Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... When acceleration is less than g—non-free fall • as falling object gains speed, force exerted by surrounding air increases • force of air resistance may continue to increase until it equals the weight • at this point, net force is zero and no further acceleration • object has reached terminal veloci ...
... When acceleration is less than g—non-free fall • as falling object gains speed, force exerted by surrounding air increases • force of air resistance may continue to increase until it equals the weight • at this point, net force is zero and no further acceleration • object has reached terminal veloci ...
POWERPOINT JEOPARDY
... Answer 4 – 30 • What is the force that can give a 1 kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s2? ...
... Answer 4 – 30 • What is the force that can give a 1 kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s2? ...
Sect. 4.4
... real pendulum) these points become attractors (for long times, the phase paths will spiral towards these points). ...
... real pendulum) these points become attractors (for long times, the phase paths will spiral towards these points). ...
43 In Fig
... 1. Understand the concept of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM); 2. Master the force law for Simple harmonic motion; 3. Understand the meaning of phase, in phase and out of phase of SHM; 4. Master the characteristic of composition of simple harmonic motion in the same direction with the same frequency; 5. ...
... 1. Understand the concept of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM); 2. Master the force law for Simple harmonic motion; 3. Understand the meaning of phase, in phase and out of phase of SHM; 4. Master the characteristic of composition of simple harmonic motion in the same direction with the same frequency; 5. ...
V - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... the flow of air through a jet engine. The principle of impulse and momentum is applied to a system S of particles during a time interval Dt, including particles which enter the system at A during that time interval and those (of the same mass Dm) which leave the system at B. The system formed by the ...
... the flow of air through a jet engine. The principle of impulse and momentum is applied to a system S of particles during a time interval Dt, including particles which enter the system at A during that time interval and those (of the same mass Dm) which leave the system at B. The system formed by the ...
EOC_chapter7 - AppServ Open Project 2.4.9
... He has speed 1.40 m/s at the crest of a slope 2.60 m high and 12.4 m long. At the bottom of the slope his speed is 6.20 m/s. Assuming that air resistance and rolling resistance can be modeled as a constant friction force of 41.0 N, find the work he did in pushing forward on his wheels during the dow ...
... He has speed 1.40 m/s at the crest of a slope 2.60 m high and 12.4 m long. At the bottom of the slope his speed is 6.20 m/s. Assuming that air resistance and rolling resistance can be modeled as a constant friction force of 41.0 N, find the work he did in pushing forward on his wheels during the dow ...
N13 Vibrations and Waves (Notes)
... If the spring is hung vertically, the only change is in the equilibrium position, which is at the point where the spring force equals the gravitational force. ...
... If the spring is hung vertically, the only change is in the equilibrium position, which is at the point where the spring force equals the gravitational force. ...
Notes for Mid
... 30m/s when it has an acceleration of 6m/s2. How long did this take? t = (30m/s)/(6m/s2) = 5s 1) A runner’s initial speed is 5m/s and he accelerates at 5m/s2 over a distance of 7.5 meters. What is his final speed? vf2 = (5m/s)2 + 2*(5m/s2)(7.5m) = 100m2/s2 or vf = 10m/s 2) Same problem except the fin ...
... 30m/s when it has an acceleration of 6m/s2. How long did this take? t = (30m/s)/(6m/s2) = 5s 1) A runner’s initial speed is 5m/s and he accelerates at 5m/s2 over a distance of 7.5 meters. What is his final speed? vf2 = (5m/s)2 + 2*(5m/s2)(7.5m) = 100m2/s2 or vf = 10m/s 2) Same problem except the fin ...
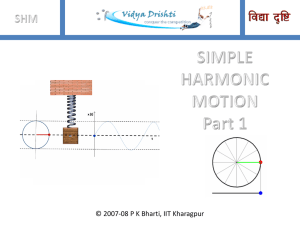
SHM Part 1 - Ask Physics
... Slideshow to see animation. Let us consider a mass attached to a spring which in turn, attached to a rigid wall. The spring-mass system lies on a frictionless surface. We know that if we stretch or compress a spring, the mass will oscillate back and forth about its equilibrium (mean) position. Equil ...
... Slideshow to see animation. Let us consider a mass attached to a spring which in turn, attached to a rigid wall. The spring-mass system lies on a frictionless surface. We know that if we stretch or compress a spring, the mass will oscillate back and forth about its equilibrium (mean) position. Equil ...
8th class Physics Bridge Program
... between which its moves. Unit : C.G.S unit : cm S.I unit : m Note: The distance travelled by body is always positive. Displacement : It is the shortest distance between between initial and final point in a definite direction. Unit : C.G.S unit : cm S.I unit : m Note : (i) For a moving body displacem ...
... between which its moves. Unit : C.G.S unit : cm S.I unit : m Note: The distance travelled by body is always positive. Displacement : It is the shortest distance between between initial and final point in a definite direction. Unit : C.G.S unit : cm S.I unit : m Note : (i) For a moving body displacem ...