AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES Systemic VS Organ
... after they've run their course. Other autoimmune diseases may run a more progressive course, particularly in certain age groups. An example is SLE, which is more likely to be fatal in younger patients. Treatment Treatment in autoimmune disease initially aims to reduce symptoms. For instance, in type ...
... after they've run their course. Other autoimmune diseases may run a more progressive course, particularly in certain age groups. An example is SLE, which is more likely to be fatal in younger patients. Treatment Treatment in autoimmune disease initially aims to reduce symptoms. For instance, in type ...
The Inflammatory Response
... atherosclerosis …… and……obesity! • Pollen and particles from smoking and pollution can constantly irritate certain tissues • Tissue damage from atherosclerosis, heart disease and wounds that don’t heal can constantly irritate certain tissues, as well. ...
... atherosclerosis …… and……obesity! • Pollen and particles from smoking and pollution can constantly irritate certain tissues • Tissue damage from atherosclerosis, heart disease and wounds that don’t heal can constantly irritate certain tissues, as well. ...
Immunopharmacology
... machanisms of action are similar, both bind to cytoplasmic peptidyl(肽基)-prolyl(脯氨酰) isomerases(异 构酶). For liver, kidney, heart, pancreas, and bone marrow transplant applications. Toxic effects: nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, hyperglycemia (requiring insulin therapy), gastrointestinal dysfunction ...
... machanisms of action are similar, both bind to cytoplasmic peptidyl(肽基)-prolyl(脯氨酰) isomerases(异 构酶). For liver, kidney, heart, pancreas, and bone marrow transplant applications. Toxic effects: nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, hyperglycemia (requiring insulin therapy), gastrointestinal dysfunction ...
skin and immune system
... – Pathogens that trigger this response are called antigens • These may be viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites •The immune response attacks the particular pathogen with a response designed especially for it •Two types of wbc’s that recognize specific antigens – B cells – pathogens and antigens in bod ...
... – Pathogens that trigger this response are called antigens • These may be viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites •The immune response attacks the particular pathogen with a response designed especially for it •Two types of wbc’s that recognize specific antigens – B cells – pathogens and antigens in bod ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... Classified according to the degree of MHC similarity between donor and host: autograft – recipient also serves as donor isograft – tissue from identical twin is grafted allograft – genetically different individuals but of the same species (humans) xenograft – individuals of different species ...
... Classified according to the degree of MHC similarity between donor and host: autograft – recipient also serves as donor isograft – tissue from identical twin is grafted allograft – genetically different individuals but of the same species (humans) xenograft – individuals of different species ...
development - LSU School of Medicine
... identify specific tests available for the diagnosis of various infectious diseases. Know the importance of proper specimen collection and its effect on results, explain the limitations of those tests (sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, cost), and describe the difference between colonizatio ...
... identify specific tests available for the diagnosis of various infectious diseases. Know the importance of proper specimen collection and its effect on results, explain the limitations of those tests (sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, cost), and describe the difference between colonizatio ...
Immunogeno: Protective mechanism for Rift Valley fever in the
... against RVF virus was reported in Katanga Province during the same survey; this serological evidence was associated with abortions cases in Cattle (Mulumba et al. 2009). Livestock immunisation is important for control of Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV) epidemics; however immunisation of susceptible d ...
... against RVF virus was reported in Katanga Province during the same survey; this serological evidence was associated with abortions cases in Cattle (Mulumba et al. 2009). Livestock immunisation is important for control of Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV) epidemics; however immunisation of susceptible d ...
Immune Responses
... The speed and effectiveness of the secondary immune response is the basis of vaccination. When someone is vaccinated, they are injected with a microbial antigen that has marker proteins that are not identified as being part of the body. Although vaccinations won’t cause severe disease symptoms, they ...
... The speed and effectiveness of the secondary immune response is the basis of vaccination. When someone is vaccinated, they are injected with a microbial antigen that has marker proteins that are not identified as being part of the body. Although vaccinations won’t cause severe disease symptoms, they ...
File - Classes with Mrs. Sheetz
... • Cytotoxic T-cells: make proteins called receptors specific to the one antigen; sticks to antigen and kills it • Suppresser T-cells: shut the immune response off when infection is gone • Memory: the body has the ability to remember/recognize a pathogen and prevent future infection ...
... • Cytotoxic T-cells: make proteins called receptors specific to the one antigen; sticks to antigen and kills it • Suppresser T-cells: shut the immune response off when infection is gone • Memory: the body has the ability to remember/recognize a pathogen and prevent future infection ...
Acquired Immune Response
... infection. Causes fever, swelling, and redness in area. The swelling and redness is called inflammation. ...
... infection. Causes fever, swelling, and redness in area. The swelling and redness is called inflammation. ...
The immune system
... • The immune system - an overview (basic concepts, features) • Developmental biology of the immune system (Dr. L. Lu) • Recent advances in lymphocyte lineage commitment (Dr. L. Lu) • Apoptosis & the molecular cell death pathways (Dr. L. Lu) • Antigen recognition by T cells & its MHC restrictions • P ...
... • The immune system - an overview (basic concepts, features) • Developmental biology of the immune system (Dr. L. Lu) • Recent advances in lymphocyte lineage commitment (Dr. L. Lu) • Apoptosis & the molecular cell death pathways (Dr. L. Lu) • Antigen recognition by T cells & its MHC restrictions • P ...
