Differentiation of Rubella Virus Strains by Neutralization Kinetics
... neutralization (K) for six strains of rubella virus was carried out over this period of the reaction. Two particularly antibody-sensitive isolates were detected. It was noted that the three strains isolated from in utero infections were poorly neutralized by heterologous antisera when compared to po ...
... neutralization (K) for six strains of rubella virus was carried out over this period of the reaction. Two particularly antibody-sensitive isolates were detected. It was noted that the three strains isolated from in utero infections were poorly neutralized by heterologous antisera when compared to po ...
325201560337pm
... parasites, dependent upon a host for life. Bacteria can be found in three basic shapes—round, rod, or spiral. While some bacteria are capable of causing disease, most are non-infectious and many have critical roles in decay, fermentation, and nutrient recycling. Bacteria help people digest food. Som ...
... parasites, dependent upon a host for life. Bacteria can be found in three basic shapes—round, rod, or spiral. While some bacteria are capable of causing disease, most are non-infectious and many have critical roles in decay, fermentation, and nutrient recycling. Bacteria help people digest food. Som ...
Feline herpesvirus infection (2012 edition) What’s new?
... Viral excretion starts as soon as 24 hours after infection and lasts for 1 to 3 weeks. Acute disease resolves within 10 to 14 days. Some animals may develop chronic lesions in the upper respiratory tract and ocular tissues. Upon infection, the virus spreads along the sensory nerves and reaches neuro ...
... Viral excretion starts as soon as 24 hours after infection and lasts for 1 to 3 weeks. Acute disease resolves within 10 to 14 days. Some animals may develop chronic lesions in the upper respiratory tract and ocular tissues. Upon infection, the virus spreads along the sensory nerves and reaches neuro ...
IS HIV SHORTSIGHTED INSIGHTS FROM A MULTISTRAIN
... HIV seems to have evolved an intermediate level of virulence that maximizes the number of potential new infections from a single infection, known as its transmission potential (Fraser et al. 2007; Shirreff et al. 2011), thus maximizing the between-host fitness of the virus. With a higher level of vi ...
... HIV seems to have evolved an intermediate level of virulence that maximizes the number of potential new infections from a single infection, known as its transmission potential (Fraser et al. 2007; Shirreff et al. 2011), thus maximizing the between-host fitness of the virus. With a higher level of vi ...
Hepatitis viruses - University of Yeditepe Faculty of Medicine, 2011
... proteinuria, hematuria, and anuria should raise the suspicion of leptospirosis. The serum creatine phosphokinase is elevated in 50% of patients. Marked jaundice accompanied by renal dysfunction in a febrile patient with leukocytosis should raise the possibility of Weil's syndrome, a severe form of ...
... proteinuria, hematuria, and anuria should raise the suspicion of leptospirosis. The serum creatine phosphokinase is elevated in 50% of patients. Marked jaundice accompanied by renal dysfunction in a febrile patient with leukocytosis should raise the possibility of Weil's syndrome, a severe form of ...
Antiviral Activity of Favipiravir (T-705) Against Lethal Rift Valley
... Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a severe disease affecting both humans and a number of agriculturally important livestock species. The causative agent, RVF virus (RVFV), is primarily transmitted through mosquito bites, with transmission also occurring by exposure to infectious aerosols and direct contact ...
... Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a severe disease affecting both humans and a number of agriculturally important livestock species. The causative agent, RVF virus (RVFV), is primarily transmitted through mosquito bites, with transmission also occurring by exposure to infectious aerosols and direct contact ...
secondary syphilis
... spirochete Treponema pallidium, • which is transmitted mainly by direct sexual intercourse (venereal syphilis) and less commonly via placenta (congenital syphilis) or by accidental inoculation from the infectious Materials • T. Pallidum spirochetes cannot be cultured but are detected by silver stain ...
