U3 S1 L3 calorimetry
... thermometer, and a known amount of water (see Figure 17.1 on p.661 of MHR). ...
... thermometer, and a known amount of water (see Figure 17.1 on p.661 of MHR). ...
2 Energy Transfer
... Imagine placing a pot of cold water on a hot stove burner. The water absorbs heat from the burner. If you put a thermometer in the water, you would see the temperature of the water increase. When the water’s temperature reached 100 ºC, the water would start to boil. Many people think that the temper ...
... Imagine placing a pot of cold water on a hot stove burner. The water absorbs heat from the burner. If you put a thermometer in the water, you would see the temperature of the water increase. When the water’s temperature reached 100 ºC, the water would start to boil. Many people think that the temper ...
Comparative Study of Rectangular, Trapezoidal and Parabolic
... important aspect of electronic equipment design. The dissipation of heat is necessary for its proper function. The heat is generated by the resistance encountered by electric current. Unless proper cooling arrangement is designed, the operating temperature exceeds permissible limit. As a consequence ...
... important aspect of electronic equipment design. The dissipation of heat is necessary for its proper function. The heat is generated by the resistance encountered by electric current. Unless proper cooling arrangement is designed, the operating temperature exceeds permissible limit. As a consequence ...
Mapping Heat Origin in Plasmonic Structures
... molecules to increase the sensitivity of the method. Figure 1 presents the setup that we used to perform both thermal (temperature and HSD) and optical (two-photon luminescence of gold) measurements. It comprises two illumination parts: a blue laser beam (473 nm) from the bottom of the sample to exc ...
... molecules to increase the sensitivity of the method. Figure 1 presents the setup that we used to perform both thermal (temperature and HSD) and optical (two-photon luminescence of gold) measurements. It comprises two illumination parts: a blue laser beam (473 nm) from the bottom of the sample to exc ...
finite volume analysis of convective heat transfer augmentation from
... The governing equations are the continuity, momentum, and energy equations. The flow is studied under the following assumptions: steadystate, constant fluid properties and no natural convection and body forces. The governing equations for steady mixed convection flow using conservation of mass, mome ...
... The governing equations are the continuity, momentum, and energy equations. The flow is studied under the following assumptions: steadystate, constant fluid properties and no natural convection and body forces. The governing equations for steady mixed convection flow using conservation of mass, mome ...
Latent Heat of Vaporisation of Liquid Nitrogen
... This deviates further from the accepted value by 1.28kJmol-1 and shows a discrepancy with equation (4), where decreasing the power from 10W to 5.15 W, a factor of 0.515, should result in the gradients in figure 5, being smaller by a factor of 0.515 to those in figure 3, so that L ...
... This deviates further from the accepted value by 1.28kJmol-1 and shows a discrepancy with equation (4), where decreasing the power from 10W to 5.15 W, a factor of 0.515, should result in the gradients in figure 5, being smaller by a factor of 0.515 to those in figure 3, so that L ...
PowerPoint - Dr. Samples` Chemistry Classes
... • What kind of substances have high heat capacities? • Water has one of the highest heat capacities, much higher than most common substances. It’s specific heat capacity is 4.184 J/g•°C. • Water can store a lot of heat energy, and this is crucial for life on our planet. • As our planet is a liquid w ...
... • What kind of substances have high heat capacities? • Water has one of the highest heat capacities, much higher than most common substances. It’s specific heat capacity is 4.184 J/g•°C. • Water can store a lot of heat energy, and this is crucial for life on our planet. • As our planet is a liquid w ...
Introduction to Thermal Circuits for Steady-State, One
... Thermal conduction and convection are often phenomenologically introduced in firstsemester optomechanical courses. Respective expressions governing the relation between heat flux, in W/ m 2 , to either a linear material’s temperature gradient (conduction) or the difference in surface and ambient tem ...
... Thermal conduction and convection are often phenomenologically introduced in firstsemester optomechanical courses. Respective expressions governing the relation between heat flux, in W/ m 2 , to either a linear material’s temperature gradient (conduction) or the difference in surface and ambient tem ...
Heat Flow Basics, Arch264
... Solar gain through windows exposed to either the direct sun, or reflected sun (reflected off the particles in the sky, creating diffuse radiation or reflected off terrestrial surface, creating beam radiation) can dramatically affect the energy balance of a building. Hence, the energy flows calculate ...
... Solar gain through windows exposed to either the direct sun, or reflected sun (reflected off the particles in the sky, creating diffuse radiation or reflected off terrestrial surface, creating beam radiation) can dramatically affect the energy balance of a building. Hence, the energy flows calculate ...
Cooling guidelines PL
... A typical feture that differs passive buildings from the traditional ones is the way of heating or cooling. This is because passive buildings are not equipped with heating or cooling installations that can usually be found in typical buildings. Cooling and heating is usually carried out along with m ...
... A typical feture that differs passive buildings from the traditional ones is the way of heating or cooling. This is because passive buildings are not equipped with heating or cooling installations that can usually be found in typical buildings. Cooling and heating is usually carried out along with m ...
Heat energy from alcohols
... Get the class to record and share the results. Do not be surprised if groups get different answers for a given alcohol. Heat losses ...
... Get the class to record and share the results. Do not be surprised if groups get different answers for a given alcohol. Heat losses ...
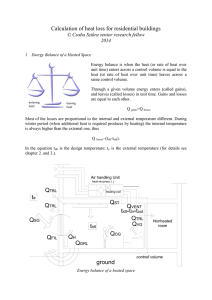
Calculation of heat loss for buildings
... Air changes per hour is a measure of how many times the air within a defined space (normally a room or house) is replaced. Air changes in a confined space are important for a variety of reasons, mainly though, we need fresh air to live. Without sufficient fresh air exchange, moisture is trapped in a ...
