Quantum entropy and its use
... Entropy is a central quantity in information theory, probability and physics. This spring school will focus on fundamental concepts and basic operational interpretations of entropy with a particular focus on applications to quantum mechanics. The goal is provide a thorough overview ranging from fund ...
... Entropy is a central quantity in information theory, probability and physics. This spring school will focus on fundamental concepts and basic operational interpretations of entropy with a particular focus on applications to quantum mechanics. The goal is provide a thorough overview ranging from fund ...
Electron Configurations
... • According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle we can not know the exact position and motion of electrons with complete certainty. • We can only describe the probable locations of electrons. • We will describe the location of electrons when the atom is at its lowest energy . • These are called ...
... • According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle we can not know the exact position and motion of electrons with complete certainty. • We can only describe the probable locations of electrons. • We will describe the location of electrons when the atom is at its lowest energy . • These are called ...
Chapter 8 - Bakersfield College
... C. Lasers use materials whose atoms have metastable states, which are excited states with relatively long lifetimes. 1. Ruby lasers use xenon-filled flash lamps to excite chromium ions in ruby rods. 2. Helium-neon lasers use an electric discharge to bring the atoms of the gas mixture to metastable l ...
... C. Lasers use materials whose atoms have metastable states, which are excited states with relatively long lifetimes. 1. Ruby lasers use xenon-filled flash lamps to excite chromium ions in ruby rods. 2. Helium-neon lasers use an electric discharge to bring the atoms of the gas mixture to metastable l ...
Chapter 7
... According to classical physics, particles move in a path determined by the particle’s velocity, position, and forces acting on it ◦ determinacy = definite, predictable future ...
... According to classical physics, particles move in a path determined by the particle’s velocity, position, and forces acting on it ◦ determinacy = definite, predictable future ...
Quantum Number, n. - Lyndhurst Schools
... • Colors from excited gases arise because electrons move between energy states in the atom. (Electronic Transition) ...
... • Colors from excited gases arise because electrons move between energy states in the atom. (Electronic Transition) ...
powerpoint slides
... smaller. Soon they will be so small that they will be directly subject to quantum rules. This is both a problem and an opportunity. We will be looking at the opportunity. ...
... smaller. Soon they will be so small that they will be directly subject to quantum rules. This is both a problem and an opportunity. We will be looking at the opportunity. ...
Gravity and Quantum Mechanics
... Applying the existing theories of Quantum Mechanics plus General Relativity gives a nonsense answer, an infinite rate of scattering. The correct theory must cure this, but it is a very difficult problem. It turns out that one can fix it if particles are not points but strings, Planck energy ...
... Applying the existing theories of Quantum Mechanics plus General Relativity gives a nonsense answer, an infinite rate of scattering. The correct theory must cure this, but it is a very difficult problem. It turns out that one can fix it if particles are not points but strings, Planck energy ...
They survive monitoring by the environment to leave `descendants
... "Decoherence selects out of the quantum 'mush' states that are stable, that can withstand the scrutiny of the environment without getting perturbed," says Zurek. These special states are called 'pointer states', and although they are still quantum states, they turn out to look like classical ones. F ...
... "Decoherence selects out of the quantum 'mush' states that are stable, that can withstand the scrutiny of the environment without getting perturbed," says Zurek. These special states are called 'pointer states', and although they are still quantum states, they turn out to look like classical ones. F ...
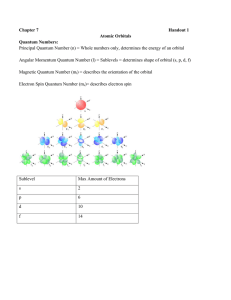
Chapter 7 Handout 1 Atomic Orbitals Quantum Numbers: Principal
... Electron Configuration Notation: ...
... Electron Configuration Notation: ...