State
... – An area with fixed boundaries – Can change because of war, purchase, annexation • Sovereignty – Absolute authority, within its territorial boundaries ...
... – An area with fixed boundaries – Can change because of war, purchase, annexation • Sovereignty – Absolute authority, within its territorial boundaries ...
The Institutionalist Paradigm
... The Institutionalist Paradigm (Liberal Institutionalism) The Institutional Foundation of International Politics ...
... The Institutionalist Paradigm (Liberal Institutionalism) The Institutional Foundation of International Politics ...
International Relations and the First Great Debate edited by Brian
... Second World War. It is during this period that the IR traditional historiography affirms that realist scholars, such as E. H. Carr and Hans Morgenthau, had an intellectual confrontation with ‘idealists’ (i.e. what is conventionally called in the discipline the ‘first great debate’) and successfully ...
... Second World War. It is during this period that the IR traditional historiography affirms that realist scholars, such as E. H. Carr and Hans Morgenthau, had an intellectual confrontation with ‘idealists’ (i.e. what is conventionally called in the discipline the ‘first great debate’) and successfully ...
John Heathershaw Department of International Relations, London
... John Heathershaw Department of International Relations, London School of Economics and Political Science j.d.heathershaw@lse.ac.uk ...
... John Heathershaw Department of International Relations, London School of Economics and Political Science j.d.heathershaw@lse.ac.uk ...
Seventh Semester - ITAM
... History of International Relations I Economics II Pol. & Social Ideas and Institutions II Problems of Contemporary Civ. II Mathematics I Computer Science I ...
... History of International Relations I Economics II Pol. & Social Ideas and Institutions II Problems of Contemporary Civ. II Mathematics I Computer Science I ...
WWI Interpreted
... such as the claim that the European powers chose to go to war with each other in order to quell unrest among their own populations, which at that time is becoming more and more politically fragmented. As Alexander Wendt states in his article “Anarchy is what States Make of It”, “All theories of int ...
... such as the claim that the European powers chose to go to war with each other in order to quell unrest among their own populations, which at that time is becoming more and more politically fragmented. As Alexander Wendt states in his article “Anarchy is what States Make of It”, “All theories of int ...
HST 10: International Relations in Historical
... Relations theory;” Mueller, Quiet Cataclysm; Hogan, The End of the Cold War; and Katzenstein, The Culture of National Security, preface and introduction. For scholarly work on the democratic peace, see Cederman, “Back to Kant;” Doyle, “Kant and Liberal Internationalism” and “Liberalism and World Po ...
... Relations theory;” Mueller, Quiet Cataclysm; Hogan, The End of the Cold War; and Katzenstein, The Culture of National Security, preface and introduction. For scholarly work on the democratic peace, see Cederman, “Back to Kant;” Doyle, “Kant and Liberal Internationalism” and “Liberalism and World Po ...
The Theory of Realism
... •Realists believe that power imbalances lead to war since powerful states, unchecked, will try to acquire more power. •Balancing by forming alliances with other states is the quickest way to check the power of potentially aggressive states. ...
... •Realists believe that power imbalances lead to war since powerful states, unchecked, will try to acquire more power. •Balancing by forming alliances with other states is the quickest way to check the power of potentially aggressive states. ...
International relations theory in policy debate
... Can troop reduction lead to relative gains for the United ...
... Can troop reduction lead to relative gains for the United ...
resumé-du-cours_realisme
... In 2000, when many analysts believed that realism ended with the end of the cold war, Waltz argued the contrary. He believed it is not the development of institutions or of democracy that would end the balance of power between states. Do democracies are really more peaceful? Do institutions are stro ...
... In 2000, when many analysts believed that realism ended with the end of the cold war, Waltz argued the contrary. He believed it is not the development of institutions or of democracy that would end the balance of power between states. Do democracies are really more peaceful? Do institutions are stro ...
Name of your country
... international organizations etc.) compete and cooperate, providing some order in international politics. Two main views of sources of governance or order • “Realism” – focus on competition and power • “Liberal-Internationalism” – focus on institutions, laws and values as basis of order ...
... international organizations etc.) compete and cooperate, providing some order in international politics. Two main views of sources of governance or order • “Realism” – focus on competition and power • “Liberal-Internationalism” – focus on institutions, laws and values as basis of order ...
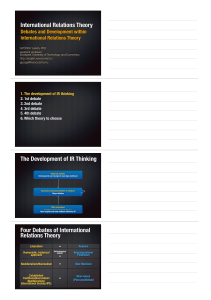
International Relations Theory The Development of IR Thinking Four
... credit is concentrated. The growth of the nation, therefore, and all our activities are in the hands of a few men. We have come to be one of the worst ruled, one of the most completely controlled and dominated Governments in the civilized world no longer a Government by free opinion, no longer a Gov ...
... credit is concentrated. The growth of the nation, therefore, and all our activities are in the hands of a few men. We have come to be one of the worst ruled, one of the most completely controlled and dominated Governments in the civilized world no longer a Government by free opinion, no longer a Gov ...
The Realist Paradigm- Hans Morgenthau
... Politics is an autonomous sphere, independent of economics and personal morality International politics is about national interests though these interests reflect the political and cultural context within which foreign policy is formulated The political ethics is different from the universal moral p ...
... Politics is an autonomous sphere, independent of economics and personal morality International politics is about national interests though these interests reflect the political and cultural context within which foreign policy is formulated The political ethics is different from the universal moral p ...
Actors in IR
... What are transnational relations? Transnational relations are regular social interactions across boundaries when at least one actor is a non-state entity. The role of transnationalism Transnational relations help non-state actors to increase their power and influence change across the world. Domesti ...
