Mapping Earth`s Surface
... Scales and Ratios A ratio compares two numbers by division. For example, the scale of a map given as a ratio is 1:250,000. At this scale, the distance between two points on the map measures 23.5 cm. How would you find the actual distance? 1. Write the scale as a fraction. ...
... Scales and Ratios A ratio compares two numbers by division. For example, the scale of a map given as a ratio is 1:250,000. At this scale, the distance between two points on the map measures 23.5 cm. How would you find the actual distance? 1. Write the scale as a fraction. ...
Maps and Globes are Models of Earth
... The latitude lines are curved slightly, this allows for a more accurate size and shape of some landmasses ...
... The latitude lines are curved slightly, this allows for a more accurate size and shape of some landmasses ...
Reading Maps - CoconinoHighSchool
... south, east & west. In between are the directions northeast, ...
... south, east & west. In between are the directions northeast, ...
Classwork Questions
... 1. What part of a map will help you to understand what colors are used? 2. How can a Compass Rose be used to help find locations on a map? 3. How does the scale bar change depending on the scale of the map? 4. How can you quickly identify what the purpose of the map is (or what it is representing)? ...
... 1. What part of a map will help you to understand what colors are used? 2. How can a Compass Rose be used to help find locations on a map? 3. How does the scale bar change depending on the scale of the map? 4. How can you quickly identify what the purpose of the map is (or what it is representing)? ...
Homework 1
... Though homework assignments can and should be discussed in a study group, the answers you submit must be in your own words. ...
... Though homework assignments can and should be discussed in a study group, the answers you submit must be in your own words. ...
The Five Themes in Geography
... 1) Explain the difference between a physical and political map? 2) Give examples of special purpose maps and how they are used ...
... 1) Explain the difference between a physical and political map? 2) Give examples of special purpose maps and how they are used ...
Unit 1 Test - Owl Teacher
... sentences and need to be at least 250 words long. Make sure your essay answer has an introduction, a body, and a clear conclusion! Please answer on the back of this page. 1. If you were planning a two day car trip to a different state, would you take a map or a globe with ...
... sentences and need to be at least 250 words long. Make sure your essay answer has an introduction, a body, and a clear conclusion! Please answer on the back of this page. 1. If you were planning a two day car trip to a different state, would you take a map or a globe with ...
Basic Geography Skills
... • Political—shows political lines that divide countries (or states) • Physical—shows the physical features of the earth (mountains, deserts, etc.) • Climate—shows the different climate regions of the earth ...
... • Political—shows political lines that divide countries (or states) • Physical—shows the physical features of the earth (mountains, deserts, etc.) • Climate—shows the different climate regions of the earth ...
What_is_Geography_fill_in_student_copy
... • Globes have a disadvantage: They cannot be complete enough to be useful and at the same time be small enough to be convenient. • Therefore, people invented ________________________________. • Maps try to show the Earth, which is round, on a flat surface. • This causes distortion, or a change in ac ...
... • Globes have a disadvantage: They cannot be complete enough to be useful and at the same time be small enough to be convenient. • Therefore, people invented ________________________________. • Maps try to show the Earth, which is round, on a flat surface. • This causes distortion, or a change in ac ...
5 Themes of Geography Worksheet
... ______________________________, but the lines of ____________________ are ______________________. ...
... ______________________________, but the lines of ____________________ are ______________________. ...
“Take Five”
... Planar projections or azimuthal—gives the shortest distance between 2 points Conical projections—projections onto a cone shape—used to show landmasses that extend over large areas going east and west Cylindrical projections or Mercator—projections onto a cylinder that shows the whole earth ...
... Planar projections or azimuthal—gives the shortest distance between 2 points Conical projections—projections onto a cone shape—used to show landmasses that extend over large areas going east and west Cylindrical projections or Mercator—projections onto a cylinder that shows the whole earth ...
Intro to Geog - PPT 1
... The scale on a map tells you the relative distance on the map to the real world. For example, a map’s scale may tell you that one inch on the map equals one mile in the ...
... The scale on a map tells you the relative distance on the map to the real world. For example, a map’s scale may tell you that one inch on the map equals one mile in the ...
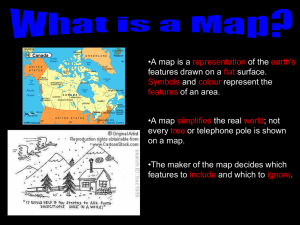
What is a Map?
... latitude and its longitude. • Who uses latitude and longitude “coordinates”? – Pilot – Captain of a Ship – GPS (Global Positioning System) ...
... latitude and its longitude. • Who uses latitude and longitude “coordinates”? – Pilot – Captain of a Ship – GPS (Global Positioning System) ...
Relocation Diffusion
... Choropleth – puts features into classes and then maps classes for each region Cartogram – adjusts the size of the country corresponds to the magnitude of the mapped feature Proportional symbol – size of the symbol corresponds to the magnitude of the mapped feature Dot – each dot represents some freq ...
... Choropleth – puts features into classes and then maps classes for each region Cartogram – adjusts the size of the country corresponds to the magnitude of the mapped feature Proportional symbol – size of the symbol corresponds to the magnitude of the mapped feature Dot – each dot represents some freq ...
Geography
... Dependence of countries on goods, resources, and knowledge from other parts of the world. ...
... Dependence of countries on goods, resources, and knowledge from other parts of the world. ...
The 5 Themes of Geography Power Point Presentation
... itself. • The only difference between a globe and the Earth itself is the scale, or size, represented on the globe. ...
... itself. • The only difference between a globe and the Earth itself is the scale, or size, represented on the globe. ...
The 5 Themes of Geography
... earth. Most accurate-not practical • A map is 2-dimensional view of the world. It is more detailed but is distorted (shapes change) • Cartography or mapping is the study or practice of making maps. • Cartographers or mapmakers are the people who do this ...
... earth. Most accurate-not practical • A map is 2-dimensional view of the world. It is more detailed but is distorted (shapes change) • Cartography or mapping is the study or practice of making maps. • Cartographers or mapmakers are the people who do this ...
Introduction to Human Geography
... because the have few people is doesn’t make much of a difference. • Used most often • Negatives: Eastern and Western areas are separated; Longitude lines do not meet (which happens in real life); the grid system (long and lat lines) do not form right angles in real life either. ...
... because the have few people is doesn’t make much of a difference. • Used most often • Negatives: Eastern and Western areas are separated; Longitude lines do not meet (which happens in real life); the grid system (long and lat lines) do not form right angles in real life either. ...
Geo-basics review
... What pattern do you notice with all of the coordinates you have located? Now use the following coordinates to identify the countries at the given ...
... What pattern do you notice with all of the coordinates you have located? Now use the following coordinates to identify the countries at the given ...