Passive House Standard Video Tutorial
... The Passive House standard is a specific construction standard for buildings with good comfort conditions during winter and summer irrespective of the climate in which they are located. Typically this includes optimised insulation levels, high performance triple glazed windows (typically the weakest ...
... The Passive House standard is a specific construction standard for buildings with good comfort conditions during winter and summer irrespective of the climate in which they are located. Typically this includes optimised insulation levels, high performance triple glazed windows (typically the weakest ...
calorimetry - Saddleback College
... The textbook discusses the transformation of energy from one form to another; e.g. from mechanical energy to thermal energy, from chemical energy to thermal energy to mechanical energy, and so on. In this experiment you will investigate some of the properties of thermal energy in transit or heat. Yo ...
... The textbook discusses the transformation of energy from one form to another; e.g. from mechanical energy to thermal energy, from chemical energy to thermal energy to mechanical energy, and so on. In this experiment you will investigate some of the properties of thermal energy in transit or heat. Yo ...
notes - superTALLteacher
... with the same amount of heat for 1 minute, what would you expect the final temperature to be? 1) 10 °C 2) 14°C 3) 18°C ...
... with the same amount of heat for 1 minute, what would you expect the final temperature to be? 1) 10 °C 2) 14°C 3) 18°C ...
Introduction - HCC Learning Web
... Specific Heat is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of substance by one degree Celsius. It can be expressed in terms of calories/(gm∙C) or joules/ (kg∙K) . Water has a relatively high specific heat of 1cal/(gm∙C). Metals usually have a low specific heat, for example lea ...
... Specific Heat is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of substance by one degree Celsius. It can be expressed in terms of calories/(gm∙C) or joules/ (kg∙K) . Water has a relatively high specific heat of 1cal/(gm∙C). Metals usually have a low specific heat, for example lea ...
Heat Sink Catalog
... thermal problems by narrowing the field of available solutions. Suitable technologies for an application can be identified by plotting the expected Power Dissipation on the X Axis and considering the entire range of intersecting along the Y Axis. Dependent upon the power used and the dynamics of the ...
... thermal problems by narrowing the field of available solutions. Suitable technologies for an application can be identified by plotting the expected Power Dissipation on the X Axis and considering the entire range of intersecting along the Y Axis. Dependent upon the power used and the dynamics of the ...
WS Specific Heat 2
... WS Specific Heat 2 1. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 19.68 g of calcium from 18.00 °C to 82.40 °C? The specific heat of calcium is 0.647 J/g°C. 2. 400.0 J of heat are applied to a sample of beryllium. Its temperature increases from 22.00 °C to 50.00 °C. What is the sample’s ma ...
... WS Specific Heat 2 1. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 19.68 g of calcium from 18.00 °C to 82.40 °C? The specific heat of calcium is 0.647 J/g°C. 2. 400.0 J of heat are applied to a sample of beryllium. Its temperature increases from 22.00 °C to 50.00 °C. What is the sample’s ma ...
Conductive heat flow at the surface is described by Fourier`s law of
... Summary and conclusions • The output of the model is a 2-D temperature-depth grid that provides a comparison with various analytical models of oceanic heat flow. • We tested the reliability of the computations using different half-spreading rates and different node spacings and verified that the mo ...
... Summary and conclusions • The output of the model is a 2-D temperature-depth grid that provides a comparison with various analytical models of oceanic heat flow. • We tested the reliability of the computations using different half-spreading rates and different node spacings and verified that the mo ...
Heat Transfer Equipment Wort kettle – External calandria
... Steam and hot water equipment – Shell and tube ...
... Steam and hot water equipment – Shell and tube ...
Historical daily gas and electrical energy flows through Great
... future scenario, it is striking that even a partial shift of the NDM demand to the electricity system results in a substantial increase in daily electrical demand. It is worth reiterating that this study only considers the daily energy use, which will significantly understate the variability in inst ...
... future scenario, it is striking that even a partial shift of the NDM demand to the electricity system results in a substantial increase in daily electrical demand. It is worth reiterating that this study only considers the daily energy use, which will significantly understate the variability in inst ...
1 2 mc = 3 2 (R / N )T R / N is the (gas constant) / molecule and is
... A degree of freedom is a coordinate needed to describe position of a molecule in space. Example: A point has 3 degrees of freedom because it requires three coordinates to describe its ...
... A degree of freedom is a coordinate needed to describe position of a molecule in space. Example: A point has 3 degrees of freedom because it requires three coordinates to describe its ...
Chapter 5, Problem 1
... Consider a steam pipe of length L = 15 ft, inner radius r1 = 2 in., outer radius r2 = 2.4 in., and thermal conductivity k = 7.2 Btu/h ⋅ ft ⋅ F. Steam is flowing through the pipe at an average temperature of 250°F, and the average convection heat transfer coefficient on the inner surface is given to ...
... Consider a steam pipe of length L = 15 ft, inner radius r1 = 2 in., outer radius r2 = 2.4 in., and thermal conductivity k = 7.2 Btu/h ⋅ ft ⋅ F. Steam is flowing through the pipe at an average temperature of 250°F, and the average convection heat transfer coefficient on the inner surface is given to ...
module 7
... The primary reason for using multipass designs is to increase the average tube side fluid velocity in a given arrangement. In a two pass arrangement the fluid flows through only half the tubes and any one point, so that the Reynold’s number is effectively doubled. Increasing the Reynolds’s number re ...
... The primary reason for using multipass designs is to increase the average tube side fluid velocity in a given arrangement. In a two pass arrangement the fluid flows through only half the tubes and any one point, so that the Reynold’s number is effectively doubled. Increasing the Reynolds’s number re ...
