Heat Pumps for Space Heating
... rejected was unavailable for further motive power recovery. William Thomson predicted that there will come a time when all fuel sources would be exhausted and thus motive power would no longer be available. Therefore, he designed a machine, which he called “Heat Multiplier”. It comprised a compresso ...
... rejected was unavailable for further motive power recovery. William Thomson predicted that there will come a time when all fuel sources would be exhausted and thus motive power would no longer be available. Therefore, he designed a machine, which he called “Heat Multiplier”. It comprised a compresso ...
Energy (download)
... • Heat: energy in transit – molecular motion – Calorie is energy required to raise temperature of 1 g water by 1ºC ...
... • Heat: energy in transit – molecular motion – Calorie is energy required to raise temperature of 1 g water by 1ºC ...
Temperature Conversions
... 4. A 400g glass coffee cup is at room temperature, 20.0ºC. It is then plunged into hot dishwater, 80.0ºC. If the temperature of the cup reaches that of the dishwater, how much heat does the cup absorb? Assume the mass of the dishwater is large enough so its temperature doesn’t change appreciably. ...
... 4. A 400g glass coffee cup is at room temperature, 20.0ºC. It is then plunged into hot dishwater, 80.0ºC. If the temperature of the cup reaches that of the dishwater, how much heat does the cup absorb? Assume the mass of the dishwater is large enough so its temperature doesn’t change appreciably. ...
The Specific Heat Capacity of Metals
... it to boil for about five minutes so that the metal reaches the temperature of the boiling water. Take the temperature of the water. Assume this is also the temperature of the metal. Record this temperature in the table. 3. Add 100 g of cold water to an insulated cup. Quickly remove the metal sample ...
... it to boil for about five minutes so that the metal reaches the temperature of the boiling water. Take the temperature of the water. Assume this is also the temperature of the metal. Record this temperature in the table. 3. Add 100 g of cold water to an insulated cup. Quickly remove the metal sample ...
Heat stress round table
... implement a specific strategy during the carry over period? • What is, from your point of view, the main limiting factor to improve conception rate during the heat stress period? ...
... implement a specific strategy during the carry over period? • What is, from your point of view, the main limiting factor to improve conception rate during the heat stress period? ...
Thermal Energy and Heat
... A quantity to measure the relationship between heat and temperature change Amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1oC Every substance has its own specific heat ...
... A quantity to measure the relationship between heat and temperature change Amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1oC Every substance has its own specific heat ...
Heat and its Transfer Study Guide
... always moves from a warmer object to a colder one. Think about a cup of hot tea. You put a cold metal spoon in the water. Soon the spoon becomes warm. Heat has moved from the hot tea to the cold spoon. The transfer of thermal energy (heat) between two objects that are touching is called conduction. ...
... always moves from a warmer object to a colder one. Think about a cup of hot tea. You put a cold metal spoon in the water. Soon the spoon becomes warm. Heat has moved from the hot tea to the cold spoon. The transfer of thermal energy (heat) between two objects that are touching is called conduction. ...
Thermal Chem Review and Key
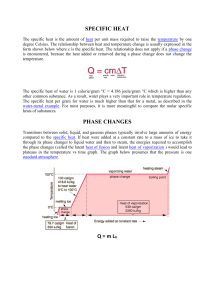
... 15. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in a phase change? Does this equation pertain to the diagonal or plateau sections on your heating and cooling curve? 16. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in increasing or decreasing the temperature of a substance? Does ...
... 15. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in a phase change? Does this equation pertain to the diagonal or plateau sections on your heating and cooling curve? 16. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in increasing or decreasing the temperature of a substance? Does ...
Power point about heat transfer
... Convection • Convection: In liquids and gases, convection happens when the part of the liquid or gas that is warmer rises. As this happens, cooler liquid or gas sinks taking the place of the warm part. • Examples? ...
... Convection • Convection: In liquids and gases, convection happens when the part of the liquid or gas that is warmer rises. As this happens, cooler liquid or gas sinks taking the place of the warm part. • Examples? ...
Specific Heat and Calorimeters
... 5) How much heat energy is needed to raise the temperature of a 425 g aluminum baking sheet from room temperature, 25 OC, to a baking temperature of 200 OC (the specific heat of aluminum is 0.897 J/g •OC)? ...
... 5) How much heat energy is needed to raise the temperature of a 425 g aluminum baking sheet from room temperature, 25 OC, to a baking temperature of 200 OC (the specific heat of aluminum is 0.897 J/g •OC)? ...
Document
... equilibrium with C. After this has happened if the adiabatic wall between A and B is replaced by a conducting wall and C is insulated from A and B by an adiabatic wall . It is found that the states of A and B change no further i.e. they are found to be in thermal equilibrium with each other. ...
... equilibrium with C. After this has happened if the adiabatic wall between A and B is replaced by a conducting wall and C is insulated from A and B by an adiabatic wall . It is found that the states of A and B change no further i.e. they are found to be in thermal equilibrium with each other. ...
Brief 2-page Summary
... Heat: energy causing a change in temperature Thermal energy: energy an object or substance possesses as temperature because of the kinetic energy of its molecules Heat flow: heat always moves from warmer objects to cooler objects Energy is can be transferred or transformed into a variety of fo ...
