Guidelines for Work in Hot Environments
... Hot Environments and the Human Body The human body functions best within a narrow internal temperature range of 36 to 38 degrees Celsius. Below this range, the body's temperature control center in the brain goes to work, directing more blood to vital internal organs and causing shivering to help kee ...
... Hot Environments and the Human Body The human body functions best within a narrow internal temperature range of 36 to 38 degrees Celsius. Below this range, the body's temperature control center in the brain goes to work, directing more blood to vital internal organs and causing shivering to help kee ...
Notes - PowerPoint
... Constant Pressure Calorimetry • By carrying out a reaction in aqueous solution in a simple calorimeter such as this one, one can indirectly measure the heat change for the system by measuring the heat change for the water in the calorimeter. • Because the specific heat for water is well known (4.18 ...
... Constant Pressure Calorimetry • By carrying out a reaction in aqueous solution in a simple calorimeter such as this one, one can indirectly measure the heat change for the system by measuring the heat change for the water in the calorimeter. • Because the specific heat for water is well known (4.18 ...
Topic 3_2__Thermal properties of matter
... temperature change, we use the simpler thermal capacity C. Q = CT thermal capacity C defined EXAMPLE: What are the thermal capacities of the ingot and the block of the previous example? SOLUTION: From the previous example Q = 1143000 J. From Q = CT we get C = Q/T. Ingot: C = 1143000/12.4 = 922 ...
... temperature change, we use the simpler thermal capacity C. Q = CT thermal capacity C defined EXAMPLE: What are the thermal capacities of the ingot and the block of the previous example? SOLUTION: From the previous example Q = 1143000 J. From Q = CT we get C = Q/T. Ingot: C = 1143000/12.4 = 922 ...
processing of low-viscosity cbt thermoplastic composites
... including toughness and recyclability, without the high viscosities normally associated with these materials. These advantages are particularly significant for the manufacture of largescale composite structures, for example, wind turbine blades. Existing technology using thermosets mean that it is g ...
... including toughness and recyclability, without the high viscosities normally associated with these materials. These advantages are particularly significant for the manufacture of largescale composite structures, for example, wind turbine blades. Existing technology using thermosets mean that it is g ...
Heat - Quia
... should be able to: • Define the quantity of heat in terms of the calorie, the kilocalorie, the joule, and the Btu. • Write and apply formulas for specific heat capacity and solve for gains and losses of heat. • Write and apply formulas for calculating the latent heats of fusion and vaporization of v ...
... should be able to: • Define the quantity of heat in terms of the calorie, the kilocalorie, the joule, and the Btu. • Write and apply formulas for specific heat capacity and solve for gains and losses of heat. • Write and apply formulas for calculating the latent heats of fusion and vaporization of v ...
MECHANICAL AND ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENTS
... quantity of makeup air. These simple devices often supplement the building’s main heating/cooling system, which deals primarily with heat gains/losses through the building skin. Even in hot, humid climates, indirect evaporative cooling can help lower the temperature of makeup air. ...
... quantity of makeup air. These simple devices often supplement the building’s main heating/cooling system, which deals primarily with heat gains/losses through the building skin. Even in hot, humid climates, indirect evaporative cooling can help lower the temperature of makeup air. ...
Applied Thermodynamics
... However, there are some processes that can be assumed internally reversible with good approximation, such as processes in cylinders with reciprocating piston. The working fluid is always in an equilibrium state in internally reversible process. But the surroundings undergo a state change that can ne ...
... However, there are some processes that can be assumed internally reversible with good approximation, such as processes in cylinders with reciprocating piston. The working fluid is always in an equilibrium state in internally reversible process. But the surroundings undergo a state change that can ne ...
Chapter 4
... ►The closed gas turbine operates as follows: ►A gas circulates through four components: turbine, compressor, and two heat exchangers at higher and lower operating temperatures, respectively. ►The turbine and compressor play the same roles as in the open gas turbine. ►As the gas passes through the hi ...
... ►The closed gas turbine operates as follows: ►A gas circulates through four components: turbine, compressor, and two heat exchangers at higher and lower operating temperatures, respectively. ►The turbine and compressor play the same roles as in the open gas turbine. ►As the gas passes through the hi ...
