Sliders – High School Worksheet
... easy to move at the same time. Use the information about friction you just learned. In order to build a structure that is difficult to move and easy to move at the same time, I would build a structure made of a material so that it has a high coefficient of static friction but a low coefficient of ki ...
... easy to move at the same time. Use the information about friction you just learned. In order to build a structure that is difficult to move and easy to move at the same time, I would build a structure made of a material so that it has a high coefficient of static friction but a low coefficient of ki ...
Momentum - college physics
... B. The total momentum of a system is conserved when the internal forces add up to zero. C. The total momentum is conserved when there are no internal forces. D. The total momentum of a system can not be conserved it the objects are interacting. ...
... B. The total momentum of a system is conserved when the internal forces add up to zero. C. The total momentum is conserved when there are no internal forces. D. The total momentum of a system can not be conserved it the objects are interacting. ...
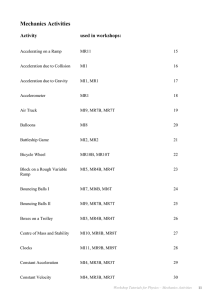
Mechanics Activities - The University of Sydney
... fluid, it looks just as it would if it were standing still. When accelerated forwards, the fluid’s surface will make an angle to the horizontal. The direction of the slope of the fluid shows you the direction of the acceleration. The fluid surface is at an angle because the net force on the fluid is ...
... fluid, it looks just as it would if it were standing still. When accelerated forwards, the fluid’s surface will make an angle to the horizontal. The direction of the slope of the fluid shows you the direction of the acceleration. The fluid surface is at an angle because the net force on the fluid is ...
F r
... Conceptualize The trophy changes its vertical position with respect to the surface of the Earth. Associated with this change in position is a change in the gravitational potential energy of the trophy–Earth system. Categorize We evaluate a change in gravitational potential energy defined in this se ...
... Conceptualize The trophy changes its vertical position with respect to the surface of the Earth. Associated with this change in position is a change in the gravitational potential energy of the trophy–Earth system. Categorize We evaluate a change in gravitational potential energy defined in this se ...
299-112-1
... where is a coefficient of proportionality (the viscosity). Aristotle’s understanding of force lacked the concepts of inertia and friction. The concept of inertia was suggested by several medieval scholars (Philoponus, Jean Buridan, Nicole Oresme, etc.), and finally Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) pos ...
... where is a coefficient of proportionality (the viscosity). Aristotle’s understanding of force lacked the concepts of inertia and friction. The concept of inertia was suggested by several medieval scholars (Philoponus, Jean Buridan, Nicole Oresme, etc.), and finally Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) pos ...
doc
... - Universal gravitation and the gravitational field - Kepler=s Laws of planetary motion - Effects near compact objects (e.g., neutron stars) ...
... - Universal gravitation and the gravitational field - Kepler=s Laws of planetary motion - Effects near compact objects (e.g., neutron stars) ...
chapter 7
... b. In a system of two or more objects, the individual objects could have linear momenta that cancel each other. In this case, the linear momentum of the system would be zero. The kinetic energies of the objects, however, are scalar quantities that are always positive; thus, the total kinetic energy ...
... b. In a system of two or more objects, the individual objects could have linear momenta that cancel each other. In this case, the linear momentum of the system would be zero. The kinetic energies of the objects, however, are scalar quantities that are always positive; thus, the total kinetic energy ...
MasteringPhysics: Assignmen
... To find the total time for spin down, just calculate when the velocity will equal zero. This is accomplished by setting the initial velocity plus the acceleration multipled by the time equal to zero and then solving for the time. One can then just subtract the time it took to reach 210 from the tota ...
... To find the total time for spin down, just calculate when the velocity will equal zero. This is accomplished by setting the initial velocity plus the acceleration multipled by the time equal to zero and then solving for the time. One can then just subtract the time it took to reach 210 from the tota ...
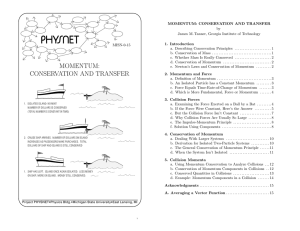
momentum: conservation and transfer
... the object we are studying implies that the object’s momentum must be changing. If you prefer to think of “the natural state” of an isolated parp/dt ticle being one of constant momentum, then you can think of F~R = d~ as stating: a changing momentum implies that other objects must be exerting a resu ...
... the object we are studying implies that the object’s momentum must be changing. If you prefer to think of “the natural state” of an isolated parp/dt ticle being one of constant momentum, then you can think of F~R = d~ as stating: a changing momentum implies that other objects must be exerting a resu ...