... spirochete Treponema pallidium, • which is transmitted mainly by direct sexual intercourse (venereal syphilis) and less commonly via placenta (congenital syphilis) or by accidental inoculation from the infectious Materials • T. Pallidum spirochetes cannot be cultured but are detected by silver stain ...
Infection
... parasites, dependent upon a host for life. Bacteria can be found in three basic shapes—round, rod, or spiral. While some bacteria are capable of causing disease, most are non-infectious and many have critical roles in decay, fermentation, and nutrient recycling. Bacteria help people digest food. Som ...
... parasites, dependent upon a host for life. Bacteria can be found in three basic shapes—round, rod, or spiral. While some bacteria are capable of causing disease, most are non-infectious and many have critical roles in decay, fermentation, and nutrient recycling. Bacteria help people digest food. Som ...
Chickenpox and Shingles Policy
... Adults with chickenpox may develop more severe disease and complications including pneumonia. Pregnant women are at particular risk of complications affecting the foetus/neonate which arise as a result of the mother contracting the infection. ...
... Adults with chickenpox may develop more severe disease and complications including pneumonia. Pregnant women are at particular risk of complications affecting the foetus/neonate which arise as a result of the mother contracting the infection. ...
MS Word - CL Davis Foundation
... Rx with such a narrow-spectrum antibiotic frequently results in a fatal overgrowth with Clostridium difficile. Enteritis has also been associated with other bacterial infections in this species (eg. Campylobacter, hemolytic E. coli). Histopathology: Changes associated with Lawsonia intracellularis, ...
... Rx with such a narrow-spectrum antibiotic frequently results in a fatal overgrowth with Clostridium difficile. Enteritis has also been associated with other bacterial infections in this species (eg. Campylobacter, hemolytic E. coli). Histopathology: Changes associated with Lawsonia intracellularis, ...
- IJASR International Journal of Academic Scientific
... Zika virus (ZIKAV) is a single-stranded positive RNA virus of the Flaviviridae family, it is most known for causing flaviviral infectious diseases Zika virus disease is a vector borne disease transmitted by several Aedes species such as Ae. hensilli, and Ae. Aegypti Ae. africanus, Ae. Luteocephalus. ...
... Zika virus (ZIKAV) is a single-stranded positive RNA virus of the Flaviviridae family, it is most known for causing flaviviral infectious diseases Zika virus disease is a vector borne disease transmitted by several Aedes species such as Ae. hensilli, and Ae. Aegypti Ae. africanus, Ae. Luteocephalus. ...
Norovirus infection in the home and the role of hygiene – an update
... precipitate death. Norovirus infection has put apparently healthy people in intensive care21 and has been associated with chronic diarrhoea among transplant patients22. Norovirus differs from other agents of gastroenteritis in a number of ways which can increase its significance in public health ter ...
... precipitate death. Norovirus infection has put apparently healthy people in intensive care21 and has been associated with chronic diarrhoea among transplant patients22. Norovirus differs from other agents of gastroenteritis in a number of ways which can increase its significance in public health ter ...
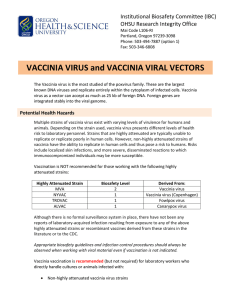
VACCINIA VIRUS and VACCINIA VIRAL VECTORS
... Other orthopox viruses that can infect humans Non-highly Attenuated Strains WR (Western Reseve) NYCBOH (strain used in vaccinia vaccine) Copenhagen Temple of Heaven Lister Cowpox ...
... Other orthopox viruses that can infect humans Non-highly Attenuated Strains WR (Western Reseve) NYCBOH (strain used in vaccinia vaccine) Copenhagen Temple of Heaven Lister Cowpox ...
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
... Young people continue to get STDs at a high rate. The age of first sexual activity is somewhat delayed compared to previous years (Finer & Philbin, 2013). Thirty percent of 15- to 16-yearolds have experienced sex compared to 16% of those younger, 48% at 17, 61% at 18, and 71% at 19. These statistics ...
