MEMBRANE TRANSPORT (Reader 1) Passive Transport Simple
... Hydrophilic molecules and very large molecules can't pass through the cell membrane by simple diffusion. They need help to pass through the membrane. The help is provided by proteins called transport proteins. This process is known as facilitated diffusion. There are two types of transport proteins: ...
... Hydrophilic molecules and very large molecules can't pass through the cell membrane by simple diffusion. They need help to pass through the membrane. The help is provided by proteins called transport proteins. This process is known as facilitated diffusion. There are two types of transport proteins: ...
Approaches Expectations
... the components that make it up. (Cellular Transport, n.d.) Part of the cell membrane is the way molecules get transported across of it through forms of passive and active transport. There are two types of transportation of molecules which are passive and active. The difference between them is that a ...
... the components that make it up. (Cellular Transport, n.d.) Part of the cell membrane is the way molecules get transported across of it through forms of passive and active transport. There are two types of transportation of molecules which are passive and active. The difference between them is that a ...
Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport
... response to different types of stimuli, such as electrical or chemical signals. A gated channel protein is a transport protein that opens a "gate," allowing a molecule to pass through the membrane. Gated channels have a binding site that is specific for a given molecule or ion. A stimulus causes the ...
... response to different types of stimuli, such as electrical or chemical signals. A gated channel protein is a transport protein that opens a "gate," allowing a molecule to pass through the membrane. Gated channels have a binding site that is specific for a given molecule or ion. A stimulus causes the ...
Document
... Factors affecting diffusion rate through a membrane • temperature ‐ ↑ temp., ↑ motion of particles • molecular weight ‐ larger molecules move slower • steepness of concentrated gradient ‐ ↑ difference, ↑ rate • membrane surface area ‐ ↑ area, ↑ rate • membrane permeability ‐ ↑ permeability, ↑ rate ...
... Factors affecting diffusion rate through a membrane • temperature ‐ ↑ temp., ↑ motion of particles • molecular weight ‐ larger molecules move slower • steepness of concentrated gradient ‐ ↑ difference, ↑ rate • membrane surface area ‐ ↑ area, ↑ rate • membrane permeability ‐ ↑ permeability, ↑ rate ...
Membrane Bound: C2-Domain Abscisic Acid
... (PYR)/PYR1-LIKE (PYL) ABA receptors. Following perception of ABA, these receptors form ternary complexes with clade A PP2C phosphatases (such as ABA INSENSITIVE1 and HYPERSENSITIVE TO ABA1), thereby inactivating them (Park et al., 2009) and unleashing a cascade of ABA responses. These ABA responses ...
... (PYR)/PYR1-LIKE (PYL) ABA receptors. Following perception of ABA, these receptors form ternary complexes with clade A PP2C phosphatases (such as ABA INSENSITIVE1 and HYPERSENSITIVE TO ABA1), thereby inactivating them (Park et al., 2009) and unleashing a cascade of ABA responses. These ABA responses ...
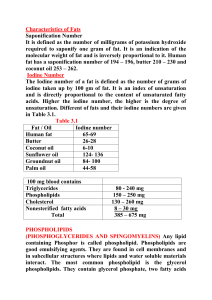
Characteristics of Fats Saponification Number It is defined as the
... and skin. Acetyl CoA is the precursor of all the C atoms in cholesterol. The level of cholesterol in body fluids is of primary importance due to its role in the development of atherosclerosis. In addition cholesterol plays an important role as a component of biomembranes and has a modulating effect ...
... and skin. Acetyl CoA is the precursor of all the C atoms in cholesterol. The level of cholesterol in body fluids is of primary importance due to its role in the development of atherosclerosis. In addition cholesterol plays an important role as a component of biomembranes and has a modulating effect ...
07_Lecture_Presentation
... • Membrane carbohydrates may be covalently bonded to lipids (forming glycolipids) or more commonly to proteins (forming glycoproteins) • Carbohydrates on the external side of the plasma membrane vary among species, individuals, and even cell types in an individual ...
