geography
... • Other types of maps used when studying American History include: – Election maps – Product maps – Battle maps ...
... • Other types of maps used when studying American History include: – Election maps – Product maps – Battle maps ...
geography
... • Other types of maps used when studying American History include: – Election maps – Product maps – Battle maps ...
... • Other types of maps used when studying American History include: – Election maps – Product maps – Battle maps ...
Geography Glossary - Arizona Geographic Alliance
... Pull factors: In migration theory, the social, political, economic, and environmental forces that drive people from their previous location to search for new ones. Push factors: In migration theory, the social, political, economic and environmental attractions of new areas that draw people away from ...
... Pull factors: In migration theory, the social, political, economic, and environmental forces that drive people from their previous location to search for new ones. Push factors: In migration theory, the social, political, economic and environmental attractions of new areas that draw people away from ...
Ch.1 - Looking at the Earth
... Title: Explains the subject Compass Rose: Shows the direction North is on the map. Labels: Explain the features of the map. Legend: Explains the symbols and the use of color on the map. Lines of Latitude: Imaginary lines that measure distance north or south of the equator. Latitude goes around the e ...
... Title: Explains the subject Compass Rose: Shows the direction North is on the map. Labels: Explain the features of the map. Legend: Explains the symbols and the use of color on the map. Lines of Latitude: Imaginary lines that measure distance north or south of the equator. Latitude goes around the e ...
Introduction to Regional Geography
... • These zones are areas of spatial change where peripheries of two adjacent realms or regions join • Zones are marked by a gradual shift (rather than a sharp break) in the characteristics that distinguish neighboring realms ...
... • These zones are areas of spatial change where peripheries of two adjacent realms or regions join • Zones are marked by a gradual shift (rather than a sharp break) in the characteristics that distinguish neighboring realms ...
Year 4 Overview
... Russain case study comparison between life in Russia and Life in England. Children must identify any key significant changes. ...
... Russain case study comparison between life in Russia and Life in England. Children must identify any key significant changes. ...
AP Human Geography Notes
... • There are various ways and patterns in which human phenomena diffuse spatially or spread across the earth’s surface – Most often we examine how culture, ideas, or technology spread from a point of origin to other parts of the world – That point of origin or place of innovation can be called a hear ...
... • There are various ways and patterns in which human phenomena diffuse spatially or spread across the earth’s surface – Most often we examine how culture, ideas, or technology spread from a point of origin to other parts of the world – That point of origin or place of innovation can be called a hear ...
contour lines - cloudfront.net
... this map? 3. What is the relief of this map? 4. As the slope on the volcano gets steeper, what happens to the distance between the contour lines? 5. What errors could your group have made in the construction of your contour map? 6. The actual contour interval is 250m. Re-label your contour lines to ...
... this map? 3. What is the relief of this map? 4. As the slope on the volcano gets steeper, what happens to the distance between the contour lines? 5. What errors could your group have made in the construction of your contour map? 6. The actual contour interval is 250m. Re-label your contour lines to ...
Introduction to Human Geography
... • Greenland and Australia become distorted but because the have few people is doesn’t make much of a difference. • Used most often • Negatives: Eastern and Western areas are separated; Longitude lines do not meet (which happens in real life); the grid system (long and lat lines) do not form right an ...
... • Greenland and Australia become distorted but because the have few people is doesn’t make much of a difference. • Used most often • Negatives: Eastern and Western areas are separated; Longitude lines do not meet (which happens in real life); the grid system (long and lat lines) do not form right an ...
landgrabdirections
... during your “Africa Land Scramble” research. Copies of the student atlas (use the political, physical, and thematic maps of Africa) Chapters 19-22 in the geography textbook on the regions of Africa and their resources Thematic maps on Google Earth (see next slide). ...
... during your “Africa Land Scramble” research. Copies of the student atlas (use the political, physical, and thematic maps of Africa) Chapters 19-22 in the geography textbook on the regions of Africa and their resources Thematic maps on Google Earth (see next slide). ...
Maps-PPT-Unit
... one, or at most two, points in any direction or along certain lines. Equidistance is important in maps which are used for analyzing velocity, e.g. ocean currents. Typically, reference lines such as the equator or a meridian are chosen to have equidistance and are termed standard parallels or standar ...
