net force
... object will move faster! o Law #3 – For every action (force), there is an opposite and equal reaction (force) Rocket ships push down with a blowing force to move up Your hand slapping a table with 25N of force will result in the table applying 25N of force back on your hand. Be able to use the ...
... object will move faster! o Law #3 – For every action (force), there is an opposite and equal reaction (force) Rocket ships push down with a blowing force to move up Your hand slapping a table with 25N of force will result in the table applying 25N of force back on your hand. Be able to use the ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
Crossword for Acceleration
... about any point is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments about that point. 5F Same as F5. 5O The abbreviation of the British unit of mass is lb. 6A & Newton’s first law states that a body remains in its state of rest or uniform motion unless 6M it is acted on by an unbalanced force, or a nonzero ...
... about any point is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments about that point. 5F Same as F5. 5O The abbreviation of the British unit of mass is lb. 6A & Newton’s first law states that a body remains in its state of rest or uniform motion unless 6M it is acted on by an unbalanced force, or a nonzero ...
Newton*s Second Law
... Newton’s first law predicts motion of objects with forces which are balanced. ...
... Newton’s first law predicts motion of objects with forces which are balanced. ...
F g - Humble ISD
... m2 = 11.0 kg as shown below. Find the acceleration of each mass and the tension in the cable. ...
... m2 = 11.0 kg as shown below. Find the acceleration of each mass and the tension in the cable. ...
Newtons 2nd law
... is a force, and is measured in Newtons. • The force of gravity causes all objects near Earth’s surface to fall with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s². • Your weight on Earth is the gravitational force between you and Earth. ...
... is a force, and is measured in Newtons. • The force of gravity causes all objects near Earth’s surface to fall with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s². • Your weight on Earth is the gravitational force between you and Earth. ...
Chapter 3 - Department Of Computer Science
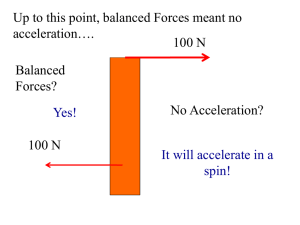
... A force’s capability may be balanced or canceled by other force(s): the net effect is then zero More than one force acts on an object: ...
... A force’s capability may be balanced or canceled by other force(s): the net effect is then zero More than one force acts on an object: ...
HW#6: Fallin` Up
... Date___________________ Block__________________ HW#6 Reading: Gravity and Motion ...
... Date___________________ Block__________________ HW#6 Reading: Gravity and Motion ...
Physics Force Worksheet
... 13. A mass of 10.0 kg (m1) rests on an incline that makes an angle of 36.9o with the horizontal. A light cord connects it to a mass m2 hanging over the top edge of the incline. a. What is the mass of m2 if the system moves at a constant velocity to the top of the ramp? b. What would the mass m 2 be ...
... 13. A mass of 10.0 kg (m1) rests on an incline that makes an angle of 36.9o with the horizontal. A light cord connects it to a mass m2 hanging over the top edge of the incline. a. What is the mass of m2 if the system moves at a constant velocity to the top of the ramp? b. What would the mass m 2 be ...
Forces and Energy Summary Sheet File
... Know that forces are measured in units called the Newton (N) Know that mass is a measured of how much matter is in an object and is measured in ...
... Know that forces are measured in units called the Newton (N) Know that mass is a measured of how much matter is in an object and is measured in ...
Instructions - People Server at UNCW
... b) Two objects are separated by a distance R. If one of the objects is replaced by another having twice as much mass and the separation distance is doubled, then the gravitational force is a) twice as much; b) half as much; c) four times as much; d) a quarter as much; e) the same. _____ c) Which of ...
... b) Two objects are separated by a distance R. If one of the objects is replaced by another having twice as much mass and the separation distance is doubled, then the gravitational force is a) twice as much; b) half as much; c) four times as much; d) a quarter as much; e) the same. _____ c) Which of ...
Newton`s 2nd Law - fhssciencerocks
... One Newton is equal to 0.225 lbs. One pound is equal to 4.448 Newtons If you push an empty cart with the same force you would use to push a full cart, the empty one will have a much greater acceleration ...
... One Newton is equal to 0.225 lbs. One pound is equal to 4.448 Newtons If you push an empty cart with the same force you would use to push a full cart, the empty one will have a much greater acceleration ...
F - Earth and Environmental Sciences
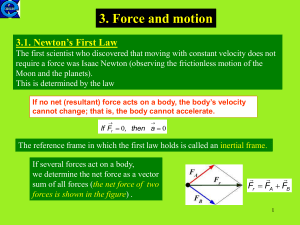
... to real or imagined bodies anywhere on Earth or in space). Every object retains its state of rest or its state of uniform, straight-line motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force (In his own statement of the first law, Newton referred to the unbalanced force as an "external agency"). This law ...
... to real or imagined bodies anywhere on Earth or in space). Every object retains its state of rest or its state of uniform, straight-line motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force (In his own statement of the first law, Newton referred to the unbalanced force as an "external agency"). This law ...
Forces in Motion
... • All forces act in pairs. • If a force is exerted, another force is exerted that is equal in size, but opposite in direction to the first force. ...
... • All forces act in pairs. • If a force is exerted, another force is exerted that is equal in size, but opposite in direction to the first force. ...
Forces & Motion ()
... reference become more complicated. This is called Special Relativity, developed by Albert Einstein. We will consider the modest speed version, which is often called ‘Galilean Relativity’ after the great Renaissance Physicist Galileo. One major difference is that time passes at the same rate in the l ...
... reference become more complicated. This is called Special Relativity, developed by Albert Einstein. We will consider the modest speed version, which is often called ‘Galilean Relativity’ after the great Renaissance Physicist Galileo. One major difference is that time passes at the same rate in the l ...