Inducing Hypothermia in Neonates on Extracorporeal Membrane
... care workers who have a wide range of training [1]. However, these methods are the slowest to act [1]. Research has shown that external means of cooling can take upwards of 6 hours to reach the target core body temperature [1]. External means of inducing hypothermia also elicits a shiver response fr ...
... care workers who have a wide range of training [1]. However, these methods are the slowest to act [1]. Research has shown that external means of cooling can take upwards of 6 hours to reach the target core body temperature [1]. External means of inducing hypothermia also elicits a shiver response fr ...
Summer Heat Protection
... relationship of fluctuations between the external and internal temperatures. For example if the outside temperature fluctuates between 10 and 40 oC and the inside temperature fluctuates between 18 and 21 oC then the external change is 30K (Kelvin) and the internal change is 3K. The relationship of A ...
... relationship of fluctuations between the external and internal temperatures. For example if the outside temperature fluctuates between 10 and 40 oC and the inside temperature fluctuates between 18 and 21 oC then the external change is 30K (Kelvin) and the internal change is 3K. The relationship of A ...
HEAT FLOW THROUGH A TYPICAL WALL IN AKURE By Adeyinka
... wall, canopy wall , Sandcrete block wall, cavities, solid of the block, conductive heat transfer, convective heat, Radiative heat transfer. 1. INTRODUCTION Building materials no matter the section of construction they belong to, they either gain or loss heat from or to the environment respectively. ...
... wall, canopy wall , Sandcrete block wall, cavities, solid of the block, conductive heat transfer, convective heat, Radiative heat transfer. 1. INTRODUCTION Building materials no matter the section of construction they belong to, they either gain or loss heat from or to the environment respectively. ...
(I) Temperature and Thermometers
... Examples of doing work are rubbing a block on a rough surface, hammering a metal object, compressing gases, etc. In all cases, a force is exerted on a body through a distance. Work is defined as: Force and distance are measured in newton (N) and metre (m) respectively, the unit of work is newt ...
... Examples of doing work are rubbing a block on a rough surface, hammering a metal object, compressing gases, etc. In all cases, a force is exerted on a body through a distance. Work is defined as: Force and distance are measured in newton (N) and metre (m) respectively, the unit of work is newt ...
Thermal Applications
... applications derive their geometrical data from the ModelBuilder. This is supplemented with application-specific data provided within the Thermal Application Category. The input data requirements of the thermal applications are summarised below. The data is managed by utility programs invoked from t ...
... applications derive their geometrical data from the ModelBuilder. This is supplemented with application-specific data provided within the Thermal Application Category. The input data requirements of the thermal applications are summarised below. The data is managed by utility programs invoked from t ...
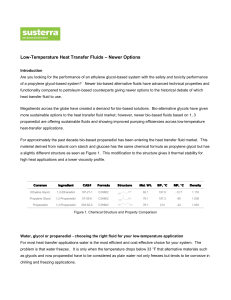
Low-Temperature Heat Transfer Fluids Newer Options
... Heat transfer fluids are widely used in food processing, commercial refrigeration, geothermal, and other lowtemperature heat-transfer applications that typically operate in a temperature range from 0°F to 42°F (-18°C to 6°C). Most heat transfer fluids have lower heat-transfer efficiencies than wate ...
... Heat transfer fluids are widely used in food processing, commercial refrigeration, geothermal, and other lowtemperature heat-transfer applications that typically operate in a temperature range from 0°F to 42°F (-18°C to 6°C). Most heat transfer fluids have lower heat-transfer efficiencies than wate ...
Use of Phase Change Materials in Construction of Buildings: A Review
... thermal performance. The inclusion of PCM in concrete yields a significant improvement in the thermal performance of the concrete. Jessica Giro-Paloma et al. (2013) suggested that the use of microencapsulated PCM has many advantages as microcapsules can handle phase change materials as core allowing ...
