Russia Chronology to Oct 1917 Pre-Enrolment
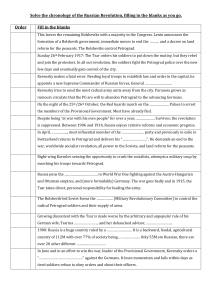
... Demand for change, defeat in the war, different nationalities all lead to opposition and protest against the regime. On …………………………… 22nd January 1905, Tsarist troops fire on unarmed protesters killing hundreds and sparking revolution. Power is now split between the Provisional Government and the …… ...
... Demand for change, defeat in the war, different nationalities all lead to opposition and protest against the regime. On …………………………… 22nd January 1905, Tsarist troops fire on unarmed protesters killing hundreds and sparking revolution. Power is now split between the Provisional Government and the …… ...
Russian Revolution Timeline
... Nicholas II (Romanov) becomes Tsar. Announces “The principle of autocracy will be maintained by me as firmly and unswervingly as by my lamented father.” ...
... Nicholas II (Romanov) becomes Tsar. Announces “The principle of autocracy will be maintained by me as firmly and unswervingly as by my lamented father.” ...
1. THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTIONARY MOVEMENT 1. In December of
... 1. Ordered the Petrograd garrison to launch an offensive against the Germans. 2. Soldiers called for an immediate overthrow of the Provisional Government. 3. Lenin tried to calm everyone down, and prevented a disorderly revolution. 4. There were epic food and fuel shortages. 5. On October 17, “Histo ...
... 1. Ordered the Petrograd garrison to launch an offensive against the Germans. 2. Soldiers called for an immediate overthrow of the Provisional Government. 3. Lenin tried to calm everyone down, and prevented a disorderly revolution. 4. There were epic food and fuel shortages. 5. On October 17, “Histo ...
Timeline of Russian Revolution
... - All workers decided to strike - After the riots and strikes, Tsar Nicholas issued the October Manifesto, a document which gave basic rights and liberties to the people and brought an end to the 1905 Russian Revolution - The Duma was also created, which gave the people a say in the government ...
... - All workers decided to strike - After the riots and strikes, Tsar Nicholas issued the October Manifesto, a document which gave basic rights and liberties to the people and brought an end to the 1905 Russian Revolution - The Duma was also created, which gave the people a say in the government ...
31-wh-russian-revolution
... The March Revolution (1917) Inspired by women textile worker strike in Petrograd Soldiers shot at then sided with strikers ...
... The March Revolution (1917) Inspired by women textile worker strike in Petrograd Soldiers shot at then sided with strikers ...
Олимпиада по истории (на английском языке) 1
... 11. Upon his return to Russia, how did Lenin view revolutionaries outside his own party? (A) As friends and allies (B) As potential Bolsheviks whom he needed to convert (C) He ignored them (D) As enemies who might be used temporarily but had to be eliminated in the end 12. What slogan did Lenin use ...
... 11. Upon his return to Russia, how did Lenin view revolutionaries outside his own party? (A) As friends and allies (B) As potential Bolsheviks whom he needed to convert (C) He ignored them (D) As enemies who might be used temporarily but had to be eliminated in the end 12. What slogan did Lenin use ...
February Revolution
The February Revolution (Russian: Февра́льская револю́ция; IPA: [fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə]) of 1917 was the first of two revolutions in Russia in 1917. It was centered on Petrograd, then the capital (now St. Petersburg), on Women's Day in March (late February in the Julian calendar). The revolution was confined to the capital and its vicinity, and lasted less than a week. It involved mass demonstrations and armed clashes with police and gendarmes, the last loyal forces of the Russian monarchy. In the last days mutinous Russian Army forces sided with the revolutionaries. The immediate result of the revolution was the abdication of Tsar Nicholas II, the end of the Romanov dynasty, and the end of the Russian Empire. The Tsar was replaced by a Russian Provisional Government under Prince Georgy Lvov. The Provisional Government was an alliance between liberals and socialists who wanted political reform. They set up a democratically-elected executive and constituent assembly. At the same time, socialists also formed the Petrograd Soviet, which ruled alongside the Provisional Government, an arrangement termed Dual Power.This revolution appeared to break out spontaneously, without any real leadership or formal planning. Russia had been suffering from a number of economic and social problems, which were compounded by the impact of World War I. Bread rioters and industrial strikers were joined on the streets by disaffected soldiers from the city's garrison. As more and more troops deserted, and with loyal troops away at the Front, the city fell into a state of chaos, leading to the overthrow of the Tsar.The February Revolution was followed in the same year by the October Revolution, bringing Bolshevik rule and a change in Russia's social structure, and paving the way for the Soviet Union.