Lecture 1: The immune system: an overview
... • The immune system - an overview (basic concepts, features) • Developmental biology of the immune system (Dr. L. Lu) • Recent advances in lymphocyte lineage commitment (Dr. L. Lu) • Apoptosis & the molecular cell death pathways (Dr. L. Lu) • Antigen recognition by T cells & its MHC restrictions • P ...
... • The immune system - an overview (basic concepts, features) • Developmental biology of the immune system (Dr. L. Lu) • Recent advances in lymphocyte lineage commitment (Dr. L. Lu) • Apoptosis & the molecular cell death pathways (Dr. L. Lu) • Antigen recognition by T cells & its MHC restrictions • P ...
Immune System
... after the development of antibodies during the actual disease Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity: resistance to a specific disease by receiving antiserum-containing antibodies from another host ...
... after the development of antibodies during the actual disease Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity: resistance to a specific disease by receiving antiserum-containing antibodies from another host ...
Acquired immunity
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
QUESTIONARY IN INFECTIOUS DISEASES, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND
... P.S. Questions N 5 and 22 – 69 require answers in infectology (etiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, clinical forms, complications, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment) and epidemiological measures and immunoprophylaxis of the specified infectious disease. Questions 76-90 require answe ...
... P.S. Questions N 5 and 22 – 69 require answers in infectology (etiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, clinical forms, complications, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment) and epidemiological measures and immunoprophylaxis of the specified infectious disease. Questions 76-90 require answe ...
PPT - Larry Smarr - California Institute for Telecommunications and
... Visualizing 5-10 Year Time Series of 150 Blood & Stool Variables Led Me to Discover a Chronic Disease ...
... Visualizing 5-10 Year Time Series of 150 Blood & Stool Variables Led Me to Discover a Chronic Disease ...
Vaccines Largest Cause of Insulin
... authors note that many authorities consider the nervous system and the immune system to be actually one system in the body. The article documents that many connections between the nervous system and every aspect of the immune system, including discoveries made back in 1945 when it was noted that eve ...
... authors note that many authorities consider the nervous system and the immune system to be actually one system in the body. The article documents that many connections between the nervous system and every aspect of the immune system, including discoveries made back in 1945 when it was noted that eve ...
such as bacteria and viruses. Platelets
... organism’s blood forever. These will recognize the antigens of this specific invader if it infects the organism again, allowing it to be destroyed much more quickly the second time. iv. If the virus is later encountered, the immune system can more easily 5. Fungal Infections a. A fungus is a member ...
... organism’s blood forever. These will recognize the antigens of this specific invader if it infects the organism again, allowing it to be destroyed much more quickly the second time. iv. If the virus is later encountered, the immune system can more easily 5. Fungal Infections a. A fungus is a member ...
(“Multiple Sclerosis”) OR (PubMed Health)
... Plasma exchange, also known as plasmapheresis, involves taking blood out of the body and removing components in the blood's plasma that are thought to be harmful. The rest of the blood, plus replacement plasma, is then transfused back into the body. This treatment has not been shown to be effective ...
... Plasma exchange, also known as plasmapheresis, involves taking blood out of the body and removing components in the blood's plasma that are thought to be harmful. The rest of the blood, plus replacement plasma, is then transfused back into the body. This treatment has not been shown to be effective ...
partner search
... obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) progressively increases. Genetic susceptibility and environmental factors play important role in the development of asthma and COPD. In 80-90% of cases the cause of COPD is tobacco smoking. The base of these diseases is a chronic inflammation of the respiratory t ...
... obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) progressively increases. Genetic susceptibility and environmental factors play important role in the development of asthma and COPD. In 80-90% of cases the cause of COPD is tobacco smoking. The base of these diseases is a chronic inflammation of the respiratory t ...
CBS_Nov_22_05
... Infectious Diseases in the World •11 million (19%) of the 57 million people who died in the world in 2002 were killed by infectious or parasitic infection [WHO, 2004] •The three main single infectious diseases are HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria, each of which causes more than 1 million deaths ...
... Infectious Diseases in the World •11 million (19%) of the 57 million people who died in the world in 2002 were killed by infectious or parasitic infection [WHO, 2004] •The three main single infectious diseases are HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria, each of which causes more than 1 million deaths ...
Aspirations Diploma Plus High School
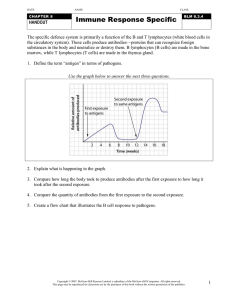
... Directions: Answer the questions below using your notes and knowledge of Biology 1. Some human white blood cells help destroy pathogenic bacteria by (1) causing mutations in the bacteria (3) producing toxins that compete with bacterial toxins (2) engulfing and digesting the bacteria (4) inserting pa ...
... Directions: Answer the questions below using your notes and knowledge of Biology 1. Some human white blood cells help destroy pathogenic bacteria by (1) causing mutations in the bacteria (3) producing toxins that compete with bacterial toxins (2) engulfing and digesting the bacteria (4) inserting pa ...