... • Membrane carbohydrates may be covalently bonded to lipids (forming glycolipids) or more commonly to proteins (forming glycoproteins) • Carbohydrates on the external side of the plasma membrane vary among species, individuals, and even cell types in an individual ...
Lecture 4
... 1. represents potential difference at non-excited state -30 to -100mV depending on cell type 2. not all ion species may have an ion channel 3. there is an unequal distribution of ions due to active pumping mechanisms - contributes to Donnan equilibrium - creates chemical diffusion gradient that cont ...
... 1. represents potential difference at non-excited state -30 to -100mV depending on cell type 2. not all ion species may have an ion channel 3. there is an unequal distribution of ions due to active pumping mechanisms - contributes to Donnan equilibrium - creates chemical diffusion gradient that cont ...
Section 8.1 Summary – pages 195
... • Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • In a cell, water always moves to reach an equal concentration on both sides of the membrane. ...
... • Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • In a cell, water always moves to reach an equal concentration on both sides of the membrane. ...
Document
... Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. Number of mitochondria per cell varies and directly correlates with the cell’s metabolic activity. Are about 1µm in diameter and 1-10 µm in length. Are dynamic structure that move, change their shapes and divide. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., ...
... Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. Number of mitochondria per cell varies and directly correlates with the cell’s metabolic activity. Are about 1µm in diameter and 1-10 µm in length. Are dynamic structure that move, change their shapes and divide. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., ...
Nerve Impulses
... knob where they travel across the cleft to the receptors on the plasma membrane of the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... knob where they travel across the cleft to the receptors on the plasma membrane of the postsynaptic neuron. ...
Lecture 8 Cell Signalling
... Concept 11.3: Transduction: Cascades of molecular interactions relay signals from receptors to target molecules in the cell • Signal transduction usually involves multiple steps • Multistep pathways can amplify a signal: A few molecules can produce a large cellular response • Multistep pathways pro ...
... Concept 11.3: Transduction: Cascades of molecular interactions relay signals from receptors to target molecules in the cell • Signal transduction usually involves multiple steps • Multistep pathways can amplify a signal: A few molecules can produce a large cellular response • Multistep pathways pro ...
Moonlighting organelles—signals and cellular architecture
... achieved under the constraint of continuous small changes and a progressive loss of the original functionality? A way out of the dilemma is so called preadaptation, where a structure conveys more than one function. In addition to its evident job, it can carry a second, often hidden or implicit, func ...
... achieved under the constraint of continuous small changes and a progressive loss of the original functionality? A way out of the dilemma is so called preadaptation, where a structure conveys more than one function. In addition to its evident job, it can carry a second, often hidden or implicit, func ...
Ch 7 Powerpoint Review
... Which of the following factors would tend to increase membrane fluidity? A A. a greater proportion of unsaturated phospholipids B. a greater proportion of saturated phospholipids C. a lower temperature D. a relatively high protein content in the membrane E. a greater proportion of relatively large ...
... Which of the following factors would tend to increase membrane fluidity? A A. a greater proportion of unsaturated phospholipids B. a greater proportion of saturated phospholipids C. a lower temperature D. a relatively high protein content in the membrane E. a greater proportion of relatively large ...
Bio102 Problems
... 6. If the environmental temperature increases, it can kill a bacterial cell (which is prokaryotic). Increased temperature can cause many problems for cells, including problems with the cell membrane. A) What problem would increased temperature cause for a membrane? The membrane becomes too permeable ...
... 6. If the environmental temperature increases, it can kill a bacterial cell (which is prokaryotic). Increased temperature can cause many problems for cells, including problems with the cell membrane. A) What problem would increased temperature cause for a membrane? The membrane becomes too permeable ...
AP Biology- The Cell / Plasma Membrane and Cellular
... by the double bonds prevent them from packing tightly together. The saturated fats are tightly packed together. Membranes must be fluid to work properly; they are usually about as fluid as salad oil The steroid cholesterol has different effects on membrane fluidity at different temperatures. At ...
... by the double bonds prevent them from packing tightly together. The saturated fats are tightly packed together. Membranes must be fluid to work properly; they are usually about as fluid as salad oil The steroid cholesterol has different effects on membrane fluidity at different temperatures. At ...
