Exam 3 Questions for Monday Feb 4th
... Directions: Answer each question below. Read ALL the choices first.b ...
... Directions: Answer each question below. Read ALL the choices first.b ...
College 5
... antiparallel β-sheet. The N-H and C=O groups of a certain strand are hydrogen bonded to C=O and N-H groups of adjacent chains that run parallel to it, but in the opposite direction. The R-side groups in each strand alternately project above and below the plane of the sheet (see fig 4.20) ...
... antiparallel β-sheet. The N-H and C=O groups of a certain strand are hydrogen bonded to C=O and N-H groups of adjacent chains that run parallel to it, but in the opposite direction. The R-side groups in each strand alternately project above and below the plane of the sheet (see fig 4.20) ...
The endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi
... SER enzymes regulate glycogen metabolism cAMP-dependent glycogen phosphorylase here! GlycogenG-1-PG-6-P Why does muscle SER lack glucose-6-phosphorylase? Why does hepatocyte SER have glucose-6-phosphorylase? ...
... SER enzymes regulate glycogen metabolism cAMP-dependent glycogen phosphorylase here! GlycogenG-1-PG-6-P Why does muscle SER lack glucose-6-phosphorylase? Why does hepatocyte SER have glucose-6-phosphorylase? ...
Moonlighting and pleiotropy among regulators of the degradation
... features. Each of the two complexes is involved in a distinct cellular activity: the CSN promotes the function of a large family of ubiquitin E3 ligases known as CRLs, while the proteasome lid is required for ubiquitin hydrolysis from proteasome substrates before degradation. Both complexes determin ...
... features. Each of the two complexes is involved in a distinct cellular activity: the CSN promotes the function of a large family of ubiquitin E3 ligases known as CRLs, while the proteasome lid is required for ubiquitin hydrolysis from proteasome substrates before degradation. Both complexes determin ...
MB207_14 - MB207Jan2010
... • The extracellular portion of the receptor contains ligand-binding domain. The cytosolic portion of the receptor contains tyrosine residues that are in fact themselves targets for tyrosine kinase portion of the receptor. → receptor + protein kinase • In some cases, the receptor and tyrosine kinase ...
... • The extracellular portion of the receptor contains ligand-binding domain. The cytosolic portion of the receptor contains tyrosine residues that are in fact themselves targets for tyrosine kinase portion of the receptor. → receptor + protein kinase • In some cases, the receptor and tyrosine kinase ...
A non-conventional nuclear import pathway Sandra Korge1, Bert
... Generating a 24 hour rhythm of the molecular circadian clock is influenced by transcriptional and translational regulation as well as post-translational processes as nucleocytoplasmic protein shuttling. As it is known for Period (PER), Cryptochrome (CRY) and other clock proteins to carry classical n ...
... Generating a 24 hour rhythm of the molecular circadian clock is influenced by transcriptional and translational regulation as well as post-translational processes as nucleocytoplasmic protein shuttling. As it is known for Period (PER), Cryptochrome (CRY) and other clock proteins to carry classical n ...
Shin-ichi Tate Research Group Activity ・ Protein dynamics and
... 【Research Subject】 Exploring functionally related morphological changes of KcsA by NMR spectroscopy ...
... 【Research Subject】 Exploring functionally related morphological changes of KcsA by NMR spectroscopy ...
11 Cell Communication
... Up to 60% of all medicines exert their effects through G-protein linked receptors. ...
... Up to 60% of all medicines exert their effects through G-protein linked receptors. ...
A Protein Pathway
... that serves as the site of protein synthesis in the cell, acting as a kind of playback head on a cassette deck. The ribosome reads the instructions provided by the mRNA molecule, and produces a chain of amino acids that folds up into the molecule we call a protein. For proteins destined for export o ...
... that serves as the site of protein synthesis in the cell, acting as a kind of playback head on a cassette deck. The ribosome reads the instructions provided by the mRNA molecule, and produces a chain of amino acids that folds up into the molecule we call a protein. For proteins destined for export o ...
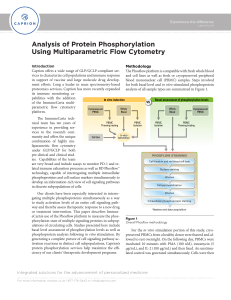
Analysis of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiparametric Flow
... stimulated in vitro exhibited marked increases in phosphorylation for all six phosphoproteins assayed when compared to unstimulated control cells. Basal levels of phosphorylation Phosphoprotein analysis of unstimulated clinical sample cells detects the basal level of protein phosphorylation. Assessm ...
... stimulated in vitro exhibited marked increases in phosphorylation for all six phosphoproteins assayed when compared to unstimulated control cells. Basal levels of phosphorylation Phosphoprotein analysis of unstimulated clinical sample cells detects the basal level of protein phosphorylation. Assessm ...
Abstract - in New Biology
... High protein diets reduce adiposity perhaps through effects on food intake and energy expenditure. Diet composition influences the gut microbiota and recent reports support this microbiome influences energy balance. We explored whether high protein diets influence the microbiome in the hindgut. Male ...
