Cell Free Protein Synthesis
... – coupled System, where DNA is used as template are generally simpler and more efficient; they also avoid problems of mRNA degradation and mRNA secondary structure – or as an uncoupled system, which requires mRNA template produced from native sources or by in vitro transcription. Uncoupled systems c ...
... – coupled System, where DNA is used as template are generally simpler and more efficient; they also avoid problems of mRNA degradation and mRNA secondary structure – or as an uncoupled system, which requires mRNA template produced from native sources or by in vitro transcription. Uncoupled systems c ...
Experiment 9: The Widely Varying Colors of d
... Possible coordination sites for metal ions in proteins are –CO2-, -CONH-, NH2, -OH (serine, threonine), -ArOH (tyrosine), -S- (cysteine), and imidazole (histidine). There are also a few coordinating groups other than amino acid residues in certain proteins; e.g., heme group. The different combinatio ...
... Possible coordination sites for metal ions in proteins are –CO2-, -CONH-, NH2, -OH (serine, threonine), -ArOH (tyrosine), -S- (cysteine), and imidazole (histidine). There are also a few coordinating groups other than amino acid residues in certain proteins; e.g., heme group. The different combinatio ...
Proteinstruktur und
... Note: the modification masses here are nominal masses Slide by David Tabb, Vanderbilt University, USA ...
... Note: the modification masses here are nominal masses Slide by David Tabb, Vanderbilt University, USA ...
CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY - Eastern Mediterranean University
... oxidative phosphorylation. • Through complex I to complex V (ATP synthase), ATP is generated. • Ineffective DNA repair system mutations = diseases ...
... oxidative phosphorylation. • Through complex I to complex V (ATP synthase), ATP is generated. • Ineffective DNA repair system mutations = diseases ...
Biochemistry Chapter 17
... Individual amino acids are carried through the blood stream to the cells where they are reassembled into needed proteins. ...
... Individual amino acids are carried through the blood stream to the cells where they are reassembled into needed proteins. ...
I. Characteristics of amino acids and folding of nascent polypeptides
... channel (leaving the precursor associated with SecYEG). and binds another segment of the precursor; the process repeats, resulting in sequential threading of the unfolded precursor protein in 20-30 amino acid segments through the Sec YEG channel. This sequential process relies on conformational chan ...
... channel (leaving the precursor associated with SecYEG). and binds another segment of the precursor; the process repeats, resulting in sequential threading of the unfolded precursor protein in 20-30 amino acid segments through the Sec YEG channel. This sequential process relies on conformational chan ...
Chemistry - WISE @ UC
... student is “Exploring the role of molecular machines in breaking apart cytoskeletal filaments”. Microtubules, the main component of the cell cytoskeleton, play fundamental roles in cellular processes ranging from cellular transport to mitosis. These roles are all intimately connected with microtubul ...
... student is “Exploring the role of molecular machines in breaking apart cytoskeletal filaments”. Microtubules, the main component of the cell cytoskeleton, play fundamental roles in cellular processes ranging from cellular transport to mitosis. These roles are all intimately connected with microtubul ...
Fig. 4.3 - glenbrook s hs
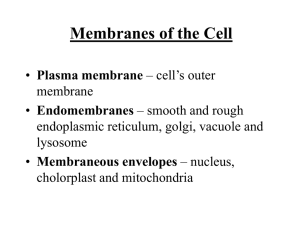
... • Semi-permeable (selectively permeable) – allows some substances to pass through, but blocks the passgae of other substances • Membranes enclose and maintain the specific chemical environment • Every membrane carries out its specific functions ...
... • Semi-permeable (selectively permeable) – allows some substances to pass through, but blocks the passgae of other substances • Membranes enclose and maintain the specific chemical environment • Every membrane carries out its specific functions ...
Bovine prolactin soluble receptor ECD ECD-11
... and reproduction. The initial step in its action is the binding to a specific membrane receptor (prolactin receptor) which belongs to the superfamily of class 1 cytokine receptors. Prolactin (PRL) is a hormone involved in a variety of important functions including ion transport and osmoregulation, s ...
... and reproduction. The initial step in its action is the binding to a specific membrane receptor (prolactin receptor) which belongs to the superfamily of class 1 cytokine receptors. Prolactin (PRL) is a hormone involved in a variety of important functions including ion transport and osmoregulation, s ...
103 Lecture Ch20b
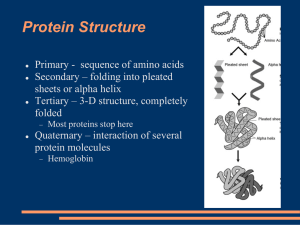
... more polypeptide subunits • The subunits each have their own tertiary structure and are held together by the same forces involved in tertiary structure • For example, hemoglobin is a globular protein that consists of four subunits, of two different types - each subunit contains a heme group for O2 b ...
... more polypeptide subunits • The subunits each have their own tertiary structure and are held together by the same forces involved in tertiary structure • For example, hemoglobin is a globular protein that consists of four subunits, of two different types - each subunit contains a heme group for O2 b ...
Protein Structures
... Hydrophobic interactions often play a key role in maintaining a protein’s shape. “R” groups in amino acids are either hydrophobic or hydrophilic and will seek aquatic or non-aquatic environments accordingly, which determines their location within the protein. Hydrogen bonds facilitate stabilization ...
... Hydrophobic interactions often play a key role in maintaining a protein’s shape. “R” groups in amino acids are either hydrophobic or hydrophilic and will seek aquatic or non-aquatic environments accordingly, which determines their location within the protein. Hydrogen bonds facilitate stabilization ...
medmicro4-weapons delivery – G+
... Studies of S. aureus Protein A, showed that membrane ‘anchor’ plays a transient role in a more ...
... Studies of S. aureus Protein A, showed that membrane ‘anchor’ plays a transient role in a more ...
Phosphoproteomics as a tool to unravel plant
... Received 1 September 2005; revised 12 September 2005 doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2005.00615.x ...
... Received 1 September 2005; revised 12 September 2005 doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2005.00615.x ...
Introduction to Proteins: Biotech 2
... Due to 20 different amino acids available The chemical and physical properties are different among the different amino acids ...
... Due to 20 different amino acids available The chemical and physical properties are different among the different amino acids ...
Posttranslational Modification
... bind to DNA and to nucleosomes and induce structural changes that affect transcription, replication and other DNA-dependent activities ...
... bind to DNA and to nucleosomes and induce structural changes that affect transcription, replication and other DNA-dependent activities ...
Biology 340 Molecular Biology
... receptors for epinephrine, serotonin, glucagon 2. ion channel receptors acetylcholine receptor at neuromuscular junction 3. tyrosine kinase linked receptors receptors for cytokines, interferons, HGF 4. receptors with intrinsic enzyme activity receptors for insulin, many growth factors Second ...
... receptors for epinephrine, serotonin, glucagon 2. ion channel receptors acetylcholine receptor at neuromuscular junction 3. tyrosine kinase linked receptors receptors for cytokines, interferons, HGF 4. receptors with intrinsic enzyme activity receptors for insulin, many growth factors Second ...
Oral nutritional supplementation (ONS) in renal
... Malnutrition is a significant problem in haemodialysis (HD) patients and estimated to be present in 30-60% of the renal population. A number of factors put this particular group of patients at risk of malnutrition; ...
... Malnutrition is a significant problem in haemodialysis (HD) patients and estimated to be present in 30-60% of the renal population. A number of factors put this particular group of patients at risk of malnutrition; ...
Cell Structure Practice: Nucleus
... When we say that the rough ER “finishes” protein, what do we mean? It folds the protein into the correct shape? ...
... When we say that the rough ER “finishes” protein, what do we mean? It folds the protein into the correct shape? ...
Recombinant Human COL9A3 protein ab158167 Product datasheet 1 Image Overview
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
Slide ()
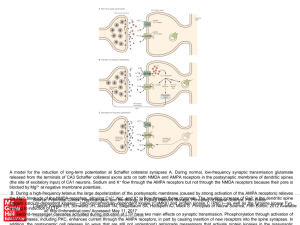
... released from the terminals of CA3 Schaffer collateral axons acts on both NMDA and AMPA receptors in the postsynaptic membrane of dendritic spines (the site of excitatory input) of CA1 neurons. Sodium and K+ flow through the AMPA receptors but not through the NMDA receptors because their pore is blo ...
... released from the terminals of CA3 Schaffer collateral axons acts on both NMDA and AMPA receptors in the postsynaptic membrane of dendritic spines (the site of excitatory input) of CA1 neurons. Sodium and K+ flow through the AMPA receptors but not through the NMDA receptors because their pore is blo ...
INTRODUCTION to BIOENERGETICS H.R. Kaback
... terminating the signal is by re-uptake of neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine, serotonin, glutamate, glycine) into the pre-synaptic cell and subsequent repackaging into synaptic vesicles. ...
... terminating the signal is by re-uptake of neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine, serotonin, glutamate, glycine) into the pre-synaptic cell and subsequent repackaging into synaptic vesicles. ...
Nick Grishin "Evolutionary Classification of Protein Domains
... Homology is frequently obscured by sequence divergence, spatial structure changes and resemblance between unrelated 3D structures. We have developed a hierarchical evolutionary classification of all proteins with experimentally determined spatial structures. ECOD (Evolutionary Classification of prot ...
... Homology is frequently obscured by sequence divergence, spatial structure changes and resemblance between unrelated 3D structures. We have developed a hierarchical evolutionary classification of all proteins with experimentally determined spatial structures. ECOD (Evolutionary Classification of prot ...
L4_Cell Communication_Fa08
... – Conversion of signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response – May be several steps with intermediaries: signal transduction pathway • relay molecules ...
... – Conversion of signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response – May be several steps with intermediaries: signal transduction pathway • relay molecules ...
Protein phosphorylation

Protein phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or modifying its function. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins. The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, and tyrosine in eukaryotes, and histidine in prokaryotes, which play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, many other amino acids can also be phosphorylated, including arginine, lysine, and cysteine. Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906 by Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research with the discovery of phosphorylated vitellin. However, it was nearly 50 years until the enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinases was discovered.