Unit 8 Student Notes
... The force exerted against the recoiling cannon is just as great as the force that drives the cannonball along the barrel. Why, then, does the cannonball undergo more acceleration than the cannon? ...
... The force exerted against the recoiling cannon is just as great as the force that drives the cannonball along the barrel. Why, then, does the cannonball undergo more acceleration than the cannon? ...
Unit 1
... We can use this expression to determine the orbital velocity (V) of a small mass orbiting a distance d from the center of a much larger mass (M) ...
... We can use this expression to determine the orbital velocity (V) of a small mass orbiting a distance d from the center of a much larger mass (M) ...
Physics Final Exam Review Packet
... Will all objects released from rest fall at the same rate? Does air resistance make any difference? ...
... Will all objects released from rest fall at the same rate? Does air resistance make any difference? ...
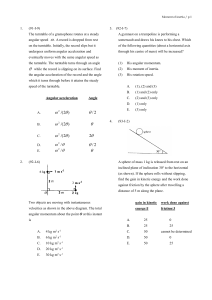
What is angular velocity? Angular speed
... Q: What is angular velocity? Angular speed? What symbols are used to denote each? What units are used? Q: What is linear velocity? Linear Speed? What symbols are used to denote each? What units are used? Q: What is tangential velocity? Tangential Speed? What symbols are used to denote each? What uni ...
... Q: What is angular velocity? Angular speed? What symbols are used to denote each? What units are used? Q: What is linear velocity? Linear Speed? What symbols are used to denote each? What units are used? Q: What is tangential velocity? Tangential Speed? What symbols are used to denote each? What uni ...
forces - jpsaos
... Earth rotates on its axis and that the planets revolve around the sun Heliocentrist – Belief in the sun centered model of the solar system. Prior belief was the geocentric model, with the Earth as the center of the universe ...
... Earth rotates on its axis and that the planets revolve around the sun Heliocentrist – Belief in the sun centered model of the solar system. Prior belief was the geocentric model, with the Earth as the center of the universe ...
Newton`s Laws…Conceptually
... 9. When you compress a sponge, which quantity changes: mass, inertia, volume, or weight? 10. What is the cause of friction, and in what direction does it act with respect to the motion of a sliding object? 11. All other things being equal, why does a heavy skydiver have a terminal speed greater than ...
... 9. When you compress a sponge, which quantity changes: mass, inertia, volume, or weight? 10. What is the cause of friction, and in what direction does it act with respect to the motion of a sliding object? 11. All other things being equal, why does a heavy skydiver have a terminal speed greater than ...
2016 sample exam
... mutual capacitance. The Lagrangian for this can be written down by noting that the energy in a current flowing through an inductance L is LI 2 /2, where I = dQ/dt is the current; the energy stored in a capacitance C is Q2 /2C; and the energy in the mutual capacitance C12 between two LC circuits is Q1 ...
... mutual capacitance. The Lagrangian for this can be written down by noting that the energy in a current flowing through an inductance L is LI 2 /2, where I = dQ/dt is the current; the energy stored in a capacitance C is Q2 /2C; and the energy in the mutual capacitance C12 between two LC circuits is Q1 ...
Unit 2 Section 4 Notes Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Astronauts in space appear to be “weightless”. This statement is NOT true because gravity exists everywhere in the universe; it is the force of attraction between 2 objects due to mass. Astronauts in orbit experience apparent weightlessness because they are in free fall. The astronauts and vehicle ...
... Astronauts in space appear to be “weightless”. This statement is NOT true because gravity exists everywhere in the universe; it is the force of attraction between 2 objects due to mass. Astronauts in orbit experience apparent weightlessness because they are in free fall. The astronauts and vehicle ...
Planet Earth - Madeira City Schools
... cause the object to change its motion - it will accelerate The magnitude of the force and the mass of the object will both influence the acceleration ...
... cause the object to change its motion - it will accelerate The magnitude of the force and the mass of the object will both influence the acceleration ...
PreAP Physics Spring Semester Practice Final
... assumptions must be made in regard to the object’s kinetic energy? a. The kinetic energy decreases. b. The kinetic energy increases. c. The kinetic energy remains constant. d. The kinetic energy decreases and then increases. ____ 34. The magnitude of the component of the force that does the work is ...
... assumptions must be made in regard to the object’s kinetic energy? a. The kinetic energy decreases. b. The kinetic energy increases. c. The kinetic energy remains constant. d. The kinetic energy decreases and then increases. ____ 34. The magnitude of the component of the force that does the work is ...
1. What is unit vector? 2. State the principle of transmissibility.
... (ii) A pull of 250 N inclined at 30° to the horizontal plane is required just to move a body kept on a rough horizontal plane. But the push required just to move the body is 300 N. If the push is inclined at 30° to the horizontal, find the weight of the body and the coefficient of friction, and the ...
... (ii) A pull of 250 N inclined at 30° to the horizontal plane is required just to move a body kept on a rough horizontal plane. But the push required just to move the body is 300 N. If the push is inclined at 30° to the horizontal, find the weight of the body and the coefficient of friction, and the ...