STABILITY AND STRATEGIC TIME
... Multiagent systems (MAS) have long been a successful means for modelling the interaction of software agents (or simply, programs) with themselves, other humans, and a given environment. In this context, there is an ever increasing need for MAS: 1. able to perform temporal inferences and 2. capable o ...
... Multiagent systems (MAS) have long been a successful means for modelling the interaction of software agents (or simply, programs) with themselves, other humans, and a given environment. In this context, there is an ever increasing need for MAS: 1. able to perform temporal inferences and 2. capable o ...
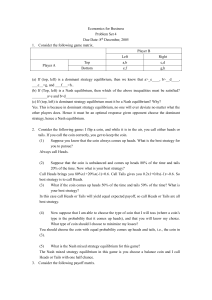
NOTES ON NASH EQUILIBRIUM 1. 2 × 2 games, pure
... Note that Ruth and Charlie would in fact be better off if they did not testify (they would spend 5 years rather than 10 years in jail). But that is not what Game theory recommends, and that is not what is observed in practice either. . . A way to express that Ruth and Charlie would be better off if ...
... Note that Ruth and Charlie would in fact be better off if they did not testify (they would spend 5 years rather than 10 years in jail). But that is not what Game theory recommends, and that is not what is observed in practice either. . . A way to express that Ruth and Charlie would be better off if ...
New complexity results about Nash equilibria
... A key concept in computational complexity theory is that of a reduction from one problem A to another problem B. Informally, a reduction maps every instance of computational problem A to a corresponding instance of computational problem B, in such a way that the answer to the former instance can be ...
... A key concept in computational complexity theory is that of a reduction from one problem A to another problem B. Informally, a reduction maps every instance of computational problem A to a corresponding instance of computational problem B, in such a way that the answer to the former instance can be ...
Multiplicative updates outperform generic no-regret learning in congestion games
... stable Nash equilibrium. The replicator dynamic and other differential equations are studied in evolutionary game theory [23, 35], which also considers associated notions of stability such as evolutionarily stable states (ESS) and neutrally stable states (NSS). The book of Fudenberg and Levine [14] ...
... stable Nash equilibrium. The replicator dynamic and other differential equations are studied in evolutionary game theory [23, 35], which also considers associated notions of stability such as evolutionarily stable states (ESS) and neutrally stable states (NSS). The book of Fudenberg and Levine [14] ...
Simulating Normal Random Variables
... for each player) with the property that no player can increase her payoff by choosing a different action, given the other players' actions. ...
... for each player) with the property that no player can increase her payoff by choosing a different action, given the other players' actions. ...
Solution Concepts
... Nash equilibrium might arrive through introspection. A second justification is that Nash equilibria are self-enforcing. If players agree on a strategy profile before independently choosing their actions, then no player will have reason to deviate if the agreed profile is a Nash equilibrium. On the o ...
... Nash equilibrium might arrive through introspection. A second justification is that Nash equilibria are self-enforcing. If players agree on a strategy profile before independently choosing their actions, then no player will have reason to deviate if the agreed profile is a Nash equilibrium. On the o ...
Graduate School of Economics Waseda University Waseda University
... Proof: It is easy to confirm that 1.=⇒ 2. Indeed, if a given choice function is ordinal potential rationalizable, then f coincides with the set of all pure strategy Nash equilibria of some ordinal potential game G = [N, (Xi )i∈N , (ui )i∈N ] or its restriction G |A . Let φ be an ordinal potential of ...
... Proof: It is easy to confirm that 1.=⇒ 2. Indeed, if a given choice function is ordinal potential rationalizable, then f coincides with the set of all pure strategy Nash equilibria of some ordinal potential game G = [N, (Xi )i∈N , (ui )i∈N ] or its restriction G |A . Let φ be an ordinal potential of ...
Behavioral conformity in games with many players
... where each society consists of one player.5 A crucial aspect of our main results will thus be to bound the number of societies independently of the size of the player set. In games with many 3 The term ‘crowding type’ is taken from Conley and Wooders (2001) and their earlier papers. Crowding types a ...
... where each society consists of one player.5 A crucial aspect of our main results will thus be to bound the number of societies independently of the size of the player set. In games with many 3 The term ‘crowding type’ is taken from Conley and Wooders (2001) and their earlier papers. Crowding types a ...
