Physics - bsparrow
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion • The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is directly proportional to the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion • The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is directly proportional to the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ...
Newton`s Laws Review
... Overall force acting on an object 12. What happens if an objects net force is unbalanced? Draw a free body diagram of this. It will accelerate, decelerate, or change direction 13. What 2 things can happen when an objects net force is equal to 0? It will be in equilibrium, meaning it will remain at r ...
... Overall force acting on an object 12. What happens if an objects net force is unbalanced? Draw a free body diagram of this. It will accelerate, decelerate, or change direction 13. What 2 things can happen when an objects net force is equal to 0? It will be in equilibrium, meaning it will remain at r ...
Name - BigEngine
... 12. Two objects, each with a mass of 8.0 x 102 kg produce a gravitational force between them of 3.7 x 10-6 N. What is the distance between them? (2 marks) ...
... 12. Two objects, each with a mass of 8.0 x 102 kg produce a gravitational force between them of 3.7 x 10-6 N. What is the distance between them? (2 marks) ...
80 Revision Motion
... 16. A pen is dropped from rest and accelerated by gravity on Earth. How far has it dropped in 2s? (ignore air resistance) (A) 9.8m (B) 19.6m (C) 12m (D) Can’t be calculated - insufficient information. 17. A ball is thrown straight upwards into the air at 6m/s. How long before it reaches its peak hei ...
... 16. A pen is dropped from rest and accelerated by gravity on Earth. How far has it dropped in 2s? (ignore air resistance) (A) 9.8m (B) 19.6m (C) 12m (D) Can’t be calculated - insufficient information. 17. A ball is thrown straight upwards into the air at 6m/s. How long before it reaches its peak hei ...
What are Newton`s laws of motion
... floor. Give the cart a push (unbalanced force) and the cart rolls. When it stops, ask students why it stopped. You might be surprised to hear them give you the same answer taught by Aristotle. It is at this point you would remind them about ...
... floor. Give the cart a push (unbalanced force) and the cart rolls. When it stops, ask students why it stopped. You might be surprised to hear them give you the same answer taught by Aristotle. It is at this point you would remind them about ...
Lecture Notes: Chapter 2 Motion
... Scientists at NASA need to consider frames of reference because all objects in space are in constant motion relative to earth. They can’t just send up a satellite or spacecraft and expect it to be at the speed of the other objects. Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object ...
... Scientists at NASA need to consider frames of reference because all objects in space are in constant motion relative to earth. They can’t just send up a satellite or spacecraft and expect it to be at the speed of the other objects. Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object ...
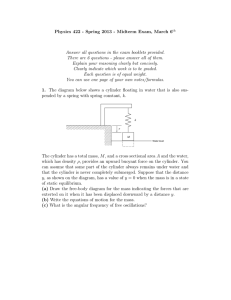
Physics 422 - Spring 2013 - Midterm Exam, March 6
... (a) Draw the free-body diagram for the mass indicating the forces that are exterted on it when it has been displaced downward by a distance y. (b) Write the equations of motion for the mass. (c) What is the angular frequency of free oscillations? ...
... (a) Draw the free-body diagram for the mass indicating the forces that are exterted on it when it has been displaced downward by a distance y. (b) Write the equations of motion for the mass. (c) What is the angular frequency of free oscillations? ...
General Physics STUDY GUIDE
... Identify a projectile’s acceleration in each direction objects at different points in time. Write and solve conservation of energy problems that are Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion (Ch. 4) Be able to draw or recognize force diagrams for an object in a consistent with these bar chart diagrams. sta ...
... Identify a projectile’s acceleration in each direction objects at different points in time. Write and solve conservation of energy problems that are Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion (Ch. 4) Be able to draw or recognize force diagrams for an object in a consistent with these bar chart diagrams. sta ...
Phys Sci Chapter 3 notes
... An archer’s arrow can have a large momentum because it has a high velocity even with a small mass. An elephant may have a low velocity, but has a large momentum because of its large mass. ...
... An archer’s arrow can have a large momentum because it has a high velocity even with a small mass. An elephant may have a low velocity, but has a large momentum because of its large mass. ...
Projectile Motion
... • Gravity, being a downward force, causes a projectile to accelerate in the downward direction. • The force of gravity could never alter the horizontal velocity of an object since perpendicular components of motion are independent of each other; – vertical force does not effect a horizontal motion. ...
... • Gravity, being a downward force, causes a projectile to accelerate in the downward direction. • The force of gravity could never alter the horizontal velocity of an object since perpendicular components of motion are independent of each other; – vertical force does not effect a horizontal motion. ...