Forces & Motion Review - Warren County Schools
... • Acceleration is caused by unbalanced forces More ...
... • Acceleration is caused by unbalanced forces More ...
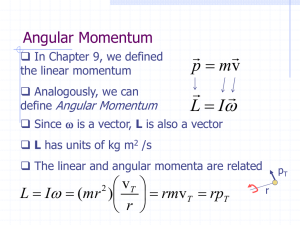
Universal Gravitation
... other with a gravitational force of 16 units. If the mass of both objects was doubled, and if the distance between the objects was doubled, then what would be the new force of attraction between the two ...
... other with a gravitational force of 16 units. If the mass of both objects was doubled, and if the distance between the objects was doubled, then what would be the new force of attraction between the two ...
Ex. 1 - Mr. Schroeder
... Bart and the Case of Inertia… 1. Bart is using a force of 60 N west to ride his skateboard, the force of friction on the skateboard is 60 N east. Bart and the skateboard have a mass of 45 kg. a. draw a free body diagram b. describe the motion of Bart and the skateboard ...
... Bart and the Case of Inertia… 1. Bart is using a force of 60 N west to ride his skateboard, the force of friction on the skateboard is 60 N east. Bart and the skateboard have a mass of 45 kg. a. draw a free body diagram b. describe the motion of Bart and the skateboard ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... According to Newton’s first law of motion, what will a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced force do? Which of Newton’s laws explain inertia? What explains the tendency of all objects to resist any change in motion? What is a measure of inertia? What causes a person to fall backward a ...
... According to Newton’s first law of motion, what will a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced force do? Which of Newton’s laws explain inertia? What explains the tendency of all objects to resist any change in motion? What is a measure of inertia? What causes a person to fall backward a ...
Newton`s 1st Law - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... velocity will continue to move at a constant velocity if no force is applied (ie, no acceleration). ...
... velocity will continue to move at a constant velocity if no force is applied (ie, no acceleration). ...
Expectations for Ch 2 & 3
... • What is a frame of reference? • A system to determine location or motion of an object. • How can I tell if something is moving and how fast? ...
... • What is a frame of reference? • A system to determine location or motion of an object. • How can I tell if something is moving and how fast? ...
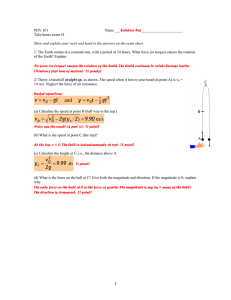
PHY 101 ... ______________________ Take home exam #1 Solution Key
... 1/ The Earth rotates at a constant rate, with a period of 24 hours. What force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth? Explain. No force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth. The Earth continues to rotate because inertia (Newton’s first law of motion). [2 points] 2/ Throw a baseball st ...
... 1/ The Earth rotates at a constant rate, with a period of 24 hours. What force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth? Explain. No force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth. The Earth continues to rotate because inertia (Newton’s first law of motion). [2 points] 2/ Throw a baseball st ...
Blank Jeopardy - the Mining Quiz List
... All objects in freefall have the same speed. T or F. It depends on if there is air ...
... All objects in freefall have the same speed. T or F. It depends on if there is air ...
12.2 Newton`s 1st and 2nd Laws of Motion
... An object moving at a constant velocity will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a nonzero net force ...
... An object moving at a constant velocity will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a nonzero net force ...
Chapter 4: Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... - seems contrary to everyday experience Inertia – tendency for an object to remain at rest, or to remain in motion with a constant velocity - all objects have inertia ...
... - seems contrary to everyday experience Inertia – tendency for an object to remain at rest, or to remain in motion with a constant velocity - all objects have inertia ...
Laws of motion Power Point
... Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion - Continued The acceleration for any object moving under the sole influence of gravity. Any moving object being acted upon only by the force of gravity is said to be "in a state of free fall." ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion - Continued The acceleration for any object moving under the sole influence of gravity. Any moving object being acted upon only by the force of gravity is said to be "in a state of free fall." ...
Chapter 4 - boykinhonors
... net force on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
... net force on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...