Intelligent Autonomous Agents
... confesses, both are released. If both confess then they get sent to jail. If one confesses and the other does not, then the confessor gets a light sentence and the other gets a heavy ...
... confesses, both are released. If both confess then they get sent to jail. If one confesses and the other does not, then the confessor gets a light sentence and the other gets a heavy ...
mechanism design
... v, ) (standard definitions apply; see book for details) with full performance (x, p). Then the expected payoff satisfy Vi() = Vi(0) + Ei[z(t) | ti=s] (dvi/ds) ds. Prepared for MICT PhD course, Department of Economics, UCL by Daniel Rogger, UCL PhD candidate ...
... v, ) (standard definitions apply; see book for details) with full performance (x, p). Then the expected payoff satisfy Vi() = Vi(0) + Ei[z(t) | ti=s] (dvi/ds) ds. Prepared for MICT PhD course, Department of Economics, UCL by Daniel Rogger, UCL PhD candidate ...
Game Theory Problem Set 4 Solutions
... area of Nash Equilibria on the upper left consists entirely of equilibria where 2 wins the object. By bidding more than v1, 2 prevents 1 from over bidding her, and by bidding less than v2, 1 gives 2 no incentive to drop her bid. 4. N = {1, 2} Ai = [0, ∞), for all i P (10 + Pj − αPi ),αPi < 10 + Pj ...
... area of Nash Equilibria on the upper left consists entirely of equilibria where 2 wins the object. By bidding more than v1, 2 prevents 1 from over bidding her, and by bidding less than v2, 1 gives 2 no incentive to drop her bid. 4. N = {1, 2} Ai = [0, ∞), for all i P (10 + Pj − αPi ),αPi < 10 + Pj ...
Winners Curse - Application of Game Theory to Insurance Pricing
... The views expressed in this presentation are those of invited contributors and not necessarily those of the IFoA. The IFoA do not endorse any of the views stated, nor any claims or representations made in this presentation and accept no responsibility or liability to any person for loss or damage su ...
... The views expressed in this presentation are those of invited contributors and not necessarily those of the IFoA. The IFoA do not endorse any of the views stated, nor any claims or representations made in this presentation and accept no responsibility or liability to any person for loss or damage su ...
The possible and the impossible in multi-agent learning
... There is a well-known condition in statistics that guarantees that all players will learn to predict in the strong sense. Namely, it suffices that each player’s forecast of the others’ behavior, conditional on his own behavior, never exclude events that have positive probability under their actual j ...
... There is a well-known condition in statistics that guarantees that all players will learn to predict in the strong sense. Namely, it suffices that each player’s forecast of the others’ behavior, conditional on his own behavior, never exclude events that have positive probability under their actual j ...
EQUILIBRIUM SELECTION IN THE NASH DEMAND GAME AN
... as the demand that k would have asked for in case of having been matched. Since such a demand is not realized it is not observed by the rest of individuals. After all matches have taken place, each individual receives the opportunity of revising her action according to an independent Bernoulli trial ...
... as the demand that k would have asked for in case of having been matched. Since such a demand is not realized it is not observed by the rest of individuals. After all matches have taken place, each individual receives the opportunity of revising her action according to an independent Bernoulli trial ...
07.9 - Sophia Antipolis
... to leave a patch not yet exhausted in order to find a new one, in spite of an uncertain travel-time. Charnov’s marginal value theorem reveals that the optimal giving up time is when the intake-rate is equal to the optimal long-term mean rate γ ∗ —that, if achieved, gives the best fitness a forager c ...
... to leave a patch not yet exhausted in order to find a new one, in spite of an uncertain travel-time. Charnov’s marginal value theorem reveals that the optimal giving up time is when the intake-rate is equal to the optimal long-term mean rate γ ∗ —that, if achieved, gives the best fitness a forager c ...
Comparing the Notions of Optimality in Strategic Games and Soft... Krzysztof R. Apt F. Rossi and K. B. Venable
... 1997), model problems with preferences using c-semirings. A c-semiring is a tuple hA, +, ×, 0, 1i, where: • A is a set, called the carrier of the semiring, and 0, 1 ∈ A; • + is commutative, associative, idempotent, 0 is its unit element, and 1 is its absorbing element; • × is associative, commutativ ...
