Conversions: 15ft × 12 in 1 ft × 2.54 cm 1 in × 1 m 100 cm = 4.57 m
... Quickie 2 An object hangs motionless from a spring. When the demonstrator pulls the mass down a certain distance and holds it there just prior to releasing it, which of the following statements are true? a) The sum of gravitational potential energy of the object and elastic potential energy of the ...
... Quickie 2 An object hangs motionless from a spring. When the demonstrator pulls the mass down a certain distance and holds it there just prior to releasing it, which of the following statements are true? a) The sum of gravitational potential energy of the object and elastic potential energy of the ...
GSCI 101A - Section 006
... boiling point is at 681 K; the latent heat of vaporization is 189,000 J/kg. You wish to boil off 4.2 kg of this substance that is initially at 155 K. How much heat is required? a) 888,000 J b) 2,210,000 J c) 2,870,000 J d) 2,150,000 J d) First, the temperature of the solid must be raised to the mel ...
... boiling point is at 681 K; the latent heat of vaporization is 189,000 J/kg. You wish to boil off 4.2 kg of this substance that is initially at 155 K. How much heat is required? a) 888,000 J b) 2,210,000 J c) 2,870,000 J d) 2,150,000 J d) First, the temperature of the solid must be raised to the mel ...
ppt - MrMaloney.com
... no difference between constant velocity motion and no motion … they both are cases of 0 acceleration. This seems weird, but think about driving in a car. ...
... no difference between constant velocity motion and no motion … they both are cases of 0 acceleration. This seems weird, but think about driving in a car. ...
PHYSICS
... 3. Hands off equipment. No touching any gadgets or equipment unless told to do so by an instructor. When you do use equipment, you may only use it for the intended use so that it does not break, and we keep everybody safe. 4. Keep the room clean and neat. This means no graffiti on any school propert ...
... 3. Hands off equipment. No touching any gadgets or equipment unless told to do so by an instructor. When you do use equipment, you may only use it for the intended use so that it does not break, and we keep everybody safe. 4. Keep the room clean and neat. This means no graffiti on any school propert ...
Honors Homework
... A proton collides elastically with another proton that is initially at rest. The incoming proton has an initial speed of 3.5 x 105 m/s and makes a collision with the second proton. After the collision, one proton moves off at an angle of 37.0 o to the original direction of motion and the second defl ...
... A proton collides elastically with another proton that is initially at rest. The incoming proton has an initial speed of 3.5 x 105 m/s and makes a collision with the second proton. After the collision, one proton moves off at an angle of 37.0 o to the original direction of motion and the second defl ...
Semester 1 Objectives:
... hits the ground, when air resistance is negligible. 9. Determine the speed and the distance fallen at any time after an object is dropped from rest, when air resistance is negligible. 10. Describe how air resistance affects the motion of falling ...
... hits the ground, when air resistance is negligible. 9. Determine the speed and the distance fallen at any time after an object is dropped from rest, when air resistance is negligible. 10. Describe how air resistance affects the motion of falling ...
Document
... and planets orbit the sun. Knowing it would be controversial, he published it only shortly before his death. Click me! ...
... and planets orbit the sun. Knowing it would be controversial, he published it only shortly before his death. Click me! ...
Newton`s Second Law 2 PPT
... The man who follows the crowd will usually get no further than the crowd. The man who walks alone is likely to find himself in places no one has ever been. —Albert Einstein. ...
... The man who follows the crowd will usually get no further than the crowd. The man who walks alone is likely to find himself in places no one has ever been. —Albert Einstein. ...
Newton`s third law of motion and friction
... A 140 kg car accelerates straight along the positive x-direction. If the car accelerates at 12 m/s², what is the force of the car’s acceleration. (µ= .4) ...
... A 140 kg car accelerates straight along the positive x-direction. If the car accelerates at 12 m/s², what is the force of the car’s acceleration. (µ= .4) ...
Physics review
... the puck were traveling in a vacuum, the net external force on the puck would be zero and it would travel with constant velocity so long as its path were unobstructed. Implicit in the discussion of Newton's first law is the concept of an inertial reference frame, which for the purposes of Newtonian ...
... the puck were traveling in a vacuum, the net external force on the puck would be zero and it would travel with constant velocity so long as its path were unobstructed. Implicit in the discussion of Newton's first law is the concept of an inertial reference frame, which for the purposes of Newtonian ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws
... 1. Electric Forces -- forces caused by the interaction of electrons. Most forces we deal with are electric. For example, when you push an object you are creating electric forces between the electrons in your hand and the electrons in the object. Mechanical and frictional forces are electrical ...
... 1. Electric Forces -- forces caused by the interaction of electrons. Most forces we deal with are electric. For example, when you push an object you are creating electric forces between the electrons in your hand and the electrons in the object. Mechanical and frictional forces are electrical ...
Multiple Choice
... 1988M3 The two uniform disks shown above have equal mass, and each can rotate on frictionless bearings about a fixed axis through its center. The smaller disk has a radius R and moment of inertia I about its axis. The larger disk has a radius 2R a. Determine the moment of inertia of the larger disk ...
... 1988M3 The two uniform disks shown above have equal mass, and each can rotate on frictionless bearings about a fixed axis through its center. The smaller disk has a radius R and moment of inertia I about its axis. The larger disk has a radius 2R a. Determine the moment of inertia of the larger disk ...
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics
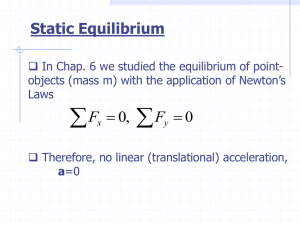
... In Chap. 6 we studied the equilibrium of pointobjects (mass m) with the application of Newton’s Laws ...
... In Chap. 6 we studied the equilibrium of pointobjects (mass m) with the application of Newton’s Laws ...