The Changing Environment - Mr. Hamilton`s Classroom
... away of land by weather and water; a natural process where soil is lost, transported, and reformed. ...
... away of land by weather and water; a natural process where soil is lost, transported, and reformed. ...
Emerging scientific challenges at the interface of surface and deep
... constraints on the latter two. Moreover, the heterogeneity of lithospheric and mantle properties in polar regions is poorly known, and could have significant impacts on our reconstructions of ice history. Finally, both viscous and elastic response to glacial loading and unloading result in stress ch ...
... constraints on the latter two. Moreover, the heterogeneity of lithospheric and mantle properties in polar regions is poorly known, and could have significant impacts on our reconstructions of ice history. Finally, both viscous and elastic response to glacial loading and unloading result in stress ch ...
Glaciers - Firelands Local Schools
... 2. Continental glacier: massive sheet of ice a. May cover millions of square kilometers & be thousands of meters thick b. Not confined by surrounding topography -- free-moving c. Currently only exist in Greenland & Argentina ...
... 2. Continental glacier: massive sheet of ice a. May cover millions of square kilometers & be thousands of meters thick b. Not confined by surrounding topography -- free-moving c. Currently only exist in Greenland & Argentina ...
Global Systems - Vocabulary Worksheet File
... We can consider that materials are moved or recycled through the Earth through several interconnected natural systems by natural processes. For example, an atom of oxygen will move through the biosphere through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration but will also enter the hydrosphere throu ...
... We can consider that materials are moved or recycled through the Earth through several interconnected natural systems by natural processes. For example, an atom of oxygen will move through the biosphere through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration but will also enter the hydrosphere throu ...
Ice Age introduction
... – Today 85% of the world’s area covered by glacier ice is accounted for by Antarctica, 11% by Greenland. (Just 4% by everywhere else!) – During the LGM, Antarctica accounted for over 30% of the total area and Greenland about 5%. – The Laurentide Ice Sheet over north-east North America accounted for ...
... – Today 85% of the world’s area covered by glacier ice is accounted for by Antarctica, 11% by Greenland. (Just 4% by everywhere else!) – During the LGM, Antarctica accounted for over 30% of the total area and Greenland about 5%. – The Laurentide Ice Sheet over north-east North America accounted for ...
Lecture32_webpost - UA Atmospheric Sciences
... Natural changes in the Earth’s climate also occur at much longer timescales ...
... Natural changes in the Earth’s climate also occur at much longer timescales ...
Paleoclimatology -
... hunting hard. Lack of sunlight combined with a shortage of fruit would have caused rickets, the disease that shaped Neanderthal’s body. Babel •The water in the ice sheets would have come out of the oceans, lowering their level and forming an ice bridge between Siberia and Alaska. It is possible it a ...
... hunting hard. Lack of sunlight combined with a shortage of fruit would have caused rickets, the disease that shaped Neanderthal’s body. Babel •The water in the ice sheets would have come out of the oceans, lowering their level and forming an ice bridge between Siberia and Alaska. It is possible it a ...
Paper Number: 466 - American Geosciences Institute
... has a role in reshaping the Earth surface by slope and aspect on surrounding meteorological conditions. The Polar Regions of the Earth are marked by the wide spread presence of cold -dry type glaciers, polythermal glaciers and Polar ice sheets. The deglaciated terrain in these regions exhibit landfo ...
... has a role in reshaping the Earth surface by slope and aspect on surrounding meteorological conditions. The Polar Regions of the Earth are marked by the wide spread presence of cold -dry type glaciers, polythermal glaciers and Polar ice sheets. The deglaciated terrain in these regions exhibit landfo ...
Observations explained by “Snowball Earth”
... Snow-covered oceans at high and middle latitudes. Where precipitation exceeds evaporation, the surface will be dry snow with albedo about 0.8. Snow-free glacier ice exposed in the subtropics. This ice will resemble the snowfree “blue ice” surfaces found near Antarctic mountains. This ice has a high ...
... Snow-covered oceans at high and middle latitudes. Where precipitation exceeds evaporation, the surface will be dry snow with albedo about 0.8. Snow-free glacier ice exposed in the subtropics. This ice will resemble the snowfree “blue ice” surfaces found near Antarctic mountains. This ice has a high ...
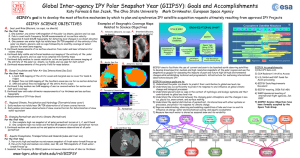
powerpoint poster - International Polar Year
... 1. One summer, one winter SAR snapshot of the polar ice sheets, glaciers and ice caps. 2. Pole to coast multi-frequency InSAR measurements of ice surface velocity 3. Repeated X-band InSAR topography for detecting local changes in ice sheet elevation 4. One summer one winter high res visible/near IR/ ...
... 1. One summer, one winter SAR snapshot of the polar ice sheets, glaciers and ice caps. 2. Pole to coast multi-frequency InSAR measurements of ice surface velocity 3. Repeated X-band InSAR topography for detecting local changes in ice sheet elevation 4. One summer one winter high res visible/near IR/ ...
Our Changing World
... been writing about it • Rocks provide the best record of Earth’s history • Most rocks form in layers as bits of gravel, sand, and mud pressed together • These are known as sedimentary rocks • These preserve a rough record of the past ...
... been writing about it • Rocks provide the best record of Earth’s history • Most rocks form in layers as bits of gravel, sand, and mud pressed together • These are known as sedimentary rocks • These preserve a rough record of the past ...