... Young people continue to get STDs at a high rate. The age of first sexual activity is somewhat delayed compared to previous years (Finer & Philbin, 2013). Thirty percent of 15- to 16-yearolds have experienced sex compared to 16% of those younger, 48% at 17, 61% at 18, and 71% at 19. These statistics ...
Article The Most Common Illness: A Review and Case Study from
... inflammation, patients with asthma tend to have basally elevated ICAM-1 expression levels in the lower airways (Wegner et al., 1990). This potentially explains the strong association between cold infections and acute asthma exacerbations. Rhinovirus infections in asthma patients are known to cause m ...
... inflammation, patients with asthma tend to have basally elevated ICAM-1 expression levels in the lower airways (Wegner et al., 1990). This potentially explains the strong association between cold infections and acute asthma exacerbations. Rhinovirus infections in asthma patients are known to cause m ...
Chlamydia trachomatis, a Hidden Epidemic: Effects on Female
... factors for contracting infection include age, with those aged 15-24 most affected, gender, with females at more risk than men, and race6. ...
... factors for contracting infection include age, with those aged 15-24 most affected, gender, with females at more risk than men, and race6. ...
Oral mucosal lesions caused by infective microorganisms I. Viruses
... of 10 to 14 days. Measles remains a major cause of childhood mortality in developing countries (36). Measles is one of a group of vaccine-preventable diseases in which vaccination programs have greatly reduced its incidence. It is an acute systemic condition with a prodrome in which the patient suff ...
... of 10 to 14 days. Measles remains a major cause of childhood mortality in developing countries (36). Measles is one of a group of vaccine-preventable diseases in which vaccination programs have greatly reduced its incidence. It is an acute systemic condition with a prodrome in which the patient suff ...
How to Treat cMRSA - Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance
... abscesses and necrotising pneumonia. Certain strains of cMRSA commonly found in Australia (particularly on the east coast) frequently express PVl toxin ...
... abscesses and necrotising pneumonia. Certain strains of cMRSA commonly found in Australia (particularly on the east coast) frequently express PVl toxin ...
KeystepsTM Modular Medicine Session 1 Module 5
... Transmission and Epidemiology Infection with FCoV is endemic within the feline population as it is a highly contagious virus. The prevalence of FCoV is thought to be approximately 40% in the general cat population but this can rise to over 80% in pedigree and multicat households. However the prevale ...
... Transmission and Epidemiology Infection with FCoV is endemic within the feline population as it is a highly contagious virus. The prevalence of FCoV is thought to be approximately 40% in the general cat population but this can rise to over 80% in pedigree and multicat households. However the prevale ...
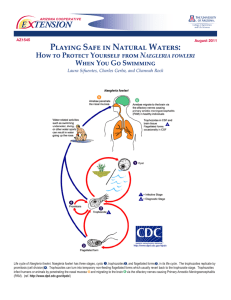
Playing Safe in Natural Waters: E TENSION Naegleria fowleri
... Because of the rarety of the infection, there isn’t substantial medical evidence at this time. Several drugs are effective against Naegleria fowleri in the laboratory and in some cases antibiotic treatment in conjunction with other experimental treatments have been shown to be effective if PAM is de ...
... Because of the rarety of the infection, there isn’t substantial medical evidence at this time. Several drugs are effective against Naegleria fowleri in the laboratory and in some cases antibiotic treatment in conjunction with other experimental treatments have been shown to be effective if PAM is de ...
Surveillance and Reporting of Infectious Disease, Healthcare
... conditions have an Infection Control (IC) alert placed on the Royal Devon & Exeter NHS Foundation Trust’s (hereafter referred to as “the Trust”) Patient Information System (PAS), on the IT system for the ‘out of hours’ GP service in Devon. Producing surveillance reports to relevant committees and gr ...
