AP Physics B Lesson Plans
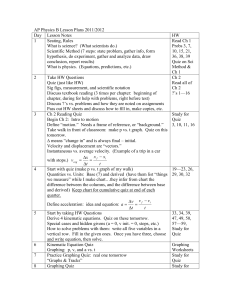
... Begin Ch 4: Dynamics (the “why” of motion) F = 0 leads to a = 0. Discuss “balanced forces” and “net.” History: pre-1600: p. 83, section 4.2. 1st Law: inertia. 2nd Law: F (net) = ma (and w = mg) m Unit for force: the Newton (N) or kg 2 s Step 1 for problem solving: draw free body diagram (FBD) Sta ...
... Begin Ch 4: Dynamics (the “why” of motion) F = 0 leads to a = 0. Discuss “balanced forces” and “net.” History: pre-1600: p. 83, section 4.2. 1st Law: inertia. 2nd Law: F (net) = ma (and w = mg) m Unit for force: the Newton (N) or kg 2 s Step 1 for problem solving: draw free body diagram (FBD) Sta ...
III. Apparent Weight - KET Virtual Physics Labs
... for a falling mass hanger. We need a system of one object – the mass hanger. Hmm. You can’t have a mass hanger without a string to attach it to. And all position measurements are associated with the cart, not the hanger. So we need a cart, but then again we don’t. We need a cart that won’t interfere ...
... for a falling mass hanger. We need a system of one object – the mass hanger. Hmm. You can’t have a mass hanger without a string to attach it to. And all position measurements are associated with the cart, not the hanger. So we need a cart, but then again we don’t. We need a cart that won’t interfere ...
ch12
... • With the inclusion of the inertial vector, the system of forces acting on the particle is equivalent to zero. The particle is in dynamic equilibrium. • Methods developed for particles in static equilibrium may be applied, e.g., coplanar forces may be represented with a closed vector polygon. • Ine ...
... • With the inclusion of the inertial vector, the system of forces acting on the particle is equivalent to zero. The particle is in dynamic equilibrium. • Methods developed for particles in static equilibrium may be applied, e.g., coplanar forces may be represented with a closed vector polygon. • Ine ...
Impulse and Momentum Review
... We’ve seen that if you want to change the momentum of an object or a system of objects, Newton’s second law says that you have to apply an unbalanced force. This implies that if there are no unbalanced forces acting on a system, the total momentum of the system must remain constant. This is another ...
... We’ve seen that if you want to change the momentum of an object or a system of objects, Newton’s second law says that you have to apply an unbalanced force. This implies that if there are no unbalanced forces acting on a system, the total momentum of the system must remain constant. This is another ...
Note 13 Newton`s Third Law
... We measured that, during the collision, the speed of the right cart went from 0 m/s to +31.8 cm/s. The time of the collision itself is about 3/30 second. The average acceleration of the right cart is ...
... We measured that, during the collision, the speed of the right cart went from 0 m/s to +31.8 cm/s. The time of the collision itself is about 3/30 second. The average acceleration of the right cart is ...
Chapter 4-4
... is called the force of static friction. • Static Friction = Fs • As long as the object doesn’t move, the static friction is always equal to the opposite in direction to the applied force. • Fs = -Fapplied • When the applied force is as great as it can be without moving the object, the force of stati ...
... is called the force of static friction. • Static Friction = Fs • As long as the object doesn’t move, the static friction is always equal to the opposite in direction to the applied force. • Fs = -Fapplied • When the applied force is as great as it can be without moving the object, the force of stati ...
10 Circular Motion
... fictitious force, unlike gravitational, electromagnetic, and nuclear forces. Nevertheless, to observers who are in a rotating system, centrifugal force is very real. Just as gravity is ever present at Earth’s surface, centrifugal force is ever present within a rotating system. ...
... fictitious force, unlike gravitational, electromagnetic, and nuclear forces. Nevertheless, to observers who are in a rotating system, centrifugal force is very real. Just as gravity is ever present at Earth’s surface, centrifugal force is ever present within a rotating system. ...
angular momentum
... A disk, for which the moment of iner3a is I1, rotates about a ver3cal, fric3onless axle with angular velocity ω0. A second disk, which has moment of iner3a I2 and is not rota3ng, drops onto the first disk, as illustrated below. The disks s3ck together, which results in their both spinning with a ...
... A disk, for which the moment of iner3a is I1, rotates about a ver3cal, fric3onless axle with angular velocity ω0. A second disk, which has moment of iner3a I2 and is not rota3ng, drops onto the first disk, as illustrated below. The disks s3ck together, which results in their both spinning with a ...
elastic-potential-energy
... What is the potential energy of the spring? 2. What is the potential energy of a spring if the spring constant is 25.0 N/m and it is compressed to .5 m past its resting position? 3. A 250. g mass is placed on the spring in #2. Assuming the spring is pointed straight up, to what height could the spri ...
... What is the potential energy of the spring? 2. What is the potential energy of a spring if the spring constant is 25.0 N/m and it is compressed to .5 m past its resting position? 3. A 250. g mass is placed on the spring in #2. Assuming the spring is pointed straight up, to what height could the spri ...