Physics 151 Week 9 Day 3
... / also rotational/rolling Friction is smallest friction Caused by electron repulsion between two objects - Friction opposes (in opposite direction of) applied force - Direction of Friction force is Opposite of direction of motion / acceleration - Parallel to motion / Resists force of acceleration Fr ...
... / also rotational/rolling Friction is smallest friction Caused by electron repulsion between two objects - Friction opposes (in opposite direction of) applied force - Direction of Friction force is Opposite of direction of motion / acceleration - Parallel to motion / Resists force of acceleration Fr ...
gravitation - Physics Unit
... (the –ve sign shows the force acts in the opposite direction to the displacement) Therefore total work done while body escapes ...
... (the –ve sign shows the force acts in the opposite direction to the displacement) Therefore total work done while body escapes ...
Vectors: Motion and Forces in Two Dimensions
... Newton's First Law • Newton's first law of motion: An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... Newton's First Law • Newton's first law of motion: An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
KINEMATICS
... Newton’s First Law Body in motion stays in motion unless acted on by outside force ...
... Newton’s First Law Body in motion stays in motion unless acted on by outside force ...
1 In the absence of a net force, a moving object will slow down and
... The acceleration due to gravity is higher on Jupiter than on Earth. The mass and weight of a rock on Jupiter compared to that on Earth would be A ...
... The acceleration due to gravity is higher on Jupiter than on Earth. The mass and weight of a rock on Jupiter compared to that on Earth would be A ...
Dynamics: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... First Law – Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. First Law – (Common) An object at rest remains at rest, and a object in motion, remains in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
... First Law – Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. First Law – (Common) An object at rest remains at rest, and a object in motion, remains in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
Lesson 1 - Physical Quantities and units - science
... take the gradient of the line. But if the acceleration is non-uniform it is, by definition, changing. So we can only work out the acceleration at specific points, or instants. We call this taking the instantaneous acceleration. Graph A shows the V-T graph of an object with non-uniform acceleration. ...
... take the gradient of the line. But if the acceleration is non-uniform it is, by definition, changing. So we can only work out the acceleration at specific points, or instants. We call this taking the instantaneous acceleration. Graph A shows the V-T graph of an object with non-uniform acceleration. ...
Chapter 11 - UCF Physics
... by a 10.0-m rope of negligible mass. They are isolated in space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds of 5.00 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. By pulling on the rope, one of th ...
... by a 10.0-m rope of negligible mass. They are isolated in space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds of 5.00 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. By pulling on the rope, one of th ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
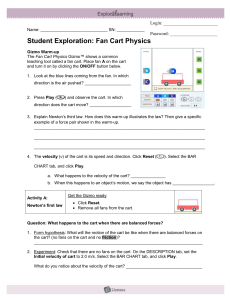
... 3. Explain Newton’s third law. How does this warm-up illustrates the law? Then give a specific example of a force pair shown in the warm-up. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
... 3. Explain Newton’s third law. How does this warm-up illustrates the law? Then give a specific example of a force pair shown in the warm-up. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________ ...