Force and Newtons Laws
... • What is the force required to push a 25kg girl in a 100kg wagon with an acceleration of 3m/s2? ...
... • What is the force required to push a 25kg girl in a 100kg wagon with an acceleration of 3m/s2? ...
Forces
... How hard they push together and they type of surfaces involved. A smooth surface is much easier to slide on. ...
... How hard they push together and they type of surfaces involved. A smooth surface is much easier to slide on. ...
SHM Notes
... spring, of constant 55 N/m, with a period of 6.58 seconds. What is the mass of the load? 3. A mass oscillates horizontally at the end of a spring of constant 85N/m. If the system has an amplitude of 11 cm, what is the maximum kinetic energy? What is the maximum potential energy? ...
... spring, of constant 55 N/m, with a period of 6.58 seconds. What is the mass of the load? 3. A mass oscillates horizontally at the end of a spring of constant 85N/m. If the system has an amplitude of 11 cm, what is the maximum kinetic energy? What is the maximum potential energy? ...
Newton s__Laws_of_Motion - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when you stub your toe? When your toe exerts a force on a rock, the ...
... skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when you stub your toe? When your toe exerts a force on a rock, the ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... If the sun and Earth are constantly pulling on one another because of gravity, why doesn’t Earth fall into the sun? Why doesn’t the moon crash into Earth? The fact that these collisions haven’t happened means there must be some other factor we haven’t yet taken into account. What are Newton’s first ...
... If the sun and Earth are constantly pulling on one another because of gravity, why doesn’t Earth fall into the sun? Why doesn’t the moon crash into Earth? The fact that these collisions haven’t happened means there must be some other factor we haven’t yet taken into account. What are Newton’s first ...
Unit 5 Review
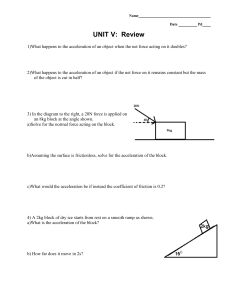
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
Physics 131 Review Translational Kinematics: Position ( ): location relative to an origin
... acceleration in the x-direction, the velocity in that direction is constant. • At any given height, the speed of the ball is the same. Forces Newton's Laws: 1st: An object in motion or an object at rest will remain in motion or at rest if no net force acts on the object. 2nd: Net force is related t ...
... acceleration in the x-direction, the velocity in that direction is constant. • At any given height, the speed of the ball is the same. Forces Newton's Laws: 1st: An object in motion or an object at rest will remain in motion or at rest if no net force acts on the object. 2nd: Net force is related t ...
Section 2: Gravity
... ▪ All objects, regardless of their mass, accelerate at the same rate when they are in free fall. Why? Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion explains it: an object’s acceleration increases if the force on it increases, but its acceleration decreases if its mass increases. So, the more massive an object is, the ...
... ▪ All objects, regardless of their mass, accelerate at the same rate when they are in free fall. Why? Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion explains it: an object’s acceleration increases if the force on it increases, but its acceleration decreases if its mass increases. So, the more massive an object is, the ...
Measurement and Kinematics
... 42. If an object is thrown, about what point will it rotate? 43. Describe the 3 types of equilibrium. 44. What is a torque? 45. How are torques calculated? 46. What is meant by rotational inertia? 47. Why does a spinning ice skater spin faster with her arms tucked in at her side? 48. For an object t ...
... 42. If an object is thrown, about what point will it rotate? 43. Describe the 3 types of equilibrium. 44. What is a torque? 45. How are torques calculated? 46. What is meant by rotational inertia? 47. Why does a spinning ice skater spin faster with her arms tucked in at her side? 48. For an object t ...
T3 F2013 9 30
... a. Angular speed of a wheel. b. Linear speed of the automobile. c. Translational kinetic energy of a wheel. d. Rotational kinetic energy of a wheel. e. Total kinetic energy of a wheel. f. Total kinetic energy of the automobile. ...
... a. Angular speed of a wheel. b. Linear speed of the automobile. c. Translational kinetic energy of a wheel. d. Rotational kinetic energy of a wheel. e. Total kinetic energy of a wheel. f. Total kinetic energy of the automobile. ...
What is this unbalanced force that acts on an
... why it is easier to push a bicycle than to push a car with the same acceleration? ...
... why it is easier to push a bicycle than to push a car with the same acceleration? ...
How Things Work - University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign
... Observations About Wind Turbines In absence of forces (wind) there is no torque and the blades ...
... Observations About Wind Turbines In absence of forces (wind) there is no torque and the blades ...
Newtons Laws and Its Application
... 1. Identify all the bodies 2. Draw a free-body diagram, show all the forces 3. Choose a convenient x-y coordinate system 4. Component equations of Newton’s second law 5. Solve all the equations ▲ Be careful about limitations of the formulas! ...
... 1. Identify all the bodies 2. Draw a free-body diagram, show all the forces 3. Choose a convenient x-y coordinate system 4. Component equations of Newton’s second law 5. Solve all the equations ▲ Be careful about limitations of the formulas! ...
DOC - People Server at UNCW
... In this lab we will be studying the moment of inertia of two rotating disks about a fixed shaft. From the Parallel Axis Theorem we know that the moment of inertia of a body rotating at a distance R from the center of mass of the body is given by I I CM MR 2 , where M is the total mass of the obj ...
... In this lab we will be studying the moment of inertia of two rotating disks about a fixed shaft. From the Parallel Axis Theorem we know that the moment of inertia of a body rotating at a distance R from the center of mass of the body is given by I I CM MR 2 , where M is the total mass of the obj ...