What is a vertebrate?
... Metacarpal bones: These are long bones, in the dog there are four main bones with sometimes a fifth making up the dewclaw. In horses most of the metacarpal bones are no longer present and the main remaining bone is very elongated. Phalanges: These are the bones of the toes or digits. There are 3 bo ...
... Metacarpal bones: These are long bones, in the dog there are four main bones with sometimes a fifth making up the dewclaw. In horses most of the metacarpal bones are no longer present and the main remaining bone is very elongated. Phalanges: These are the bones of the toes or digits. There are 3 bo ...
Mollusks
... Most species of mollusks have an open circulatory system, in which the blood is not always inside blood vessels. Most mollusks that live in water have gills, organs that allow oxygen from the water to enter the body. Biologists classify mollusks into groups based on physical characteristics such as ...
... Most species of mollusks have an open circulatory system, in which the blood is not always inside blood vessels. Most mollusks that live in water have gills, organs that allow oxygen from the water to enter the body. Biologists classify mollusks into groups based on physical characteristics such as ...
mollusca classification
... 2. The shell is often reduced. 3. Operculum is never present. 4. They are terrestrial but some live in fresh water. ...
... 2. The shell is often reduced. 3. Operculum is never present. 4. They are terrestrial but some live in fresh water. ...
GCSE PE Revision Booklet
... INDIVIDUAL NEEDS - Whether training to compete or training for health, everyone has different personal needs. People vary in height, size, shape, fitness and preference. Therefore, even though they have the same goals they may not reach them by the same means. PROGRESSIVE OVERLOAD - Putting greater ...
... INDIVIDUAL NEEDS - Whether training to compete or training for health, everyone has different personal needs. People vary in height, size, shape, fitness and preference. Therefore, even though they have the same goals they may not reach them by the same means. PROGRESSIVE OVERLOAD - Putting greater ...
Mollusca - Net Start Class
... the body of the mollusk the space between the mantle and the actual body is called the mantle cavity This cavity in some mollusks acts as a lung In other mollusks, it contains gills that capture the oxygen from the water when the water passes through the cavity ...
... the body of the mollusk the space between the mantle and the actual body is called the mantle cavity This cavity in some mollusks acts as a lung In other mollusks, it contains gills that capture the oxygen from the water when the water passes through the cavity ...
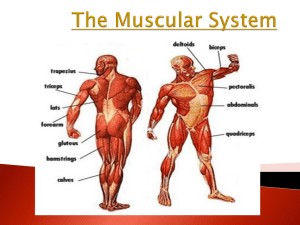
The Muscular System
... In order to contract (move), your muscles require energy in the form of ATP. (Adenosine Triphosphate) Muscles can produce ATP in two different ways. We have discussed aerobic respiration where oxygen is required. The second way is called anaerobic respiration which does NOT require oxygen. ◦ Anaerob ...
... In order to contract (move), your muscles require energy in the form of ATP. (Adenosine Triphosphate) Muscles can produce ATP in two different ways. We have discussed aerobic respiration where oxygen is required. The second way is called anaerobic respiration which does NOT require oxygen. ◦ Anaerob ...
Mollusca
... Identifying Characteristics of Phylum: -triploblastic with true coelom -bilateral symmetry; some with secondary assymetry -soft, usually unsegmented body consisting of anterior head, ventral foot and dorsal visceral mass -body usually enclosed by thin fleshy mantle -mantle usually secretes hard exte ...
... Identifying Characteristics of Phylum: -triploblastic with true coelom -bilateral symmetry; some with secondary assymetry -soft, usually unsegmented body consisting of anterior head, ventral foot and dorsal visceral mass -body usually enclosed by thin fleshy mantle -mantle usually secretes hard exte ...
Tài liệu PDF
... Orthopedist An orthopedist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating disorders and injuries related to the musculoskeletal system. Some orthopedic problems can be treated with medications, exercises, braces, and other devices, but others may be best treated with surgery ([link]). ...
... Orthopedist An orthopedist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating disorders and injuries related to the musculoskeletal system. Some orthopedic problems can be treated with medications, exercises, braces, and other devices, but others may be best treated with surgery ([link]). ...
Section 07 Lecture Notes
... Torsion = a twisting phenomenon where the shell alters the position of the visceral organs 180 degrees, only occurs in gastropods Fouling = arrangement of anus anteriorly creates problems of wastes being washed back over gills Class Bivalvia: (Pelecypoda) mussels, clams, scallops, oysters, and ...
... Torsion = a twisting phenomenon where the shell alters the position of the visceral organs 180 degrees, only occurs in gastropods Fouling = arrangement of anus anteriorly creates problems of wastes being washed back over gills Class Bivalvia: (Pelecypoda) mussels, clams, scallops, oysters, and ...
Name Chapter 13 Forensic Anthropology Study
... _____12. Explain the role of the periosteum in maintenance of bone. Periosteum is a membrane that serves an important role in keeping bones moist and aiding in the repair of injuries. _____13. Describe how bone is constantly being repaired and replaced as we grow. This process continues throughout o ...
... _____12. Explain the role of the periosteum in maintenance of bone. Periosteum is a membrane that serves an important role in keeping bones moist and aiding in the repair of injuries. _____13. Describe how bone is constantly being repaired and replaced as we grow. This process continues throughout o ...
File
... Haversian Canals are channels in the bone through which blood vessels (veins and arteries) can pass. Nutrients get to the bone through these little tubes Spongy Bone is the lighter weight but tough bone fibres inside the compact bone. Bone Marrow is the region in the middle of the bone where blood c ...