... conditions have an Infection Control (IC) alert placed on the Royal Devon & Exeter NHS Foundation Trust’s (hereafter referred to as “the Trust”) Patient Information System (PAS), on the IT system for the ‘out of hours’ GP service in Devon. Producing surveillance reports to relevant committees and gr ...
9 Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis)
... Sweet’s disease occurs most frequently on the face, neck, forearms and dorsal hands of middle-aged women. Several days to 4 weeks after upper respiratory tract infection, multiple painful and sharply circumscribed dark reddish edematous erythema 10 mm to 25 mm in diameter occur suddenly, accompanied ...
... Sweet’s disease occurs most frequently on the face, neck, forearms and dorsal hands of middle-aged women. Several days to 4 weeks after upper respiratory tract infection, multiple painful and sharply circumscribed dark reddish edematous erythema 10 mm to 25 mm in diameter occur suddenly, accompanied ...
Bacterial meningitis
... A newborn infected with group B strep bacteria can develop meningitis or other life-threatening infections soon after birth. ...
... A newborn infected with group B strep bacteria can develop meningitis or other life-threatening infections soon after birth. ...
Evolving Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Virus in the United States
... the past 2 decades, chronic infection in 3 million or more residents now accounts for more disease and death in the United States than does human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/AIDS. Current trends in the epidemiology of HCV infection include an apparent increase in young, often suburban heroin injecti ...
... the past 2 decades, chronic infection in 3 million or more residents now accounts for more disease and death in the United States than does human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/AIDS. Current trends in the epidemiology of HCV infection include an apparent increase in young, often suburban heroin injecti ...
Factors Causing Uterine Infections in Cattle
... experienced an 8 percent reduction in first service conception rate compared with herdmates that were not infected. This effect would likely have been more severe if the herds had not been participating in a routine herd health program in which uterine infections and other postpartum reproductive pr ...
... experienced an 8 percent reduction in first service conception rate compared with herdmates that were not infected. This effect would likely have been more severe if the herds had not been participating in a routine herd health program in which uterine infections and other postpartum reproductive pr ...
Herpes simplex
.jpg?width=300)
Herpes simplex (Greek: ἕρπης herpēs, ""creeping"" or ""latent"") is a viral disease caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Other disorders caused by herpes simplex include: herpetic whitlow when it involves the fingers, herpes of the eye, herpes infection of the brain, and neonatal herpes when it affects a newborn, among others.There are two types of herpes simplex virus, type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 more commonly causes oral infections while HSV-2 more commonly causes genital infections. They are transmitted by direct contact with body fluids or lesions of an infected individual. Transmission may still occur when symptoms are not present. Genital herpes is classified as a sexually transmitted infection. It may be spread to an infant during childbirth. After infection, the viruses are transported along sensory nerves to the nerve cell bodies, where they reside lifelong. Causes of recurrence may include: decreased immune function, stress, and sunlight exposure. Oral and genital herpes is usually diagnosed based on the presenting symptoms. The diagnosis may be confirmed by viral culture or detecting herpes DNA in fluid from blisters. Testing the blood for antibodies against the virus can confirm a previous infection but will be negative in new infections.The most effective method of avoiding genital infections is by avoiding vaginal, oral and anal sex. Condom use decreases the risk somewhat. Daily antiviral medication taken by someone who has the infection can also reduce spread. There is no available vaccine and once infected, there is no cure. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) and topical lidocaine may be used to help with the symptoms. Treatments with antiviral medication such as aciclovir or valaciclovir can lessen the severity of symptomatic episodes.Worldwide rates of either HSV-1 or HSV-2 are between 60% and 95% in adults. HSV-1 is usually acquired during childhood. Rates of both increase as people age. Rates of HSV-1 are between 70% and 80% in populations of low socioeconomic status and 40% to 60% in populations of improved socioeconomic status. An estimated 536 million people worldwide (16% of the population) were infected with HSV-2 as of 2003 with greater rates among women and those in the developing world. Most people with HSV-2 do not realize that they are infected.