... one, or at most two, points in any direction or along certain lines. Equidistance is important in maps which are used for analyzing velocity, e.g. ocean currents. Typically, reference lines such as the equator or a meridian are chosen to have equidistance and are termed standard parallels or standar ...
Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Chapter Outline Introduction
... Culture is divided into “What people care about,” or beliefs, values, and customs, and “What people take care of,” or material culture. The first definition is covered in Chapters 5, 6, and 7, on language, religion, and ethnicity. The second is covered in Chapters 4, 10, 11, 12, and 13, especially ...
... Culture is divided into “What people care about,” or beliefs, values, and customs, and “What people take care of,” or material culture. The first definition is covered in Chapters 5, 6, and 7, on language, religion, and ethnicity. The second is covered in Chapters 4, 10, 11, 12, and 13, especially ...
Geography Maps & Distortion
... Equal-area maps show the sizes of places accurately. However, they distort shape near the poles. This is called shape distortion. ...
... Equal-area maps show the sizes of places accurately. However, they distort shape near the poles. This is called shape distortion. ...
geography
... • Other types of maps used when studying American History include: – Election maps – Product maps – Battle maps ...
... • Other types of maps used when studying American History include: – Election maps – Product maps – Battle maps ...
Reading Maps - CoconinoHighSchool
... south, east & west. In between are the directions northeast, ...
... south, east & west. In between are the directions northeast, ...
Chapter 1
... Using latitude and longitude gives you the absolute location of any spot in the world Having only a general idea about where a place is located is called relative location ...
... Using latitude and longitude gives you the absolute location of any spot in the world Having only a general idea about where a place is located is called relative location ...
3. Read the text on the two map projections and answer the
... Projection construction is also affected by how the shape of the Earth is approximated. In the following discussion on projection categories, a sphere is assumed. A).......... a shape which bulges around the equator. Selecting a model for a shape of the Earth involves choosing between the advantages ...
... Projection construction is also affected by how the shape of the Earth is approximated. In the following discussion on projection categories, a sphere is assumed. A).......... a shape which bulges around the equator. Selecting a model for a shape of the Earth involves choosing between the advantages ...
AP Human Geography Notes
... • There are various ways and patterns in which human phenomena diffuse spatially or spread across the earth’s surface – Most often we examine how culture, ideas, or technology spread from a point of origin to other parts of the world – That point of origin or place of innovation can be called a hear ...
... • There are various ways and patterns in which human phenomena diffuse spatially or spread across the earth’s surface – Most often we examine how culture, ideas, or technology spread from a point of origin to other parts of the world – That point of origin or place of innovation can be called a hear ...
Cartography - Map Types, Cartographic Communication, Map
... Once a cartographer decides on the scale of his map (large scale or small scale) , he has to make some hard choices: what to leave out, how represent thematic data, and how many classes of data to represent. These decisions will make maps inherently inaccurate since they will not show the world as i ...
... Once a cartographer decides on the scale of his map (large scale or small scale) , he has to make some hard choices: what to leave out, how represent thematic data, and how many classes of data to represent. These decisions will make maps inherently inaccurate since they will not show the world as i ...
Matching - Fort Bend ISD
... ____1. The clothing, language, food, music, jobs, religion, literature, and technology that a group of people share is an expression of their A. government. C. culture. B. multiculturalism. D. economics. ...
... ____1. The clothing, language, food, music, jobs, religion, literature, and technology that a group of people share is an expression of their A. government. C. culture. B. multiculturalism. D. economics. ...
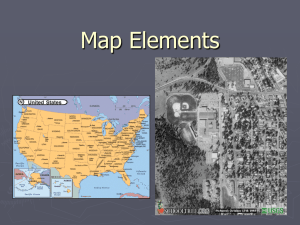
Map

A map is a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, and themes.Many maps are static two-dimensional, geometrically accurate (or approximately accurate) representations of three-dimensional space, while others are dynamic or interactive, even three-dimensional. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or imagined, without regard to context or scale; e.g. brain mapping, DNA mapping and extraterrestrial mapping.Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word ""map"" comes from the medieval Latin Mappa mundi, wherein mappa meant napkin or cloth and mundi the world. Thus, ""map"" became the shortened term referring to a two-dimensional representation of the surface of the world.