Momentum - eAcademy
... 1. Arnold Palmer is practicing his golf swing. When using his seven iron, a constant force of 1500 N acts on the 0.75 kg golf ball. Determine the impulse and change in speed of the object when he follows through with his swing (t = 0.015 seconds) and when he chips the shot (t = 0.0005 seconds). 2. A ...
... 1. Arnold Palmer is practicing his golf swing. When using his seven iron, a constant force of 1500 N acts on the 0.75 kg golf ball. Determine the impulse and change in speed of the object when he follows through with his swing (t = 0.015 seconds) and when he chips the shot (t = 0.0005 seconds). 2. A ...
MATH10222, Chapter 2: Newtonian Dynamics 1 Newton`s Laws 2
... Having considered motion confined to a line in the previous section, we now go on to consider motion confined to a plane. At any given instant in time the particle’s position relative to the origin of a coordinate system is denoted by r(t). At this same instant the particle is moving in the directio ...
... Having considered motion confined to a line in the previous section, we now go on to consider motion confined to a plane. At any given instant in time the particle’s position relative to the origin of a coordinate system is denoted by r(t). At this same instant the particle is moving in the directio ...
04_Testbank
... D) The molecules in the water are moving faster than the molecules in the oven. E) The water has a higher heat content than the oven. Answer: E 30) The amount of gravitational potential energy released as an object falls depends on A) its mass and the distance it falls. B) its mass and its speed at ...
... D) The molecules in the water are moving faster than the molecules in the oven. E) The water has a higher heat content than the oven. Answer: E 30) The amount of gravitational potential energy released as an object falls depends on A) its mass and the distance it falls. B) its mass and its speed at ...
... 42. When Earth and the Moon are separated by a distance of 3.84 × 108 meters, the magnitude of the gravitational force of attraction between them is 2.0 × 1020 newtons. What would be the magnitude of this gravitational force of attraction if Earth and the Moon were separated by a distance of 1.92 × ...
10.hamilton11e_ppt_13
... NEWTON’S LAWS AND ROTATIONAL EQUIVALENTS 1. A body continues in a state of rest or uniform rotation about its axis unless acted upon by an external force. 2. The acceleration of a rotating body is directly proportional to the torque causing it, is in the same direction as the torque, and is inverse ...
... NEWTON’S LAWS AND ROTATIONAL EQUIVALENTS 1. A body continues in a state of rest or uniform rotation about its axis unless acted upon by an external force. 2. The acceleration of a rotating body is directly proportional to the torque causing it, is in the same direction as the torque, and is inverse ...
[SESSION-2012-2013] KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN Zonal Institute of Education & Training
... The purpose of this Study Material is to help learners study more effectively and efficiently. It is designed to help increase the retention of what they are studying for the purpose of using it more successfully at a later time—while taking a test. For the academic year 2012-13 the task has been al ...
... The purpose of this Study Material is to help learners study more effectively and efficiently. It is designed to help increase the retention of what they are studying for the purpose of using it more successfully at a later time—while taking a test. For the academic year 2012-13 the task has been al ...
question 2 - Larbert High School
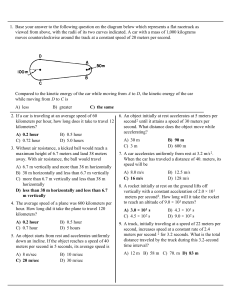
... A cannonball is fired horizontally at 40ms-1 from the top of a vertical cliff and hits a target. The height of the cliff above sea-level is 80m as shown below. Calculate or find: a) Time taken for the cannonball to hit the target. b) Horizontal displacement of the cannonball. c) The resultant veloci ...
... A cannonball is fired horizontally at 40ms-1 from the top of a vertical cliff and hits a target. The height of the cliff above sea-level is 80m as shown below. Calculate or find: a) Time taken for the cannonball to hit the target. b) Horizontal displacement of the cannonball. c) The resultant veloci ...
A 1 - Andes Physics Tutor
... driver who does not wear a seatbelt continues to move forward with a speed of 20 m/s (due to inertia) until something solid is encountered. The driver now comes to rest in a much shorter distance -- perhaps only a centimeter. Find the net force acting on a 52 kg driver who is decelerated from 20 m/s ...
... driver who does not wear a seatbelt continues to move forward with a speed of 20 m/s (due to inertia) until something solid is encountered. The driver now comes to rest in a much shorter distance -- perhaps only a centimeter. Find the net force acting on a 52 kg driver who is decelerated from 20 m/s ...
psaa forces worksheet
... speed and direction of motion will not change. If the forces on an object are in balance, the object’s velocity is constant. a. This simply means that if an object is not moving, the object will stay still. b. If the object is moving, it will continue in a straight line at a constant speed. c. What ...
... speed and direction of motion will not change. If the forces on an object are in balance, the object’s velocity is constant. a. This simply means that if an object is not moving, the object will stay still. b. If the object is moving, it will continue in a straight line at a constant speed. c. What ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy
... and over the displacement s, the speed of the car will increase. Newton's 2nd law: acceleration of the car, a = F mCar Starting with velocity v0 , find the final speed. ...
... and over the displacement s, the speed of the car will increase. Newton's 2nd law: acceleration of the car, a = F mCar Starting with velocity v0 , find the final speed. ...
Slide 1
... be wise to begin with a few nails and work upward to more nails? Answer: No, no, no! There would be one less physics teacher if the demonstration were performed with fewer nails. The resulting greater pressure would cause harm. ...
... be wise to begin with a few nails and work upward to more nails? Answer: No, no, no! There would be one less physics teacher if the demonstration were performed with fewer nails. The resulting greater pressure would cause harm. ...
Textbook Practice Problems
... How does a seat belt keep a passenger from being injured in a car crash? Why does a bus need a larger, more powerful engine than a small car to have the same acceleration? If I reduce the mass of my automobile, will it take more or less force from the engine to accelerate the car? ...
... How does a seat belt keep a passenger from being injured in a car crash? Why does a bus need a larger, more powerful engine than a small car to have the same acceleration? If I reduce the mass of my automobile, will it take more or less force from the engine to accelerate the car? ...
sy18_nov02_f11
... Two blocks of mass m1 = M and m2 = 2M are both sliding towards you on a frictionless surface. The linear momentum of block 1 is half the linear momentum of block 2. You apply the same constant force to both objects in order to bring them to rest. What is the ratio of the two stopping distances d2/d1 ...
... Two blocks of mass m1 = M and m2 = 2M are both sliding towards you on a frictionless surface. The linear momentum of block 1 is half the linear momentum of block 2. You apply the same constant force to both objects in order to bring them to rest. What is the ratio of the two stopping distances d2/d1 ...











![[SESSION-2012-2013] KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN Zonal Institute of Education & Training](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008846751_1-2b4b3b69c179d4de9cadbe3a1137f0be-300x300.png)