... High protein diets reduce adiposity perhaps through effects on food intake and energy expenditure. Diet composition influences the gut microbiota and recent reports support this microbiome influences energy balance. We explored whether high protein diets influence the microbiome in the hindgut. Male ...
Chapter 5 – The Proteins and Amino Acids
... amounts sufficient to meet physiological need. Since all body cells contain protein, routine maintenance and repair of body tissue requires a continual supply of amino acids to synthesize proteins. Growth of new tissue requires additional protein. The Functions of Body Proteins The major role of die ...
... amounts sufficient to meet physiological need. Since all body cells contain protein, routine maintenance and repair of body tissue requires a continual supply of amino acids to synthesize proteins. Growth of new tissue requires additional protein. The Functions of Body Proteins The major role of die ...
Review Sheet for Test on Cell Membrane and Cells
... DNA can be in the form of chromatin or chromosomes (depending if the cell is dividing or not) Compare the structure and function of a vacuole in a plant cell to a vacuole in a freshwater protist. Steps in Making a ProteinNucleus contains DNA that instructs how to make the protein. Ribosome makes the ...
... DNA can be in the form of chromatin or chromosomes (depending if the cell is dividing or not) Compare the structure and function of a vacuole in a plant cell to a vacuole in a freshwater protist. Steps in Making a ProteinNucleus contains DNA that instructs how to make the protein. Ribosome makes the ...
Bio1A Unit 1-3 The Cell Notes File
... Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another – Are not part of the endomembrane system – Have a double membrane – Contain their own circular DNA & ribosomes (small) ~20% of protein made inside • Mitochondria (plants and animals) are the sites of cellular respiration, a metabo ...
... Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another – Are not part of the endomembrane system – Have a double membrane – Contain their own circular DNA & ribosomes (small) ~20% of protein made inside • Mitochondria (plants and animals) are the sites of cellular respiration, a metabo ...
CH 107 SI Summer 2015 Worksheet 13 Answers What are the two
... α-helices and β-sheets Hydrogen bonds 2. What types of interactions can be present in tertiary protein structure? Rank the interactions from strongest to weakest. disulfide bonds >> salt bridges > hydrogen bonds > hydrophilic interactions > hydrophobic interactions 3. Compare and contrast globular a ...
... α-helices and β-sheets Hydrogen bonds 2. What types of interactions can be present in tertiary protein structure? Rank the interactions from strongest to weakest. disulfide bonds >> salt bridges > hydrogen bonds > hydrophilic interactions > hydrophobic interactions 3. Compare and contrast globular a ...
Name__________________________________
... 2. Which structure is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes? ...
... 2. Which structure is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes? ...
Alphabodies – working inside the cell
... can only address another 10%, that exist as extracellular proteins. It is therefore estimated that the vast majority of all potential protein targets, more than 80%, are currently considered ‘undruggable’ by the two main classes of therapeutic drugs.1 A large number of these undruggable targets belo ...
... can only address another 10%, that exist as extracellular proteins. It is therefore estimated that the vast majority of all potential protein targets, more than 80%, are currently considered ‘undruggable’ by the two main classes of therapeutic drugs.1 A large number of these undruggable targets belo ...
AP Biology
... This chapter is often considered difficult as you have not covered it in your introductory biology course. Plan on reading this chapter at least twice and go slowly. I would suggest that you read the key concepts in bold first and then for each concept, look at the headings, then the figures and the ...
... This chapter is often considered difficult as you have not covered it in your introductory biology course. Plan on reading this chapter at least twice and go slowly. I would suggest that you read the key concepts in bold first and then for each concept, look at the headings, then the figures and the ...
Translation (Protein Synthesis)
... • mRNA from nucleus Through cytoplasm to the ribosome mRNA start codon AUG signals beginning of protein ...
... • mRNA from nucleus Through cytoplasm to the ribosome mRNA start codon AUG signals beginning of protein ...
Death or Damage of Dopamine neurons
... The hallmark pathology of Parkinson’s disease is the damage and death of dopamine producing neurons in the brain. Dopamine plays a role in controlling movement, cognition, learning, and mood, explaining the dementia and difficulty with motor control exhibited by patients with deficits in the product ...
... The hallmark pathology of Parkinson’s disease is the damage and death of dopamine producing neurons in the brain. Dopamine plays a role in controlling movement, cognition, learning, and mood, explaining the dementia and difficulty with motor control exhibited by patients with deficits in the product ...
Chapter 14 Oxidative Phosphorylation Prokaryotes are bacteria
... Eukaryotes contain multiple chromosomes surrounded by a membrane (nucleus) and membrane-bound organelles. Some organelles such as the nucleus and mitochondrion have two membranes. Animal Cell ...
... Eukaryotes contain multiple chromosomes surrounded by a membrane (nucleus) and membrane-bound organelles. Some organelles such as the nucleus and mitochondrion have two membranes. Animal Cell ...
Protein phosphorylation

Protein phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or modifying its function. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins. The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, and tyrosine in eukaryotes, and histidine in prokaryotes, which play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, many other amino acids can also be phosphorylated, including arginine, lysine, and cysteine. Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906 by Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research with the discovery of phosphorylated vitellin. However, it was nearly 50 years until the enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinases was discovered.