... 2. The Temperature t on a certain Celsius thermometric scale is given by means of a property through a relation t = a ln p + b Where a and b are constants and p is the property of the fluid .If at the ice point and steam points the values of pare found to be 4 and 20 respectively, What will be tempe ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.




















![BTD QUESTION BANK[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009330461_1-f5de3108f7a7a17ebe3a8cbd391865db-300x300.png)