... Haversian Canals are channels in the bone through which blood vessels (veins and arteries) can pass. Nutrients get to the bone through these little tubes Spongy Bone is the lighter weight but tough bone fibres inside the compact bone. Bone Marrow is the region in the middle of the bone where blood c ...
3 Invertebrate Structure
... outer layer or periostracum is a rough layer constructed of a hornlike protein called chonchiolin. As a clam grows the periostracum and prismatic are deposited only once by cell along the mantle edge while the nacreous is deposited continuously. (D) Soft Anatomy Obtain a preserved specimen. To open ...
... outer layer or periostracum is a rough layer constructed of a hornlike protein called chonchiolin. As a clam grows the periostracum and prismatic are deposited only once by cell along the mantle edge while the nacreous is deposited continuously. (D) Soft Anatomy Obtain a preserved specimen. To open ...
Integumentary system
... Berachiodialis major palmaris longus Flexor carpi radialis – a good example of how muscles are named by their function and location – named carpi because of the bones that it helps move, the carples – name of radialis is made by the bone that its attached to, the radius ...
... Berachiodialis major palmaris longus Flexor carpi radialis – a good example of how muscles are named by their function and location – named carpi because of the bones that it helps move, the carples – name of radialis is made by the bone that its attached to, the radius ...
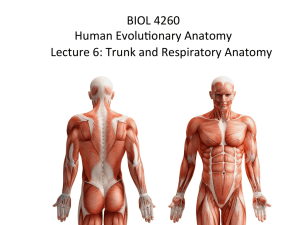
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu$onary Anatomy Lecture 6: Trunk and
... skull-‐22 bones associated bones Hyoid+6 auditory bones vertebral column bony thorax ...
... skull-‐22 bones associated bones Hyoid+6 auditory bones vertebral column bony thorax ...
Hypothetical ancestral mollusc (HAM)
... They construct burrows in soft marine sediments which they inhabit head downwards. They ingest sediment, or may be selective carnivores or scavengers. Many typical molluscan characteristics are either absent or reduced: no shell, no foot, and the mantle covers the entire body. Lacking a foot, they m ...
... They construct burrows in soft marine sediments which they inhabit head downwards. They ingest sediment, or may be selective carnivores or scavengers. Many typical molluscan characteristics are either absent or reduced: no shell, no foot, and the mantle covers the entire body. Lacking a foot, they m ...
Crayfish dissection guide
... posterior ones is a pair of powerful muscles that extend ventrally to insert on the mandibles. To reveal the extent of the stomach, remove the muscles attached to it and separate the lobes of the digestive glands anterior to the heart. Observe the larger, gastric stomach and the smaller, posterior ...
... posterior ones is a pair of powerful muscles that extend ventrally to insert on the mandibles. To reveal the extent of the stomach, remove the muscles attached to it and separate the lobes of the digestive glands anterior to the heart. Observe the larger, gastric stomach and the smaller, posterior ...
B. Circulation - s3.amazonaws.com
... Are Male at the front end and female at the back end They can be seen mating in large chains They lay up to 80 million eggs in a group, and resemble spaghetti ...
... Are Male at the front end and female at the back end They can be seen mating in large chains They lay up to 80 million eggs in a group, and resemble spaghetti ...
ANNELIDS Annelida Read the passage below, which covers topics
... Read the passage below, which covers topics from your textbook. Answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passage below, which covers topics from your textbook. Answer the questions that follow. ...
Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy
... parts of any organised structure. The word anatomy means cutting up – the method by which the study of the structure of living things is made possible. In general scientific literature, it is virtually synonymous with morphology, the scientific study of shape and s ...
... parts of any organised structure. The word anatomy means cutting up – the method by which the study of the structure of living things is made possible. In general scientific literature, it is virtually synonymous with morphology, the scientific study of shape and s ...
LABORATORY EXERCISE 5 PHYLUM MOLLUSCA
... Enter your data on the class master sheet. How do your data compare with those from other animals? Why are the data so varied? How might one "normalize" the data so that results from one animal can be compared with those of others? Are the results produced by all the animals more "significant" than ...
... Enter your data on the class master sheet. How do your data compare with those from other animals? Why are the data so varied? How might one "normalize" the data so that results from one animal can be compared with those of others? Are the results produced by all the animals more "significant" than ...
Chapter 07
... What are the two main bones of the skull? What types of bones are in the ribcage? What are the spine and pelvis? What are the bones of the arm? What are the bones of the hand? What are the bones of the leg? What are the bones of the foot? ...
... What are the two main bones of the skull? What types of bones are in the ribcage? What are the spine and pelvis? What are the bones of the arm? What are the bones of the hand? What are the bones of the leg? What are the bones of the foot? ...
Biology 320 Invertebrate Zoology Fall 2005
... Eat a variety of prey items, but clams, snails, and crustaceans ...
... Eat a variety of prey items, but clams, snails, and crustaceans ...
PE Revision – Powerpoint of whole specification 2012
... Aerobic Training – when the body is being worked at a level at which it is capable of supplying the oxygen and fuel demanded. This means that the body will be respiring aerobically; glucose + oxygen give the products of carbon dioxide and water, excreted as perspiration and exhalation. Aerobic trai ...
... Aerobic Training – when the body is being worked at a level at which it is capable of supplying the oxygen and fuel demanded. This means that the body will be respiring aerobically; glucose + oxygen give the products of carbon dioxide and water, excreted as perspiration and exhalation. Aerobic trai ...
Foot

The foot (plural feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails.