How fast is the speed of thought?
... are comparable to results from the cat visual system, which show delays of 5-15 ms between different visual areas [10]. All the studies mentioned above report a considerable overlap in cell activity in different visual areas, such that most of the neurons at different stages in the visual system are ...
... are comparable to results from the cat visual system, which show delays of 5-15 ms between different visual areas [10]. All the studies mentioned above report a considerable overlap in cell activity in different visual areas, such that most of the neurons at different stages in the visual system are ...
lecture9
... Reaching and grasping actions require close coordination, but depend on different kinds of visual information... Reaching: egocentric (where is object relative to me) Transform visual information about object location into movement direction. ...
... Reaching and grasping actions require close coordination, but depend on different kinds of visual information... Reaching: egocentric (where is object relative to me) Transform visual information about object location into movement direction. ...
Visual Field Defects - Northwestern Medical Review
... Note: As general rule lesions that are located farther away from the lateral geniculate bodies and closer to the visual cortex are presented with a more prominent macular sparring. 32. Northwestern Medical Review, Bare Minimum Review Series, 2012 ...
... Note: As general rule lesions that are located farther away from the lateral geniculate bodies and closer to the visual cortex are presented with a more prominent macular sparring. 32. Northwestern Medical Review, Bare Minimum Review Series, 2012 ...
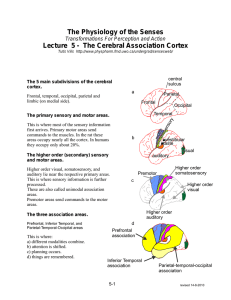
The Cerebral Association Cortex
... brain. The retina and visual cortex see both the person and the bike but attention limits what gets further down into the what stream. We are blind to what does not get through the bottleneck. Visual perception is a two stage process Stage 1) an early stage that performs rapid low level processing o ...
... brain. The retina and visual cortex see both the person and the bike but attention limits what gets further down into the what stream. We are blind to what does not get through the bottleneck. Visual perception is a two stage process Stage 1) an early stage that performs rapid low level processing o ...
Cones
... Visual pathway: transmission of nerve impulses Visual cortex: occipital lobe of cerebral cortex primary visual receiving area: sides of the calcarine fissure visual processing & perception occurs here Stimulus: Light in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The Sensory organ is the Ey ...
... Visual pathway: transmission of nerve impulses Visual cortex: occipital lobe of cerebral cortex primary visual receiving area: sides of the calcarine fissure visual processing & perception occurs here Stimulus: Light in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The Sensory organ is the Ey ...
class_2015_readinglist
... conclusion, this new approach to brain mapping may not only serve to identify novel functional subdivisions, but to reveal their connectivity as well. Bichot, N. P., et al. (2005). "Parallel and serial neural mechanisms for visual search in macaque area V4." Science 308(5721): 529-534. To find a tar ...
... conclusion, this new approach to brain mapping may not only serve to identify novel functional subdivisions, but to reveal their connectivity as well. Bichot, N. P., et al. (2005). "Parallel and serial neural mechanisms for visual search in macaque area V4." Science 308(5721): 529-534. To find a tar ...
2320Lecture22
... Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? ...
... Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? ...
Mirror neurons: A sensorimotor representation system
... lead to different results. Interestingly, it is the saccade mode which leads to the illusion, while the fixation mode results in the correct perception. Scanning through the known geometrical illusions, quite a number of them were found to disappear with stationary fixation (Fischer et al. 2001b). I ...
... lead to different results. Interestingly, it is the saccade mode which leads to the illusion, while the fixation mode results in the correct perception. Scanning through the known geometrical illusions, quite a number of them were found to disappear with stationary fixation (Fischer et al. 2001b). I ...
encoding - WordPress.com
... allows the perceived item of use or interest to be converted into a construct that can be stored within the brain and recalled later from short term or long term memory. Working memory stores information for immediate use or manipulation which is aided through hooking onto previously archived items ...
... allows the perceived item of use or interest to be converted into a construct that can be stored within the brain and recalled later from short term or long term memory. Working memory stores information for immediate use or manipulation which is aided through hooking onto previously archived items ...
Document
... • ON cells responded with an excitatory burst when the retina was illuminated, OFF cells responded when the light was turned off, and ON/OFF cells responded briefly when the light went on and again when it went off. • Kuffler (1952, 1953), recording from ganglion cells in the retina of the cat, disc ...
... • ON cells responded with an excitatory burst when the retina was illuminated, OFF cells responded when the light was turned off, and ON/OFF cells responded briefly when the light went on and again when it went off. • Kuffler (1952, 1953), recording from ganglion cells in the retina of the cat, disc ...
Overview of the Seven Perceptual Styles
... What Makes Perceptual Styles a Different Way of Learning? Perceptual learning styles are the means by which learners extract information from their surroundings through the use of their five senses. Individuals have different "pathways" that are specific to them. When information enters that "pathwa ...
... What Makes Perceptual Styles a Different Way of Learning? Perceptual learning styles are the means by which learners extract information from their surroundings through the use of their five senses. Individuals have different "pathways" that are specific to them. When information enters that "pathwa ...
Pattern recognition and visual word forms
... d Visual Word Form Area (VWFA), which mediates between pecific input, and more abstract linguistic areas responsible for emantic and phonological processes. Although the precise ns from VWFA to systems involved in lexical, semantic and ...
... d Visual Word Form Area (VWFA), which mediates between pecific input, and more abstract linguistic areas responsible for emantic and phonological processes. Although the precise ns from VWFA to systems involved in lexical, semantic and ...
Study Guide Solutions
... Lateral inhibition means that the activity of a neuron may be inhibited by inputs coming from neurons that respond to neighboring regions of the visual field. Lateral inhibition is important for enhancing the neural representation of edges, regions of an image where the light intensity sharply chang ...
... Lateral inhibition means that the activity of a neuron may be inhibited by inputs coming from neurons that respond to neighboring regions of the visual field. Lateral inhibition is important for enhancing the neural representation of edges, regions of an image where the light intensity sharply chang ...
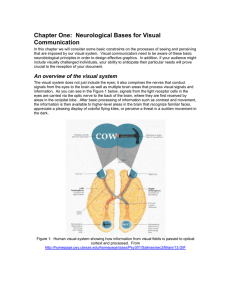
Chapter One: Neurological Bases for Visual Communication
... Overall, about one in 10 people has some form of visual anomaly, so unless you’re designing for an extremely small, well-known audience (almost never), you need to take visual differences into account. Don’t just rely on one feature (color, shape, or contrast) to communicate important information in ...
... Overall, about one in 10 people has some form of visual anomaly, so unless you’re designing for an extremely small, well-known audience (almost never), you need to take visual differences into account. Don’t just rely on one feature (color, shape, or contrast) to communicate important information in ...
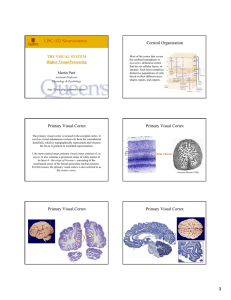
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization Primary Visual Cortex
... results in low performance in spatial tasks, most often poor visuo-motor control. Some patients with optic ataxia have no difficulty identifying an object, but their visually guided behavior is so impaired that they cannot grasp it properly! ...
... results in low performance in spatial tasks, most often poor visuo-motor control. Some patients with optic ataxia have no difficulty identifying an object, but their visually guided behavior is so impaired that they cannot grasp it properly! ...
Chapter 6
... Dorsal stream – a system of interconnected regions of visual cortex involved in the perception of spatial location, beginning with the striate cortex and ending with the posterior parietal cortex Ventral stream – a system of interconnected regions of visual cortex involved in the perception of form, ...
... Dorsal stream – a system of interconnected regions of visual cortex involved in the perception of spatial location, beginning with the striate cortex and ending with the posterior parietal cortex Ventral stream – a system of interconnected regions of visual cortex involved in the perception of form, ...
Visual System - UAB School of Optometry
... ganglion cells in the retina, connects to parvo cells in LGN, is most strongly associated with extrastriate visual areas in the inferior temporal lobe. Neurons respond well to color and fine detail, not so strongly to rapid motion or low contrast. Magnocellular System: originates with the parasol ga ...
... ganglion cells in the retina, connects to parvo cells in LGN, is most strongly associated with extrastriate visual areas in the inferior temporal lobe. Neurons respond well to color and fine detail, not so strongly to rapid motion or low contrast. Magnocellular System: originates with the parasol ga ...
The Eye: III. Central Neurophysiology of Vision
... ► Postganglionic fibers excite the ciliary muscle and sphincter of the iris. ► Sympathetic fibers originate in the intermediolateral horn cells of the superior cervical ganglion. ► Postganglionic fibers spread along the corotid artery and eventually innervate the radial fibers of the iris. ...
... ► Postganglionic fibers excite the ciliary muscle and sphincter of the iris. ► Sympathetic fibers originate in the intermediolateral horn cells of the superior cervical ganglion. ► Postganglionic fibers spread along the corotid artery and eventually innervate the radial fibers of the iris. ...
Low vision and brain plasticity Symposium abstract
... Visual field defects are considered irreversible because the retina and optic nerve do no regenerate. Yet, there is some potential for neural repair and recovery of the visual fields. This is accomplished by the brain which analyses and interprets visual information and is able to amplify residual s ...
... Visual field defects are considered irreversible because the retina and optic nerve do no regenerate. Yet, there is some potential for neural repair and recovery of the visual fields. This is accomplished by the brain which analyses and interprets visual information and is able to amplify residual s ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... • The receptive field refers to the part of the visual field that either excites or inhibits a cell in the visual system of the brain. • For a receptor, the receptive field is the point in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field ...
... • The receptive field refers to the part of the visual field that either excites or inhibits a cell in the visual system of the brain. • For a receptor, the receptive field is the point in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field ...
Eagleman Ch 5. Vision
... Patients who lose their vision hallucinate that they still see objects around them. ...
... Patients who lose their vision hallucinate that they still see objects around them. ...
CVI
... tube and is feed by j-tube (into his intestines) for about 20 hours a day. He struggles with chronic vomiting and Richard has been in and out of the hospital for them frequently. At home the family continues to pump his stomach, by a big suction machine, several times a day for about 30 minutes. Dev ...
... tube and is feed by j-tube (into his intestines) for about 20 hours a day. He struggles with chronic vomiting and Richard has been in and out of the hospital for them frequently. At home the family continues to pump his stomach, by a big suction machine, several times a day for about 30 minutes. Dev ...
Basic Architecture of the Visual Cortex
... • (II) The second pathway goes from V1, MT to the parietal cortex and is used for analysis of movements and positions • of objects. The ventral stream puts most emphasis on the central visual field while the motion analysis concentrates more on the periphery Lennie argues that these two visual strea ...
... • (II) The second pathway goes from V1, MT to the parietal cortex and is used for analysis of movements and positions • of objects. The ventral stream puts most emphasis on the central visual field while the motion analysis concentrates more on the periphery Lennie argues that these two visual strea ...
Economic Attention Networks: Associative Memory and Resource
... More rapid learning of simpler procedures ...
... More rapid learning of simpler procedures ...
Visual memory

Visual memory describes the relationship between perceptual processing and the encoding, storage and retrieval of the resulting neural representations. Visual memory occurs over a broad time range spanning from eye movements to years in order to visually navigate to a previously visited location. Visual memory is a form of memory which preserves some characteristics of our senses pertaining to visual experience. We are able to place in memory visual information which resembles objects, places, animals or people in a mental image. The experience of visual memory is also referred to as the mind's eye through which we can retrieve from our memory a mental image of original objects, places, animals or people. Visual memory is one of several cognitive systems, which are all interconnected parts that combine to form the human memory. Types of palinopsia, the persistence or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed, is a dysfunction of visual memory.