Sea Level Change and Climate - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... O (0.24%) has 8 protons and 8 neutrons, 16O (99.76%) has 8 protons and 10 neutrons Subtle differences in how these atoms behave in the world. 16O is lighter and therefore more easily evaporated. δ18O is a measure of the relative abundance of these two isotopes. Positive values have more 18O and nega ...
... O (0.24%) has 8 protons and 8 neutrons, 16O (99.76%) has 8 protons and 10 neutrons Subtle differences in how these atoms behave in the world. 16O is lighter and therefore more easily evaporated. δ18O is a measure of the relative abundance of these two isotopes. Positive values have more 18O and nega ...
1) THIS IS THE WARMEST CLIMATE ZONE ON EARTH, AND THE
... a) global warming & El Nina c) global warming & the end of an ice age ...
... a) global warming & El Nina c) global warming & the end of an ice age ...
Orbital-Scale Interactions in the Climate System
... Strong summer insolation peaks pace rapid deglaciations ...
... Strong summer insolation peaks pace rapid deglaciations ...
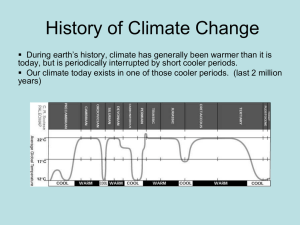
History of Climate Change
... 2. When seasonal variations in radiation received in the Northern Hemisphere are the greatest; glaciers retreat and we enter into an interglacial period. ...
... 2. When seasonal variations in radiation received in the Northern Hemisphere are the greatest; glaciers retreat and we enter into an interglacial period. ...
now and ice cores from antarctica , greenland and high altitude
... pollution became extremely important during the 20th century as a ...
... pollution became extremely important during the 20th century as a ...
Chapter 20
... Glacial Landforms and the Ice Age This chapter examines the role of glacial ice as a denudation and landforming agent. Glacial ice had a major impact on the landscapes of midlatitude and subarctic regions during the past Ice Age and still covers many high latitude and high elevation areas of the Ear ...
... Glacial Landforms and the Ice Age This chapter examines the role of glacial ice as a denudation and landforming agent. Glacial ice had a major impact on the landscapes of midlatitude and subarctic regions during the past Ice Age and still covers many high latitude and high elevation areas of the Ear ...
Question of Glaciation
... retreating glacier. A detached block of ice, buried in these deposits, has melted allowing the deposits to ‘cave in’ creating a kettle hole. ...
... retreating glacier. A detached block of ice, buried in these deposits, has melted allowing the deposits to ‘cave in’ creating a kettle hole. ...
doc
... The James Ross Island Volcanic Group is a large (c. 6000 km2) basaltic volcanic field situated in northern Antarctic Peninsula and dominated by the long-lived (> 6.25 m.y.) Mount Haddington stratovolcano. It is in a pivotal position (northerly latitude, low elevation) to record the dynamics of the a ...
... The James Ross Island Volcanic Group is a large (c. 6000 km2) basaltic volcanic field situated in northern Antarctic Peninsula and dominated by the long-lived (> 6.25 m.y.) Mount Haddington stratovolcano. It is in a pivotal position (northerly latitude, low elevation) to record the dynamics of the a ...
Name: Group: Date: ______ 4-ESS2-1. Evidence of Weathering and
... weathering agents Physical Changes ...
... weathering agents Physical Changes ...
Earth`s Frozen Water
... warm air and water weaken the ice. This breaking up process is called calving. • If a flat piece falls off and forms a broken sheet on the water, it’s called pack ice. • If a large chunk breaks off and floats off into the ocean, it’s called an iceberg. ...
... warm air and water weaken the ice. This breaking up process is called calving. • If a flat piece falls off and forms a broken sheet on the water, it’s called pack ice. • If a large chunk breaks off and floats off into the ocean, it’s called an iceberg. ...
Earth`s Frozen Water
... warm air and water weaken the ice. This breaking up process is called calving. • If a flat piece falls off and forms a broken sheet on the water, it’s called pack ice. • If a large chunk breaks off and floats off into the ocean, it’s called an iceberg. ...
... warm air and water weaken the ice. This breaking up process is called calving. • If a flat piece falls off and forms a broken sheet on the water, it’s called pack ice. • If a large chunk breaks off and floats off into the ocean, it’s called an iceberg. ...
Save PDF - Greens/EFA
... The climate interacts with the Earth's crust through the changing mass of water and ice that is shifted around the planet. Actually the pressure of water and ice on the crust is enormous: 1 cubic metre of water weighs 1 tonne, while the same volume of ice weighs up to 0.9 tonnes. When the weight of ...
... The climate interacts with the Earth's crust through the changing mass of water and ice that is shifted around the planet. Actually the pressure of water and ice on the crust is enormous: 1 cubic metre of water weighs 1 tonne, while the same volume of ice weighs up to 0.9 tonnes. When the weight of ...
Cryosphere

The cryosphere (from the Greek κρύος kryos, ""cold"", ""frost"" or ""ice"" and σφαῖρα sphaira, ""globe, ball"") is those portions of Earth's surface where water is in solid form, including sea ice, lake ice, river ice, snow cover, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, and frozen ground (which includes permafrost). Thus, there is a wide overlap with the hydrosphere. The cryosphere is an integral part of the global climate system with important linkages and feedbacks generated through its influence on surface energy and moisture fluxes, clouds, precipitation, hydrology, atmospheric and oceanic circulation. Through these feedback processes, the cryosphere plays a significant role in the global climate and in climate model response to global changes. The term deglaciation describes the retreat of cryospheric features.