Temperature Differences in the Beam Screen
... • The cooled length increases linearly with the mass flow • With Neon the cooled length can be doubled • Enlarging the diameter of the capillaries is an easy and effective way to increase the cooled length • Instabilities due to high velocities can be avoided • The available space should be used ...
... • The cooled length increases linearly with the mass flow • With Neon the cooled length can be doubled • Enlarging the diameter of the capillaries is an easy and effective way to increase the cooled length • Instabilities due to high velocities can be avoided • The available space should be used ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... B. Kinetic Theory of Matter C. Thermal Energy D. Transfer of Heat 3. The total energy of the particles in an object is often called A. temperature. B. thermal energy. C. kinetic energy. D. heat transfer. 4. When thermal energy changes in two objects of different temperature that are touching each ot ...
... B. Kinetic Theory of Matter C. Thermal Energy D. Transfer of Heat 3. The total energy of the particles in an object is often called A. temperature. B. thermal energy. C. kinetic energy. D. heat transfer. 4. When thermal energy changes in two objects of different temperature that are touching each ot ...
FSK Shield - Fi-Foil
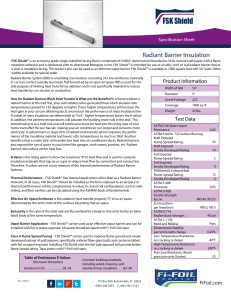
... a class A insulation facing. The product also can be used as an effective vapor barrier. FSK Shield™ is available in 1000 square foot rolls 54” wide. Other widths available by special order. Radiant Barrier System (RBS) is a building construction consisting of a low emittance (normally 0.1 or less) ...
... a class A insulation facing. The product also can be used as an effective vapor barrier. FSK Shield™ is available in 1000 square foot rolls 54” wide. Other widths available by special order. Radiant Barrier System (RBS) is a building construction consisting of a low emittance (normally 0.1 or less) ...
Beat the Heat
... and intense warm-up can influence performance during a subsequent event. Countermeasures to offset large increases in temperature during warm-up are suggested below. TIME TRIAL These events (30-75 min) are likely to be the most affected by heat stress. During a long time-trial, high power outputs ar ...
... and intense warm-up can influence performance during a subsequent event. Countermeasures to offset large increases in temperature during warm-up are suggested below. TIME TRIAL These events (30-75 min) are likely to be the most affected by heat stress. During a long time-trial, high power outputs ar ...
Document
... 26.2 Convection and Sea Breezes On a smaller scale near coastlines, convection is responsible for sea breezes. During the daytime, land is much hotter than the ocean. A sea breeze is created when hot air over the land rises due to convection and is replaced by cooler air from the ocean. At ...
... 26.2 Convection and Sea Breezes On a smaller scale near coastlines, convection is responsible for sea breezes. During the daytime, land is much hotter than the ocean. A sea breeze is created when hot air over the land rises due to convection and is replaced by cooler air from the ocean. At ...
chapter 4 : heat
... A bullet traveling at 60 m s 1 hit a sand bag. The temperature of the bullet rises by 4.5 0 C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of the bullet. ...
... A bullet traveling at 60 m s 1 hit a sand bag. The temperature of the bullet rises by 4.5 0 C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of the bullet. ...
Temperature Regulation
... when mild, and produce medical problems, when severe B. Mammals and birds are endotherms ...
... when mild, and produce medical problems, when severe B. Mammals and birds are endotherms ...
Thermochemistry - Harrison High School
... In calculating the total energy required to heat a chunk of ice from a temperature in the area of Part A all the way to a temperature in the area of Part E requires five different steps. The energy from each step (given in kJ) is then added up to give the total energy involved in this (Physical or C ...
... In calculating the total energy required to heat a chunk of ice from a temperature in the area of Part A all the way to a temperature in the area of Part E requires five different steps. The energy from each step (given in kJ) is then added up to give the total energy involved in this (Physical or C ...
HTC Heat Transfer Compound
... conductivity of the material applied; best results are achieved when a uniform, thin coat is applied between the mating surfaces. Apply a thin layer of compound to one of the contact surfaces using a brush, spatula, roller, automated system or screen printing technique. Ensure that the entire interf ...
... conductivity of the material applied; best results are achieved when a uniform, thin coat is applied between the mating surfaces. Apply a thin layer of compound to one of the contact surfaces using a brush, spatula, roller, automated system or screen printing technique. Ensure that the entire interf ...
Cogeneration

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Trigeneration or combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP) refers to the simultaneous generation of electricity and useful heating and cooling from the combustion of a fuel or a solar heat collector. Cogeneration is a thermodynamically efficient use of fuel. In separate production of electricity, some energy must be discarded as waste heat, but in cogeneration this thermal energy is put to use. All thermal power plants emit heat during electricity generation, which can be released into the natural environment through cooling towers, flue gas, or by other means. In contrast, CHP captures some or all of the by-product for heating, either very close to the plant, or—especially in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe—as hot water for district heating with temperatures ranging from approximately 80 to 130 °C. This is also called combined heat and power district heating (CHPDH). Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures (100–180 °C, 212–356 °F) can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling.The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator and the resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating as described in cogeneration. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW) a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Trigeneration differs from cogeneration in that the waste heat is used for both heating and cooling, typically in an absorption refrigerator. CCHP systems can attain higher overall efficiencies than cogeneration or traditional power plants. In the United States, the application of trigeneration in buildings is called building cooling, heating and power (BCHP). Heating and cooling output may operate concurrently or alternately depending on need and system construction.Cogeneration was practiced in some of the earliest installations of electrical generation. Before central stations distributed power, industries generating their own power used exhaust steam for process heating. Large office and apartment buildings, hotels and stores commonly generated their own power and used waste steam for building heat. Due to the high cost of early purchased power, these CHP operations continued for many years after utility electricity became available.