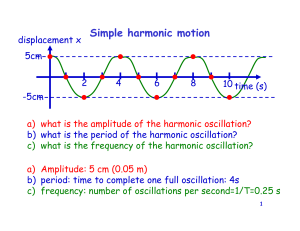
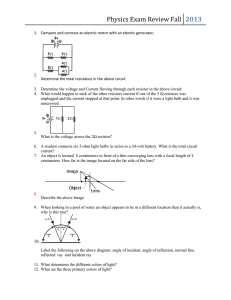
ProblemsOscillations
... constant of 19.6 N/m oscillates on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the spring is compressed by 0.04 and then released determine: a) the maximum speed of the object b) the speed of the object when the spring is compressed by 0.015 m c) when it is stretched by 0.015 m d) for what value of x does ...
... constant of 19.6 N/m oscillates on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the spring is compressed by 0.04 and then released determine: a) the maximum speed of the object b) the speed of the object when the spring is compressed by 0.015 m c) when it is stretched by 0.015 m d) for what value of x does ...
Name____________________________ Date_______________
... 3. How many important discoveries did Isaac Newton make while he was studying at home as a man? What were the important discoveries made? ...
... 3. How many important discoveries did Isaac Newton make while he was studying at home as a man? What were the important discoveries made? ...
Laws of Motion
... 3. How many important discoveries did Isaac Newton make while he was studying at home as a man? What were the important discoveries made? ...
... 3. How many important discoveries did Isaac Newton make while he was studying at home as a man? What were the important discoveries made? ...
Chapter 7
... 1. The gravitational attraction of Earth and the Sun provides a centripetal acceleration explaining Earth's orbit 2. The gravitational and inertial masses of an object are equivalent. 3. The radial line segment from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. 3. What concept ...
... 1. The gravitational attraction of Earth and the Sun provides a centripetal acceleration explaining Earth's orbit 2. The gravitational and inertial masses of an object are equivalent. 3. The radial line segment from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. 3. What concept ...
A Force - Cloudfront.net
... • Objects fall to ground at the same rate because acceleration due to gravity is the same for ALL objects • Why? Acceleration depends on both force and mass. – A heavier object experiences a greater gravitational force, BUT it is also harder to accelerate. – Galileo was a genius. ...
... • Objects fall to ground at the same rate because acceleration due to gravity is the same for ALL objects • Why? Acceleration depends on both force and mass. – A heavier object experiences a greater gravitational force, BUT it is also harder to accelerate. – Galileo was a genius. ...
go up, go down, push me, and throw me away
... 5-5.1 Illustrate the effects of force (including magnetism, gravity, and friction) on motion. ...
... 5-5.1 Illustrate the effects of force (including magnetism, gravity, and friction) on motion. ...
Mass and Weight
... The force of gravity on any object is actually the weight of the object! So this means that because weight is a force it is measured in NEWTONS! The thing we usually call ‘weight’ and is measured in kilograms and grams is really called the MASS! ...
... The force of gravity on any object is actually the weight of the object! So this means that because weight is a force it is measured in NEWTONS! The thing we usually call ‘weight’ and is measured in kilograms and grams is really called the MASS! ...
Newton`s 1st Law
... Anticipatory Set:(“The Hook” -- something to excite the student about the subject matter) “An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.” Th ...
... Anticipatory Set:(“The Hook” -- something to excite the student about the subject matter) “An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.” Th ...
Force and Motion
... Lamont wants to move a 4,800 gram box from the floor to a shelf directly above the box. It takes Lamont 8 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 0.4 meters from the ground. It takes 12 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 1.2 meters off the ground. How much more work in joules is required ...
... Lamont wants to move a 4,800 gram box from the floor to a shelf directly above the box. It takes Lamont 8 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 0.4 meters from the ground. It takes 12 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 1.2 meters off the ground. How much more work in joules is required ...
sample106f
... For isolated systems: net = 0 L is constant L = 0 L0 = I00 = Lf = Iff Equilibrium: forces = 0 and torques = 0, If net force on a system is zero, then the net torque is the same for any chosen rotation axis. COG definition: point about which torques due to gravity alone add to zero. ...
... For isolated systems: net = 0 L is constant L = 0 L0 = I00 = Lf = Iff Equilibrium: forces = 0 and torques = 0, If net force on a system is zero, then the net torque is the same for any chosen rotation axis. COG definition: point about which torques due to gravity alone add to zero. ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frames Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs higher force. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained ...
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frames Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs higher force. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained ...
Rotational Dynamics
... • The angular acceleration this torque produces depends on the mass of the rotating object and upon the distribution of its mass with respect to the axis of rotation. • If the mass remains fixed in position, torque and angular acceleration are directly proportional. • If the mass is closer to the ...
... • The angular acceleration this torque produces depends on the mass of the rotating object and upon the distribution of its mass with respect to the axis of rotation. • If the mass remains fixed in position, torque and angular acceleration are directly proportional. • If the mass is closer to the ...
File
... Explain direct and indirect proportion as it relates to Newton's Second law. Explain why force is a vector. Apply the formulas to a given physical situation. Illustrate Newton’s Second Law of Motion using physical examples. ...
... Explain direct and indirect proportion as it relates to Newton's Second law. Explain why force is a vector. Apply the formulas to a given physical situation. Illustrate Newton’s Second Law of Motion using physical examples. ...
the forces are exerted on different objects
... different objects. Make sure you don’t use them as if they were acting on the same object. ...
... different objects. Make sure you don’t use them as if they were acting on the same object. ...
Short Answer
... 14. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between the pitcher and home plate? How does each of these forces change the ball’s motion? Classify the forces acting on the ball as ba ...
... 14. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between the pitcher and home plate? How does each of these forces change the ball’s motion? Classify the forces acting on the ball as ba ...