chapter 12 human remains
... In males the index finger is sometimes shorter than the third finger. ...
... In males the index finger is sometimes shorter than the third finger. ...
Chapter 3 – early studies of the central nervous system
... nerves equally excitable at all times? ...
... nerves equally excitable at all times? ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... Pertaining to measurements of quantity and including such properties as size, number, and capacity. When data are quantified, they’re expressed numerically and can be tested ...
... Pertaining to measurements of quantity and including such properties as size, number, and capacity. When data are quantified, they’re expressed numerically and can be tested ...
Anthropology and Human Evolution
... that the offspring were always one of the two colours. He developed the theory of dominant traits and applied it ...
... that the offspring were always one of the two colours. He developed the theory of dominant traits and applied it ...
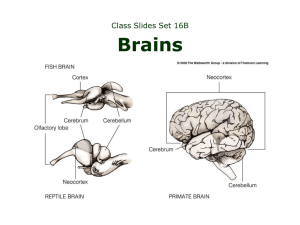
BOX 42.1 HOW DO WE LEARN ABOUT BRAIN EVOLUTION? There
... early primates already differ from most early mammals by having more neocortex in proportion to the rest of the brain, and more neocortex devoted to the temporal lobe where visual processing occurs. This implies a greater emphasis on functions mediated by neocortex and a greater emphasis especially ...
... early primates already differ from most early mammals by having more neocortex in proportion to the rest of the brain, and more neocortex devoted to the temporal lobe where visual processing occurs. This implies a greater emphasis on functions mediated by neocortex and a greater emphasis especially ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ 94: A Meeting of Minds Read pages F
... There is ample evidence for Darwin’s theory. Variation can be observed. We know that genes are passed down to offspring (not acquired traits). 4. What is natural selection? Natural selection is when an organism has traits that allow it to live long enough to reproduce and then they pass on those tra ...
... There is ample evidence for Darwin’s theory. Variation can be observed. We know that genes are passed down to offspring (not acquired traits). 4. What is natural selection? Natural selection is when an organism has traits that allow it to live long enough to reproduce and then they pass on those tra ...
Lecture: Biological Anthropology
... 2) how and why dominant cultures or ways of thinking (“hegemony”) work in the world. For ex., what happens when we question a dominant way of thinking, such as the idea that the “nuclear family” is best ...
... 2) how and why dominant cultures or ways of thinking (“hegemony”) work in the world. For ex., what happens when we question a dominant way of thinking, such as the idea that the “nuclear family” is best ...
Brain
... cerebral cortex of the brain. The cerebral cortex integrates sensory information and selects responses. Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 9th ed., p. 107 ...
... cerebral cortex of the brain. The cerebral cortex integrates sensory information and selects responses. Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 9th ed., p. 107 ...
Assignment 1 Key
... d. chemical energy produced by chemicals from the brain e. none of the above; Descartes did not believe the brain played a role in physical movement ...
... d. chemical energy produced by chemicals from the brain e. none of the above; Descartes did not believe the brain played a role in physical movement ...
Inanimate and Animate Objects
... human beings. The word anthropology is derived from two Greek words “anthropos” meaning humans and “logia” meaning study. Anthropology involves the study of people, both in the past and in the present day, using many methods including studying and classifying fossils and artifacts, and analyzing the ...
... human beings. The word anthropology is derived from two Greek words “anthropos” meaning humans and “logia” meaning study. Anthropology involves the study of people, both in the past and in the present day, using many methods including studying and classifying fossils and artifacts, and analyzing the ...
PowerPoint1 - Central Church of Christ, Georgetown, Kentucky
... Special Theory of Evolution There is a theory which states that many living animals [and plants-DAE] can be observed over the course of time to undergo changes so that new species are formed. This can be called the “Special Theory of Evolution” and can be demonstrated in certain cases by experime ...
... Special Theory of Evolution There is a theory which states that many living animals [and plants-DAE] can be observed over the course of time to undergo changes so that new species are formed. This can be called the “Special Theory of Evolution” and can be demonstrated in certain cases by experime ...
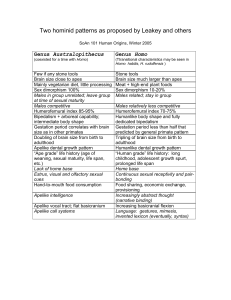
Aust-Homo Differences
... predicted by general primate pattern Tripling of brain size from birth to adulthood Humanlike dental growth pattern “Human grade” life history: long childhood, adolescent growth spurt, prolonged life span ...
... predicted by general primate pattern Tripling of brain size from birth to adulthood Humanlike dental growth pattern “Human grade” life history: long childhood, adolescent growth spurt, prolonged life span ...
Anthropology (and Refrigerators)
... Anthropology is the study of humankind over the entire world and throughout time. • Anthropologists study: • existing cultures and human behavior (cultural anthropology) • traditions (folklore) • prehistoric cultures and lifeways (archaeology) • the biological makeup and evolution of humans (physic ...
