Physics Jeopardy - San Juan Unified School District
... Template created by Pamela Lovin/LRHS, Wake County Public Schools, South Carolina ...
... Template created by Pamela Lovin/LRHS, Wake County Public Schools, South Carolina ...
1101 Lab 8 - Oscillations
... exert when stretched, you need to know their spring constants. One book recommends a static approach, in which objects of different weights hang from the spring and the displacement from equilibrium is measured. Another book suggests a dynamic approach, in which an object hanging from the end of a s ...
... exert when stretched, you need to know their spring constants. One book recommends a static approach, in which objects of different weights hang from the spring and the displacement from equilibrium is measured. Another book suggests a dynamic approach, in which an object hanging from the end of a s ...
Final Exam
... the sum of the kinetic and gravitational potential energy is conserved during the block’s motion. We will use this conservation equation in the second part to find the minimum height the block must start from to make it around the loop. Place the origin of the coordinate system directly below the bl ...
... the sum of the kinetic and gravitational potential energy is conserved during the block’s motion. We will use this conservation equation in the second part to find the minimum height the block must start from to make it around the loop. Place the origin of the coordinate system directly below the bl ...
Slide 1
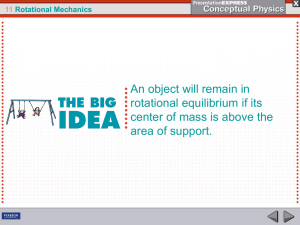
... 11.3 Center of Gravity Center of mass is often called center of gravity, the average position of all the particles of weight that make up an object. For almost all objects on and near Earth, these terms are interchangeable. There can be a small difference between center of gravity and center of mass ...
... 11.3 Center of Gravity Center of mass is often called center of gravity, the average position of all the particles of weight that make up an object. For almost all objects on and near Earth, these terms are interchangeable. There can be a small difference between center of gravity and center of mass ...
p - Effingham County Schools
... The product of the object’s mass, m, and the object’s velocity, v, is defined as the momentum of the object. Momentum is measured in kg·m/s. An object’s momentum, also known as linear momentum, is represented by the following equation: ...
... The product of the object’s mass, m, and the object’s velocity, v, is defined as the momentum of the object. Momentum is measured in kg·m/s. An object’s momentum, also known as linear momentum, is represented by the following equation: ...
AP QUIZ #5 2D MOTION AP FR Quiz #5 2D Motion
... Explain why you drew the graphs as you did and how you determined your answers. There are no forces in the horizontal direction (ignoring air resistance) so both rocks will have a constant horizontal velocity. Since Rock B is slower than Rock A, it will have a smaller horizontal velocity. Both rocks ...
... Explain why you drew the graphs as you did and how you determined your answers. There are no forces in the horizontal direction (ignoring air resistance) so both rocks will have a constant horizontal velocity. Since Rock B is slower than Rock A, it will have a smaller horizontal velocity. Both rocks ...