Motion
... • “The law of inertia” • Every object retains its state of rest or its state of uniform straight-line motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force • Inertia resists any changes in motion ...
... • “The law of inertia” • Every object retains its state of rest or its state of uniform straight-line motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force • Inertia resists any changes in motion ...
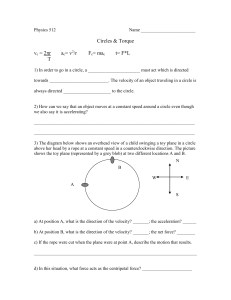
Rotational Motion Objectives: After reviewing this section you should
... handle, you will notice that it seems much heavier than if you lift the same mass with a short handle. A tight rope walker uses a long pole while balancing on the rope. This helps him maintain his balance because most of the mass of the pole is far away from the center of rotation. The pole has a la ...
... handle, you will notice that it seems much heavier than if you lift the same mass with a short handle. A tight rope walker uses a long pole while balancing on the rope. This helps him maintain his balance because most of the mass of the pole is far away from the center of rotation. The pole has a la ...
PowerPoint Presentation - 5. Universal Laws of Motion
... • Any object which is being acted upon only by the force of gravity is said to be in a state of free fall. There are two important motion characteristics which are true of free-falling objects: – Free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance. – All free-falling objects (on Earth) accelerate d ...
... • Any object which is being acted upon only by the force of gravity is said to be in a state of free fall. There are two important motion characteristics which are true of free-falling objects: – Free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance. – All free-falling objects (on Earth) accelerate d ...
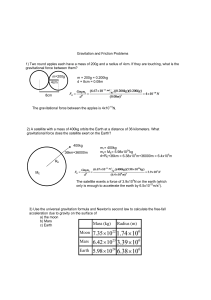
Wksht Momentum Review
... Date: _______________ Period: ________ Momentum Review Show work on a separate piece of paper 1. A 1400 kilogram car crashes into a tree. It was going 20.0 meters per second and it was brought to rest in 0.4 seconds. Find the average force exerted on the car during the collision. 2. A wagon has a mo ...
... Date: _______________ Period: ________ Momentum Review Show work on a separate piece of paper 1. A 1400 kilogram car crashes into a tree. It was going 20.0 meters per second and it was brought to rest in 0.4 seconds. Find the average force exerted on the car during the collision. 2. A wagon has a mo ...
NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... • NEWTON’S FIRST LAW OF MOTION: Every object continues in its state of rest, or uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. • MASS: measure of the inertia of an object • FORCE: measure of the magnitude and direction of the interactions ...
... • NEWTON’S FIRST LAW OF MOTION: Every object continues in its state of rest, or uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. • MASS: measure of the inertia of an object • FORCE: measure of the magnitude and direction of the interactions ...
phys1443-fall04-111004
... The torque due to tangential force Ft is Ft r mat r mr I The tangential force Ft is ...
... The torque due to tangential force Ft is Ft r mat r mr I The tangential force Ft is ...
Newton Laws of Motion
... Newton’s third law of motion. 2. Demonstrate a change in speed or direction of an object’s motion with the use of unbalanced forces ...
... Newton’s third law of motion. 2. Demonstrate a change in speed or direction of an object’s motion with the use of unbalanced forces ...
2009F Exam 2
... 1. [5%] Two cars having different weights are traveling on a level surface at different constant velocities. Within the same time interval, greater force will always be required to stop the car that has the greater what? (A) kinetic energy (B) weight (C) momentum (D) velocity 2. [5%] When an object ...
... 1. [5%] Two cars having different weights are traveling on a level surface at different constant velocities. Within the same time interval, greater force will always be required to stop the car that has the greater what? (A) kinetic energy (B) weight (C) momentum (D) velocity 2. [5%] When an object ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The action force is gravity pulling the ball down Every object exerts a gravitational force (creates gravity) That means that the ball is also creating a gravitational force on the Earth Why can’t you see the effect of the ball’s gravity on Earth? Earth is so massive, that you can not ...
... The action force is gravity pulling the ball down Every object exerts a gravitational force (creates gravity) That means that the ball is also creating a gravitational force on the Earth Why can’t you see the effect of the ball’s gravity on Earth? Earth is so massive, that you can not ...
Take-Home Packet to Accompany In
... Gravity: This is the attraction of a massive body on objects at or near its surface. Mass: This is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. Weight: This is a force; it is the pull of gravity on a mass. Galileo Galilei: This Italian scientist described how objects fall in a vacuum. Newton’s Fi ...
... Gravity: This is the attraction of a massive body on objects at or near its surface. Mass: This is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. Weight: This is a force; it is the pull of gravity on a mass. Galileo Galilei: This Italian scientist described how objects fall in a vacuum. Newton’s Fi ...