14.2 Newton`s second law and gravity
... 14.2 Force, mass and acceleration • Force causes acceleration, and mass resists acceleration. • Newton’s second law relates the force on an object, the mass of the object, and its acceleration. • Force causes acceleration, and mass resists acceleration. ...
... 14.2 Force, mass and acceleration • Force causes acceleration, and mass resists acceleration. • Newton’s second law relates the force on an object, the mass of the object, and its acceleration. • Force causes acceleration, and mass resists acceleration. ...
Wednesday, June 25, 2008
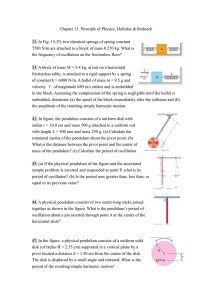
... from the center of the earth, and its point of greatest distance is 25.1x106m from the center of the earth. The speed of the satellite at the perigee is 8450 m/s. Find the speed at the apogee. Angular momentum is ...
... from the center of the earth, and its point of greatest distance is 25.1x106m from the center of the earth. The speed of the satellite at the perigee is 8450 m/s. Find the speed at the apogee. Angular momentum is ...
NFL Video Transcript
... Science of NFL Football - Newton’s Second Law of Motion LESTER HOLT reporting: To be an NFL kicker takes more than just nerves of steel and a strong leg. It also requires help from one of the key laws of physics. MORTEN ANDERSEN (Former NFL Kicker): It’s easy to say, well, I just kicked the ball. W ...
... Science of NFL Football - Newton’s Second Law of Motion LESTER HOLT reporting: To be an NFL kicker takes more than just nerves of steel and a strong leg. It also requires help from one of the key laws of physics. MORTEN ANDERSEN (Former NFL Kicker): It’s easy to say, well, I just kicked the ball. W ...
Glossary of Terms Handout
... Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Compare with Laser. In the Deep Space Network, masers are used as low-noise amplifiers of downlink signals, and also as frequency standards. Mass -- A fundamental property of an object comprising a numerical measure of its inertia; mass is the amoun ...
... Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Compare with Laser. In the Deep Space Network, masers are used as low-noise amplifiers of downlink signals, and also as frequency standards. Mass -- A fundamental property of an object comprising a numerical measure of its inertia; mass is the amoun ...
Circular Motion
... cannonball fired from the top of a high mountain. • If a cannonball were fired with a small horizontal speed, it would follow a parabolic path and soon hit Earth below. • Fired faster, its path would be less curved and it would hit Earth farther away. • If the cannonball were fired fast enough, its ...
... cannonball fired from the top of a high mountain. • If a cannonball were fired with a small horizontal speed, it would follow a parabolic path and soon hit Earth below. • Fired faster, its path would be less curved and it would hit Earth farther away. • If the cannonball were fired fast enough, its ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... the object will remain moving at the same velocity. No change in velocity. No acceleration. ...
... the object will remain moving at the same velocity. No change in velocity. No acceleration. ...
Chapter 2 - Bakersfield College
... C. Terminal speed is the maximum speed a falling object obtains when the force due to downward acceleration of gravity is balanced by the upward force of air resistance. D. The terminal speed for any object depends on the object's size, shape, and mass. ...
... C. Terminal speed is the maximum speed a falling object obtains when the force due to downward acceleration of gravity is balanced by the upward force of air resistance. D. The terminal speed for any object depends on the object's size, shape, and mass. ...
UNIT 2 REVIEW SHEET Answers sp 10
... acceleration due to gravity is 25 m/s2, that same object would weigh what on Earth and on Jupiter? On Jupiter it would have a mass of ? Weight on Earth Fw = mg 120(10) = Weight on Jupiter Fw = mg 120 (25)= The object would have the same mass on Jupiter as it does on Earth. Mass doesn’t change. 2. Wh ...
... acceleration due to gravity is 25 m/s2, that same object would weigh what on Earth and on Jupiter? On Jupiter it would have a mass of ? Weight on Earth Fw = mg 120(10) = Weight on Jupiter Fw = mg 120 (25)= The object would have the same mass on Jupiter as it does on Earth. Mass doesn’t change. 2. Wh ...
Chapter 12 powerpoint
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object. Gravitational force is an attractive force that acts between any two masses. Gravitational force depends upon mass and ...
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object. Gravitational force is an attractive force that acts between any two masses. Gravitational force depends upon mass and ...
Physics
... 7. What is the minimum velocity to keep the marble at the top of the vertical loop on track if the radius is 20 cm? b) If the marble moves faster than this velocity what forces make it go in a circle? 8. What force is needed to make a 10 kg mass go at 10 m/sec in a circle of radius 10m? Part II. ...
... 7. What is the minimum velocity to keep the marble at the top of the vertical loop on track if the radius is 20 cm? b) If the marble moves faster than this velocity what forces make it go in a circle? 8. What force is needed to make a 10 kg mass go at 10 m/sec in a circle of radius 10m? Part II. ...