... thermal performance. The inclusion of PCM in concrete yields a significant improvement in the thermal performance of the concrete. Jessica Giro-Paloma et al. (2013) suggested that the use of microencapsulated PCM has many advantages as microcapsules can handle phase change materials as core allowing ...
Chapter 10: Vapor and Combined Power Cycles
... To improve the cycle thermal efficiency, the average temperature at which heat is added must be increased. One way to do this is to allow the steam leaving the boiler to expand the steam in the turbine to an intermediate pressure. A portion of the steam is extracted from the turbine and sent to a re ...
... To improve the cycle thermal efficiency, the average temperature at which heat is added must be increased. One way to do this is to allow the steam leaving the boiler to expand the steam in the turbine to an intermediate pressure. A portion of the steam is extracted from the turbine and sent to a re ...
Topic 5 - Lloyd Crosby
... a. Definition of thermal equilibrium Thermal equilibrium is a state in which heat does not flow between a system and its surroundings because they are both at the same temperature. b. Reaching thermal equilibrium For a system in thermal contact with its surroundings (meaning not thermally insulated) ...
... a. Definition of thermal equilibrium Thermal equilibrium is a state in which heat does not flow between a system and its surroundings because they are both at the same temperature. b. Reaching thermal equilibrium For a system in thermal contact with its surroundings (meaning not thermally insulated) ...
Second Progress Report.pdf
... TE modules onto personal computer microprocessors and operating the computers over various levels of processing. For electrical power generation, a TE module was able to generate a small amount of power in microwatts. Automobile manufacturers have also investigated the use of TE devices for waste he ...
... TE modules onto personal computer microprocessors and operating the computers over various levels of processing. For electrical power generation, a TE module was able to generate a small amount of power in microwatts. Automobile manufacturers have also investigated the use of TE devices for waste he ...
Chapter 4
... wax(7) and mineral oil(1) 118 - 126 degrees F 113 - 121 for lower extremities 6x more heat than water ...
... wax(7) and mineral oil(1) 118 - 126 degrees F 113 - 121 for lower extremities 6x more heat than water ...
CALORPLAST Heat Exchangers
... The CALORPLAST heat exchanger is designed in modular elements connected to provide the required heat transfer surface area for a specific application. The exchanger modules are one foot wide and are available in the following lengths: 1.7, 2.4, 3.1, 3.7, 4.4, 5.0, 5.7, 7.0, and 8.3 ft. The modules ...
... The CALORPLAST heat exchanger is designed in modular elements connected to provide the required heat transfer surface area for a specific application. The exchanger modules are one foot wide and are available in the following lengths: 1.7, 2.4, 3.1, 3.7, 4.4, 5.0, 5.7, 7.0, and 8.3 ft. The modules ...
Cogeneration

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Trigeneration or combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP) refers to the simultaneous generation of electricity and useful heating and cooling from the combustion of a fuel or a solar heat collector. Cogeneration is a thermodynamically efficient use of fuel. In separate production of electricity, some energy must be discarded as waste heat, but in cogeneration this thermal energy is put to use. All thermal power plants emit heat during electricity generation, which can be released into the natural environment through cooling towers, flue gas, or by other means. In contrast, CHP captures some or all of the by-product for heating, either very close to the plant, or—especially in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe—as hot water for district heating with temperatures ranging from approximately 80 to 130 °C. This is also called combined heat and power district heating (CHPDH). Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures (100–180 °C, 212–356 °F) can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling.The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator and the resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating as described in cogeneration. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW) a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Trigeneration differs from cogeneration in that the waste heat is used for both heating and cooling, typically in an absorption refrigerator. CCHP systems can attain higher overall efficiencies than cogeneration or traditional power plants. In the United States, the application of trigeneration in buildings is called building cooling, heating and power (BCHP). Heating and cooling output may operate concurrently or alternately depending on need and system construction.Cogeneration was practiced in some of the earliest installations of electrical generation. Before central stations distributed power, industries generating their own power used exhaust steam for process heating. Large office and apartment buildings, hotels and stores commonly generated their own power and used waste steam for building heat. Due to the high cost of early purchased power, these CHP operations continued for many years after utility electricity became available.