... Air changes per hour is a measure of how many times the air within a defined space (normally a room or house) is replaced. Air changes in a confined space are important for a variety of reasons, mainly though, we need fresh air to live. Without sufficient fresh air exchange, moisture is trapped in a ...
SOLUTIONS: HOMEWORK #6
... 6-10C Heat engines are cyclic devices that receive heat from a source, convert some of it to work, and reject the rest to a sink. 6-12C No. Because 100% of the work can be converted to heat. 6-15C No. Such an engine violates the Kelvin-Planck statement of the second law of thermodynamics. 6-20 The p ...
... 6-10C Heat engines are cyclic devices that receive heat from a source, convert some of it to work, and reject the rest to a sink. 6-12C No. Because 100% of the work can be converted to heat. 6-15C No. Such an engine violates the Kelvin-Planck statement of the second law of thermodynamics. 6-20 The p ...
Part L Overview
... • Each dwelling should have a minimum level of energy provision from renewable energy technologies equivalent to – 10 kWh/m2/annum of thermal energy, or – 4 kWh/m2/annum of electrical energy, or – A combination of these which would have equivalent effect ...
... • Each dwelling should have a minimum level of energy provision from renewable energy technologies equivalent to – 10 kWh/m2/annum of thermal energy, or – 4 kWh/m2/annum of electrical energy, or – A combination of these which would have equivalent effect ...
Activity P47: Electrical Equivalent of Heat (Voltage Sensor and
... Record the minimum and maximum temperatures (values of y). Calculate and record the change in temperature of the water. ...
... Record the minimum and maximum temperatures (values of y). Calculate and record the change in temperature of the water. ...
What is Heat Stress? » Keep the “Fun” in Fun Runs. » How do you
... illness. Even in cool weather, heat illness may occur in people exercising at high intensity for more than about 45 minutes. The risk of heat illness is obviously greater in hot and humid weather because: • during high intensity exercise in hot weather people may not be able to produce enough sweat ...
... illness. Even in cool weather, heat illness may occur in people exercising at high intensity for more than about 45 minutes. The risk of heat illness is obviously greater in hot and humid weather because: • during high intensity exercise in hot weather people may not be able to produce enough sweat ...
Seeing Energy in Everything
... Ice is a solid and the particles move slowly, water is a liquid where the particles are warmer and moving faster, water vaopor is a gas where the particles are even hotter and moving very fast in every direction ...
... Ice is a solid and the particles move slowly, water is a liquid where the particles are warmer and moving faster, water vaopor is a gas where the particles are even hotter and moving very fast in every direction ...
Steam Heating Specification
... The vendor shall confirm compatibility of the steam trap being specified by others. A mechanical trap (inverted bucket, float, free-float) with continuous air purging capability is the most robust choice for a heating system. If another type trap is being specified by others, vendor shall approve or ...
... The vendor shall confirm compatibility of the steam trap being specified by others. A mechanical trap (inverted bucket, float, free-float) with continuous air purging capability is the most robust choice for a heating system. If another type trap is being specified by others, vendor shall approve or ...
Exam 4 - Nicholls State University
... d. Not enough information 2. You want to take apart a couple of steel parts held together by brass screws, but the parts are stuck. What should you do to remove the screws? (The coefficient of linear expansion for steel is 11 ×10-6 °C-1. The coefficient for brass is 19×10-6 °C-1.) a. heat the parts ...
... d. Not enough information 2. You want to take apart a couple of steel parts held together by brass screws, but the parts are stuck. What should you do to remove the screws? (The coefficient of linear expansion for steel is 11 ×10-6 °C-1. The coefficient for brass is 19×10-6 °C-1.) a. heat the parts ...
HEAT OF FUSION AND MECHANICAL EQUIVALENT OF HEAT
... cal/g·°C. The specific heat of aluminum is 0.215 cal/g·°C, and the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g·°C. For the thermometer furnished with the equipment the product mtct is 0.80 cal/°C. The masses of the copper band, the copper cylinder, and the water can all be determined by weighing. With thes ...
... cal/g·°C. The specific heat of aluminum is 0.215 cal/g·°C, and the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g·°C. For the thermometer furnished with the equipment the product mtct is 0.80 cal/°C. The masses of the copper band, the copper cylinder, and the water can all be determined by weighing. With thes ...
Cogeneration

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Trigeneration or combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP) refers to the simultaneous generation of electricity and useful heating and cooling from the combustion of a fuel or a solar heat collector. Cogeneration is a thermodynamically efficient use of fuel. In separate production of electricity, some energy must be discarded as waste heat, but in cogeneration this thermal energy is put to use. All thermal power plants emit heat during electricity generation, which can be released into the natural environment through cooling towers, flue gas, or by other means. In contrast, CHP captures some or all of the by-product for heating, either very close to the plant, or—especially in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe—as hot water for district heating with temperatures ranging from approximately 80 to 130 °C. This is also called combined heat and power district heating (CHPDH). Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures (100–180 °C, 212–356 °F) can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling.The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator and the resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating as described in cogeneration. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW) a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Trigeneration differs from cogeneration in that the waste heat is used for both heating and cooling, typically in an absorption refrigerator. CCHP systems can attain higher overall efficiencies than cogeneration or traditional power plants. In the United States, the application of trigeneration in buildings is called building cooling, heating and power (BCHP). Heating and cooling output may operate concurrently or alternately depending on need and system construction.Cogeneration was practiced in some of the earliest installations of electrical generation. Before central stations distributed power, industries generating their own power used exhaust steam for process heating. Large office and apartment buildings, hotels and stores commonly generated their own power and used waste steam for building heat. Due to the high cost of early purchased power, these CHP operations continued for many years after utility electricity became available.