Insane in the Membrane
... We have been talking about cells being a unit of organization in biology. Let's look at the cell membrane and see how that membrane keeps all of the pieces inside. When you think about a membrane, imagine it is like a big plastic bag with some tiny holes. That bag holds all of the cell pieces and fl ...
... We have been talking about cells being a unit of organization in biology. Let's look at the cell membrane and see how that membrane keeps all of the pieces inside. When you think about a membrane, imagine it is like a big plastic bag with some tiny holes. That bag holds all of the cell pieces and fl ...
Dietary Protein and Lipid Requirements of Golden Shiners and
... class distribution were noted. Feed intake did not differ between the two groups. These studies suggest that the typical protein level of many commercial baitfish feeds (32 percent) can be lowered substantially depending on the availability of natural foods in the pond. Lowering the protein level o ...
... class distribution were noted. Feed intake did not differ between the two groups. These studies suggest that the typical protein level of many commercial baitfish feeds (32 percent) can be lowered substantially depending on the availability of natural foods in the pond. Lowering the protein level o ...
Celltransport3
... • Hydrostatic pressure - the force exerted on the membrane by water • In capillaries, blood pressure forces water, salts, nutrients and solutes into tissue fluid, while larger particles like blood cells and protein are held back ...
... • Hydrostatic pressure - the force exerted on the membrane by water • In capillaries, blood pressure forces water, salts, nutrients and solutes into tissue fluid, while larger particles like blood cells and protein are held back ...
28P PROCEEDINGS OF THE BIOCHEMICAL SOCIETY
... The restorationof succinoxidase activity by phospholipidshas abehaviour that is inline withthe above effect. We conclude that there is an initial increase of binding sites for phospholipids at low salt concentrations, and an inhibition of binding randomly on all sites available at higher salt concen ...
... The restorationof succinoxidase activity by phospholipidshas abehaviour that is inline withthe above effect. We conclude that there is an initial increase of binding sites for phospholipids at low salt concentrations, and an inhibition of binding randomly on all sites available at higher salt concen ...
Cell Transport Notes
... NO… because particles are in constant motion When the # of particles is equal on both sides of the membrane then equilibrium is reached When particles reach equilibrium the rate of diffusion is equal across the membrane Membrane ...
... NO… because particles are in constant motion When the # of particles is equal on both sides of the membrane then equilibrium is reached When particles reach equilibrium the rate of diffusion is equal across the membrane Membrane ...
CASE 1
... endocrine system, which integrates tissue and organ functions through chemical signals (hormones) secreted from endocrine glands. However, it is known that all cells, even those outside the two “classical” communications systems, normally can sense and respond to physical and chemical signals in the ...
... endocrine system, which integrates tissue and organ functions through chemical signals (hormones) secreted from endocrine glands. However, it is known that all cells, even those outside the two “classical” communications systems, normally can sense and respond to physical and chemical signals in the ...
Cell signaling - Lectures For UG-5
... Signaling begins with the binding of a ligand to a TGF beta type II receptor. Ligand binding induces formation of complexes containing 2 copies of RI and RII. The RII is a serine/threonine receptor kinase. It catalyzes the phosphorylation of the RI. Each class of ligand binds to a specific RII. In m ...
... Signaling begins with the binding of a ligand to a TGF beta type II receptor. Ligand binding induces formation of complexes containing 2 copies of RI and RII. The RII is a serine/threonine receptor kinase. It catalyzes the phosphorylation of the RI. Each class of ligand binds to a specific RII. In m ...
Lipid raft
The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids and protein receptors organized in glycolipoprotein microdomains termed lipid rafts. These specialized membrane microdomains compartmentalize cellular processes by serving as organizing centers for the assembly of signaling molecules, influencing membrane fluidity and membrane protein trafficking, and regulating neurotransmission and receptor trafficking. Lipid rafts are more ordered and tightly packed than the surrounding bilayer, but float freely in the membrane bilayer. Although more common in plasma membrane, lipid rafts have also been reported in other parts of the cell, such as Golgi and lysosomes.