... Anthropology is the study of humankind over the entire world and throughout time. • Anthropologists study: • existing cultures and human behavior (cultural anthropology) • traditions (folklore) • prehistoric cultures and lifeways (archaeology) • the biological makeup and evolution of humans (physic ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... – Anthropometry - measurement of body parts – Primatology: study of nonhuman primates – Osteology: study of skeletons ...
... – Anthropometry - measurement of body parts – Primatology: study of nonhuman primates – Osteology: study of skeletons ...
Review Book Topic D: Evolution - wfs
... 5. Homo sapiens is currently the only species of hominid, but other species existed in the past. At various points in hominid evolution, several species co-existed, for example, Homo sapiens with Homo neanderthalensis. 6. Many hominid fossils have been found, dated, and assigned to a species. The ev ...
... 5. Homo sapiens is currently the only species of hominid, but other species existed in the past. At various points in hominid evolution, several species co-existed, for example, Homo sapiens with Homo neanderthalensis. 6. Many hominid fossils have been found, dated, and assigned to a species. The ev ...
File
... Ethnography provides an account of a Studies language particular community, in its social and society or culture cultural contexts across space and over time. Ethnology examines, interprets, analyzes and compares the results of ethnographic data from different societies ...
... Ethnography provides an account of a Studies language particular community, in its social and society or culture cultural contexts across space and over time. Ethnology examines, interprets, analyzes and compares the results of ethnographic data from different societies ...
Toumaï`s - NOPR
... been thought to be the cradle of human evolution. If Brunet’s group is correct, hominids must have become distinct from chimpanzees significantly earlier than that, spreading out across central and east Africa in the age before Toumaï walked the Earth. It hints at, “…an early Sahelanthropus pan Afri ...
... been thought to be the cradle of human evolution. If Brunet’s group is correct, hominids must have become distinct from chimpanzees significantly earlier than that, spreading out across central and east Africa in the age before Toumaï walked the Earth. It hints at, “…an early Sahelanthropus pan Afri ...
The Girld Who Took Care of the turkeys
... • The study of humanity – All people, in all times, all places • From our evolutionary origins millions of years ago (5 - 7 m.y.a.) • To today’s worldwide diversity of peoples and ...
... • The study of humanity – All people, in all times, all places • From our evolutionary origins millions of years ago (5 - 7 m.y.a.) • To today’s worldwide diversity of peoples and ...
Evolution2
... 5-6 mya, a line of apes diverged into modern common chimpanzees and bonobos and hominids: o Bipedal apes that includes modern humans Oldest known ________________(4mya) Bipedal but still could climb trees H.habilis 2 mya used stone tools increased cranial capacity Homo erectus 1.7mya large ...
... 5-6 mya, a line of apes diverged into modern common chimpanzees and bonobos and hominids: o Bipedal apes that includes modern humans Oldest known ________________(4mya) Bipedal but still could climb trees H.habilis 2 mya used stone tools increased cranial capacity Homo erectus 1.7mya large ...
Human Evolution
... – The thigh bone evolved into a slightly more angular position to move the center of gravity toward the geometric center of the body. – The knee and ankle joints became increasingly robust to better support increased weight. – To support the increased weight on each vertebra in the upright position, ...
... – The thigh bone evolved into a slightly more angular position to move the center of gravity toward the geometric center of the body. – The knee and ankle joints became increasingly robust to better support increased weight. – To support the increased weight on each vertebra in the upright position, ...
Physical Anthropology Study Guide, Exam 1
... of its associated words (holistic, biocultural, multidisciplinary, etc.). Understand scientific method (hypothesis versus theory, etc.) and review our discussion of how science attempts to answer questions about the world. What do scientific methods have to do with anthropology and other social scie ...
... of its associated words (holistic, biocultural, multidisciplinary, etc.). Understand scientific method (hypothesis versus theory, etc.) and review our discussion of how science attempts to answer questions about the world. What do scientific methods have to do with anthropology and other social scie ...
Craniometry

Craniometry is measurement of the cranium (the main part of the skull), usually the human cranium. It is a subset of cephalometry, measurement of the head. It is distinct from phrenology, the pseudoscience that tried to link personality and character to head shape, and physiognomy, which tried the same for facial features. However, these fields have all claimed the ability to predict traits or intelligence.They were once intensively practised in anthropology, in particular in physical anthropology in the 19th and the first part of the 20th century. Theories attempting to scientifically justify the segregation of society based on race became popular at this time, one of their prominent figures being Georges Vacher de Lapouge (1854–1936), who divided humanity into various, hierarchized, different ""races"", spanning from the ""Aryan white race, dolichocephalic"" (from the Ancient Greek kephalê, head, and dolikhos, long and thin), to the ""brachycephalic"" (short and broad-headed) race. On the other hand, craniometry was also used as evidence against the existence of a ""Nordic race"" and also by Franz Boas who used the cephalic index to show the influence of environmental factors. Charles Darwin used craniometry and the study of skeletons to demonstrate his theory of evolution first expressed in On the Origin of Species (1859).More direct measurements involve examinations of brains from corpses, or more recently, imaging techniques such as MRI, which can be used on living persons. Such measurements are used in research on neuroscience and intelligence.