Review - Worth County Schools
... Momentum • A measure of how hard it is to stop a moving object. • Related to both mass and velocity. • Possessed by all moving objects. ...
... Momentum • A measure of how hard it is to stop a moving object. • Related to both mass and velocity. • Possessed by all moving objects. ...
Catalyst – October (Prime # between 11 and 17
... Field Forces – forces that exist between objects even in the absence of physical contact between the objects ...
... Field Forces – forces that exist between objects even in the absence of physical contact between the objects ...
Name - MrsMaier
... N for 0.10 s. Assuming that the ice surface is frictionless: a) What is the acceleration of each boy? (6.0 m/s2, 4.0 m/s2) b) What speed will each boy reach after the 0.10 s? (0.60 m/s, 0.40 m/s) c) Does it matter which boy did the pushing? Explain, using Newton’s Laws of Motion. ...
... N for 0.10 s. Assuming that the ice surface is frictionless: a) What is the acceleration of each boy? (6.0 m/s2, 4.0 m/s2) b) What speed will each boy reach after the 0.10 s? (0.60 m/s, 0.40 m/s) c) Does it matter which boy did the pushing? Explain, using Newton’s Laws of Motion. ...
force - Cloudfront.net
... Law of Conservation of Momentum • The momentum of an object doesn’t change unless its mass, velocity, or both change. • Momentum can be transferred from one object to another. • If a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t change. ...
... Law of Conservation of Momentum • The momentum of an object doesn’t change unless its mass, velocity, or both change. • Momentum can be transferred from one object to another. • If a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t change. ...
energy - RHIG - Wayne State University
... 1. Planets move in elliptical orbits about the sun with the sun at one focus. 2. The area per unit time swept out by a radius vector from the sun to a planet is constant. 3. The square of a planet’s period is proportional to the cube of the major axis of the planet’s orbit. ...
... 1. Planets move in elliptical orbits about the sun with the sun at one focus. 2. The area per unit time swept out by a radius vector from the sun to a planet is constant. 3. The square of a planet’s period is proportional to the cube of the major axis of the planet’s orbit. ...
OWL Ch02 Review Game
... as Earth and has the same gravitational acceleration, but has twice the mass. If you weigh 700 N on Earth, on the new planet ...
... as Earth and has the same gravitational acceleration, but has twice the mass. If you weigh 700 N on Earth, on the new planet ...
Newton`s Laws
... every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Ex: As you sit on your chair, your weight pushes down on the chair while the chair pushes up on you. Ex: When rowing a boat, the oar pushes on the water while the water pushes on the oar. ...
... every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Ex: As you sit on your chair, your weight pushes down on the chair while the chair pushes up on you. Ex: When rowing a boat, the oar pushes on the water while the water pushes on the oar. ...
Chapter 10-Forces - Solon City Schools
... Satellites orbit the earth in circular paths because of centripetal force. Satellites in orbit around Earth continually fall toward Earth, but because Earth is curved they travel around it. ...
... Satellites orbit the earth in circular paths because of centripetal force. Satellites in orbit around Earth continually fall toward Earth, but because Earth is curved they travel around it. ...
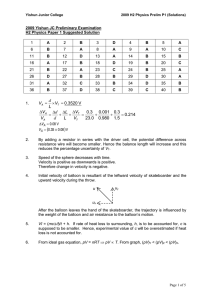
2009-YJC-PH-H2-P1-Prelim-soln
... For C and D, the CG lies in the middle of the rod so knife-edge is placed correctly below the CG. For B, the CG is off-centre to the right since material B is concentrated to the right. For A, the CG is also off-centre to the right since material B is concentrated to the right, but the knife-edge is ...
... For C and D, the CG lies in the middle of the rod so knife-edge is placed correctly below the CG. For B, the CG is off-centre to the right since material B is concentrated to the right. For A, the CG is also off-centre to the right since material B is concentrated to the right, but the knife-edge is ...
Forces and Motion
... • 3rd Law – when an object exerts a force on a second object, that object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object ...
... • 3rd Law – when an object exerts a force on a second object, that object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object ...