... Heat: energy causing a change in temperature Thermal energy: energy an object or substance possesses as temperature because of the kinetic energy of its molecules Heat flow: heat always moves from warmer objects to cooler objects Energy is can be transferred or transformed into a variety of fo ...
Name
... 3. Thermochemistry – the study of ___________________________ in a chemical reaction. 4. Types of Chemical Reactions a. Exothermic Reactions - ________________ heat into their surroundings -Heat is a ________________ of the reaction. -combustion reactions are exothermic -C3H8 + 5O2 ...
... 3. Thermochemistry – the study of ___________________________ in a chemical reaction. 4. Types of Chemical Reactions a. Exothermic Reactions - ________________ heat into their surroundings -Heat is a ________________ of the reaction. -combustion reactions are exothermic -C3H8 + 5O2 ...
Chapter 11A 4-7 - WVU Plasma Physics
... the infrared (and therefore heat) on our planet. • Why it doesn’t get super cold at night, unlike the dark side of the moon (-280° F). Also why it doesn’t get super hot either (bright side of the moon is 260°F). • So far, the greenhouse effect sounds pretty good, huh? ...
... the infrared (and therefore heat) on our planet. • Why it doesn’t get super cold at night, unlike the dark side of the moon (-280° F). Also why it doesn’t get super hot either (bright side of the moon is 260°F). • So far, the greenhouse effect sounds pretty good, huh? ...
18493 Demonstrate knowledge of heat transfer in a seafood
... Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Accred ...
... Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Accred ...
File
... • When the heat capacity, C, is large the transfer of a given amount of heat to a system leads to only a small rise in temperature; but when it is small the same amount of heat can cause a large rise in temperature. • The magnitude of C depends on the size of the system: a bigger body requires more ...
... • When the heat capacity, C, is large the transfer of a given amount of heat to a system leads to only a small rise in temperature; but when it is small the same amount of heat can cause a large rise in temperature. • The magnitude of C depends on the size of the system: a bigger body requires more ...
Specific Heat
... Learning Check 2. Two objects are sitting next to each other in the sunlight. Object A gets hotter than object B. A. Object A has a lower specific heat than object B B. Object A has a higher specific heat than object B C. Both objects have the same specific heat ...
... Learning Check 2. Two objects are sitting next to each other in the sunlight. Object A gets hotter than object B. A. Object A has a lower specific heat than object B B. Object A has a higher specific heat than object B C. Both objects have the same specific heat ...
Bacon¹s inductive method, example of heat.
... nothing more than those laws and determinations of absolute actuality which govern and constitute any simple nature, as heat, light, weight, in every kind of matter and subject that is susceptible of them (Bacon IV [1901], 145–6); They are not identical with natural law, but with definitions of simp ...
... nothing more than those laws and determinations of absolute actuality which govern and constitute any simple nature, as heat, light, weight, in every kind of matter and subject that is susceptible of them (Bacon IV [1901], 145–6); They are not identical with natural law, but with definitions of simp ...
SC.4.P.11.1-11.2 - Energy Transfer and Transformation
... • A change in thermal energy can lead to a change in phase or state of matter. • Temperature is a measure of thermal energy. ...
... • A change in thermal energy can lead to a change in phase or state of matter. • Temperature is a measure of thermal energy. ...
"heat of fusion". - IES Al
... know, because the 1700-fold increase in volume when water is sprayed on a fire or hot surface can be explosive and dangerous. ...
... know, because the 1700-fold increase in volume when water is sprayed on a fire or hot surface can be explosive and dangerous. ...
Note: Moving air
... Question: Describe how conduction, convection, and radiation play a role in losing heat through a double-pane window. Answer: Heat is conducted through the solid glass and through the four air films, two on each side of each sheet of glass. The air films do the bulk of the insulating! If the space b ...
... Question: Describe how conduction, convection, and radiation play a role in losing heat through a double-pane window. Answer: Heat is conducted through the solid glass and through the four air films, two on each side of each sheet of glass. The air films do the bulk of the insulating! If the space b ...
Cogeneration

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Trigeneration or combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP) refers to the simultaneous generation of electricity and useful heating and cooling from the combustion of a fuel or a solar heat collector. Cogeneration is a thermodynamically efficient use of fuel. In separate production of electricity, some energy must be discarded as waste heat, but in cogeneration this thermal energy is put to use. All thermal power plants emit heat during electricity generation, which can be released into the natural environment through cooling towers, flue gas, or by other means. In contrast, CHP captures some or all of the by-product for heating, either very close to the plant, or—especially in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe—as hot water for district heating with temperatures ranging from approximately 80 to 130 °C. This is also called combined heat and power district heating (CHPDH). Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures (100–180 °C, 212–356 °F) can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling.The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator and the resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating as described in cogeneration. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW) a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Trigeneration differs from cogeneration in that the waste heat is used for both heating and cooling, typically in an absorption refrigerator. CCHP systems can attain higher overall efficiencies than cogeneration or traditional power plants. In the United States, the application of trigeneration in buildings is called building cooling, heating and power (BCHP). Heating and cooling output may operate concurrently or alternately depending on need and system construction.Cogeneration was practiced in some of the earliest installations of electrical generation. Before central stations distributed power, industries generating their own power used exhaust steam for process heating. Large office and apartment buildings, hotels and stores commonly generated their own power and used waste steam for building heat. Due to the high cost of early purchased power, these CHP operations continued for many years after utility electricity became available.