... What are transnational relations? Transnational relations are regular social interactions across boundaries when at least one actor is a non-state entity. The role of transnationalism Transnational relations help non-state actors to increase their power and influence change across the world. Domesti ...
1. A) Classical realism states that it is fundamentally the nature of
... A) Classical realism states that it is fundamentally the nature of humans that pushes states and individuals to act in a way that places interests over ideologies. Seeks to explain international politics as a result of human nature. ...
... A) Classical realism states that it is fundamentally the nature of humans that pushes states and individuals to act in a way that places interests over ideologies. Seeks to explain international politics as a result of human nature. ...
PhD - Political Science
... means of warfare? Select one such norm: explain where it came from, how it spread through the international system, and became accepted by (most) states. Second, do norms actually shape the behavior of states with regard to a stigmatized or proscribed means of force? If so, how? Give concrete histor ...
... means of warfare? Select one such norm: explain where it came from, how it spread through the international system, and became accepted by (most) states. Second, do norms actually shape the behavior of states with regard to a stigmatized or proscribed means of force? If so, how? Give concrete histor ...
what is theory? - WW Norton & Company
... Waltz, Theory of International Politics • Structure of the international system determines state behavior • System lacks an overarching authority • Importance of distribution of capabilities of states • Balance of power among states is determined by structure of the system • International cooperatio ...
... Waltz, Theory of International Politics • Structure of the international system determines state behavior • System lacks an overarching authority • Importance of distribution of capabilities of states • Balance of power among states is determined by structure of the system • International cooperatio ...
International Relations
... determined by the size of its territory • human nature is essentially good • states acts like rational individuals in pursuing national interests ...
... determined by the size of its territory • human nature is essentially good • states acts like rational individuals in pursuing national interests ...
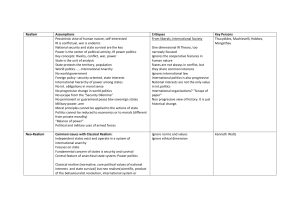
Realism Assumptions Critiques Key Persons Pessimistic view of
... • Socialist Feminism: Focus on economic equality. Same working conditions, payment and social rights. • Radical Feminism: 1960s. Not just a matter of inequality. It claims not only equality but liberation in all levels of society (public realm, family rel). State should regulate both public and priv ...
... • Socialist Feminism: Focus on economic equality. Same working conditions, payment and social rights. • Radical Feminism: 1960s. Not just a matter of inequality. It claims not only equality but liberation in all levels of society (public realm, family rel). State should regulate both public and priv ...
Liberalism - R. Allen Bolar
... Are the realists correct? Does the realist view of international politics match ...
... Are the realists correct? Does the realist view of international politics match ...
Course Outline - Pima Community College
... Describe the various approaches to the study of international relations. Differentiate a number of historic and contemporary international systems. Demonstrate the ability to describe the actors of international systems. Explain foreign policies of international actors. Examine the major forms of in ...
... Describe the various approaches to the study of international relations. Differentiate a number of historic and contemporary international systems. Demonstrate the ability to describe the actors of international systems. Explain foreign policies of international actors. Examine the major forms of in ...
AAA 15) Constructivism in International Relations
... shaping international relations Whether IR take place in an anarchical system of states or a legally ordered society of states is a function of divergent or convergent national identities ...
... shaping international relations Whether IR take place in an anarchical system of states or a legally ordered society of states is a function of divergent or convergent national identities ...
GREAT DEBATES IN INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS THEORY
... The battle lines were drawn between the likes of Hedley Bull on the Traditionalist side, and Morton Kaplan on the Behaviouralist. There were other recognizable figures on either side, such as Carr and Schelling, as well as divisions within opposing camps, but Bull and Kaplan’s arguments get to the h ...
... The battle lines were drawn between the likes of Hedley Bull on the Traditionalist side, and Morton Kaplan on the Behaviouralist. There were other recognizable figures on either side, such as Carr and Schelling, as well as divisions within opposing camps, but Bull and Kaplan’s arguments get to the h ...
LECTURE 1 What is International Relations and what is its
... progress and human possibilities." From the realist perspective, incompatible goals and conflict are the defining features of world politics. Without enforceable international rules, decision makers have little choice but to compete with other states for security, status, and wealth. The competition ...
... progress and human possibilities." From the realist perspective, incompatible goals and conflict are the defining features of world politics. Without enforceable international rules, decision makers have little choice but to compete with other states for security, status, and wealth. The competition ...
International relations

International relations (IR) or international affairs, depending on academic institution, is either a field of political science or an interdisciplinary academic field similar to global studies, in which students take a variety of internationally focused courses in social science and humanities disciplines. In both cases, the field studies relationships among countries, the roles of sovereign states, inter-governmental organizations (IGOs), international non-governmental organizations (INs), non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and multinational corporations (MNCs). International relations is an academic and a public policy field, and so can be positive and normative, because it analyzes and formulates the foreign policy of a given State.As political activity, international relations dates from the time of the Greek historian Thucydides (c. 460–395 BC), and, in the early 20th century, became a discrete academic field (No. 5901 in the 4-digit UNESCO Nomenclature) within political science. In practice International Relations and International Affairs forms a separate academic program or field from Political Science, and the courses taught therein are highly interdisciplinary.For example, international relations draws from the fields of: technology and engineering, economics, history, and international law, philosophy, geography, social work, sociology, anthropology, criminology, psychology, gender studies, cultural studies, culturology, diplomacy. The scope of international relations comprehends globalization, diplomatic relations, state sovereignty, international security, ecological sustainability, nuclear proliferation, nationalism, economic development, global finance, as well as terrorism and organized crime, human security, foreign interventionism, and human rights, as well, as, more recently, comparative religion.