Torque - Studentportalen
... Acceleration of a yo-yo • We have translation and rotation, so we use Newton’s second law for the acceleration of the center of mass and the rotational analog of Newton’s second law for the angular acceleration about the center of mass. ...
... Acceleration of a yo-yo • We have translation and rotation, so we use Newton’s second law for the acceleration of the center of mass and the rotational analog of Newton’s second law for the angular acceleration about the center of mass. ...
Conceptual Questions
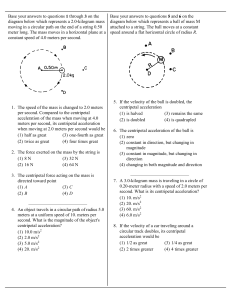
... constant of 2.0 × 106 N/m. What is the maximum compression of the spring? (Neglect the mass of the spring.) 15. The kinetic friction force between a 60.0-kg object and a horizontal surface is 50.0 N. If the initial speed of the object is 25.0 m/s, what distance will it slide before coming to a stop? ...
... constant of 2.0 × 106 N/m. What is the maximum compression of the spring? (Neglect the mass of the spring.) 15. The kinetic friction force between a 60.0-kg object and a horizontal surface is 50.0 N. If the initial speed of the object is 25.0 m/s, what distance will it slide before coming to a stop? ...
First Diploma in Engineering Mathematics for Engineering
... The following question gives the student the opportunity to gain D2 by demonstrating the ability to carry out chained calculations using an electronic calculator. Note: to achieve D2 you will need to be observed performing the chained calculations, and a witness statement will be signed. a) The forc ...
... The following question gives the student the opportunity to gain D2 by demonstrating the ability to carry out chained calculations using an electronic calculator. Note: to achieve D2 you will need to be observed performing the chained calculations, and a witness statement will be signed. a) The forc ...
Second Powerpoint
... by a net external force. The acceleration is proportional to the net force and is in the direction which the net force acts. This law is commonly applied to the vertical component of velocity. ...
... by a net external force. The acceleration is proportional to the net force and is in the direction which the net force acts. This law is commonly applied to the vertical component of velocity. ...
document
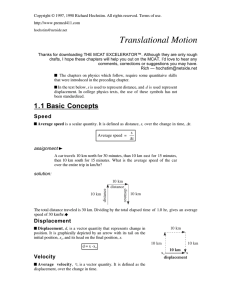
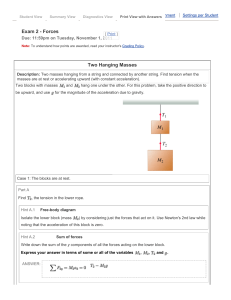
... will have on the acceleration. The 0.5 N force is applied to two 500 g carts hooked together as shown below right. ...
... will have on the acceleration. The 0.5 N force is applied to two 500 g carts hooked together as shown below right. ...
Friction notes
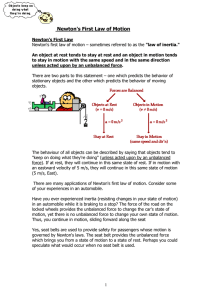
... unbalanced force. Unbalanced force causes change in speed of the object or change in the direction of the object. If unbalanced force is removed completely, the object would continue to move with the velocity it has acquired till then. Misconceptions: Movement and acceleration are not the same thing ...
... unbalanced force. Unbalanced force causes change in speed of the object or change in the direction of the object. If unbalanced force is removed completely, the object would continue to move with the velocity it has acquired till then. Misconceptions: Movement and acceleration are not the same thing ...
Physics 2211 Lecture 27
... Force of gravity acts on the object as though all the mass were located at the CM of the object. (Proof coming up!) If we pivot the object somewhere else, it will orient itself so that the CM is directly below the pivot. This fact can be used to find the CM of odd-shaped objects. ...
... Force of gravity acts on the object as though all the mass were located at the CM of the object. (Proof coming up!) If we pivot the object somewhere else, it will orient itself so that the CM is directly below the pivot. This fact can be used to find the CM of odd-shaped objects. ...
Lesson 10 notes - Angular Measurement - science
... the walls of the groove in the record friction between road and tyres component of gravity horizontal component of lift on the wings ...
... the walls of the groove in the record friction between road and tyres component of gravity horizontal component of lift on the wings ...
Instructions Grading Scheme
... Partial credit will be granted as follows: (a) If you mark only one answer and it is the correct answer, you earn 6 points. (b) If you mark two answers, one of which is the correct answer, you earn 3 points. (c) If you mark no answers, or more than two, you earn 0 points. MC3 and MC4: multiple-choic ...
... Partial credit will be granted as follows: (a) If you mark only one answer and it is the correct answer, you earn 6 points. (b) If you mark two answers, one of which is the correct answer, you earn 3 points. (c) If you mark no answers, or more than two, you earn 0 points. MC3 and MC4: multiple-choic ...
v = 2Пr ac = v2 ∑F = mac = m v2 T r r Circular Motion – Practice
... 3. A physics student swings a small rubber ball attached to a string over her head in a horizontal, circular path. The piece of string is 2.0 meters long and the ball makes 5 revolutions per second. What is the ball’s centripetal acceleration? ...
... 3. A physics student swings a small rubber ball attached to a string over her head in a horizontal, circular path. The piece of string is 2.0 meters long and the ball makes 5 revolutions per second. What is the ball’s centripetal acceleration? ...
Torque
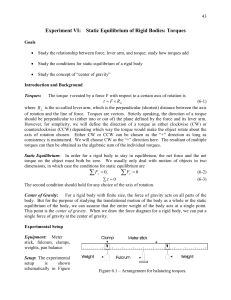
... counterclockwise (CCW) depending which way the torque would make the object rotate about the axis of rotation chosen. Either CW or CCW can be chosen as the “+” direction as long as consistency is maintained. We will choose CW as the “+” direction here. The resultant of multiple torques can then be o ...
... counterclockwise (CCW) depending which way the torque would make the object rotate about the axis of rotation chosen. Either CW or CCW can be chosen as the “+” direction as long as consistency is maintained. We will choose CW as the “+” direction here. The resultant of multiple torques can then be o ...