... 1997), model problems with preferences using c-semirings. A c-semiring is a tuple hA, +, ×, 0, 1i, where: • A is a set, called the carrier of the semiring, and 0, 1 ∈ A; • + is commutative, associative, idempotent, 0 is its unit element, and 1 is its absorbing element; • × is associative, commutativ ...
Playing Large Games using Simple Strategies
... support (in the number of available pure strategies). Moreover the strategy of each player in such an equilibrium is uniform on a small multiset and can be expressed in polylogarithmically many bits. In our opinion, this is an interesting observation on the structure of competitive behavior in vario ...
... support (in the number of available pure strategies). Moreover the strategy of each player in such an equilibrium is uniform on a small multiset and can be expressed in polylogarithmically many bits. In our opinion, this is an interesting observation on the structure of competitive behavior in vario ...
ProbSet7.pdf
... two quantities to find the quantities in the Nash-Cournot equilibrium of this game. Hence find the prices and the profits in this equilibrium. (c) (5 points) Solve the inverse demand functions to get the (direct) demand functions, expressing each of Q1 and Q2 in terms of both prices P1 and P2 . (d) (8 ...
... two quantities to find the quantities in the Nash-Cournot equilibrium of this game. Hence find the prices and the profits in this equilibrium. (c) (5 points) Solve the inverse demand functions to get the (direct) demand functions, expressing each of Q1 and Q2 in terms of both prices P1 and P2 . (d) (8 ...
Nash Equilibrium in Tullock Contests
... ”Behavioral Variation in Tullock Contests”, joint with F. Mengel and Ph. Reiss ...
... ”Behavioral Variation in Tullock Contests”, joint with F. Mengel and Ph. Reiss ...
Bayesian Learning and Convergence to Nash
... players as well as the actions over time each player-type will choose. Each player then maximizes her expected utility for the in®nite horizon game given that belief. Second, suppose that the beliefs of players are such that if one player assigns probability zero to an event, then all other players ...
... players as well as the actions over time each player-type will choose. Each player then maximizes her expected utility for the in®nite horizon game given that belief. Second, suppose that the beliefs of players are such that if one player assigns probability zero to an event, then all other players ...
6 The Mixing Problem: Purification and Conjectures
... implementation costs, but in this case they play a critical role in evaluating the relative costs of playing a mixed strategy best response or any of the pure strategies in its support. Hence the mixing problem: why bother ...
... implementation costs, but in this case they play a critical role in evaluating the relative costs of playing a mixed strategy best response or any of the pure strategies in its support. Hence the mixing problem: why bother ...
30. TYPE OF THE RETAILER PROBLEM WITH COMPLETE INFORMATION WITH NASH EQUALIBRIA REPEATEDLY
... demand of one can be reallocated to another, then the small firms may want to see the order/production of the leader before they place their orders. In the Stackelberg version of the competitive retailer problem, there is a market leader retailer and other is the follower. The leader makes his decis ...
... demand of one can be reallocated to another, then the small firms may want to see the order/production of the leader before they place their orders. In the Stackelberg version of the competitive retailer problem, there is a market leader retailer and other is the follower. The leader makes his decis ...
Answers to Midterm Exam II
... result. For completeness, note that (High, Low) and (Low, High) can’t be Nash given these two conditions – the player who gets X always wants to switch and get 8 instead. These two conditions also imply that playing High is a dominant strategy for both players: playing High always pays more than pla ...
... result. For completeness, note that (High, Low) and (Low, High) can’t be Nash given these two conditions – the player who gets X always wants to switch and get 8 instead. These two conditions also imply that playing High is a dominant strategy for both players: playing High always pays more than pla ...
Kin selection and Evolution of Sympathy
... • Selection is for utility and sympathy, not strategies (as in Alger-Weibull theory). • Individuals cannot determine sympathies of others, can only observe actions. • Mutants act as if probability that their opponent is like them is r. • Normals almost never see mutants. They act as if opponent is s ...
... • Selection is for utility and sympathy, not strategies (as in Alger-Weibull theory). • Individuals cannot determine sympathies of others, can only observe actions. • Mutants act as if probability that their opponent is like them is r. • Normals almost never see mutants. They act as if opponent is s ...