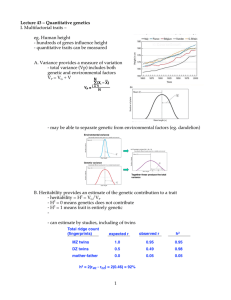
1 Lecture 43 â Quantitative genetics I. Multifactorial traits â eg
... - H2 = 0 means genetics does not contribute - H2 = 1 means trait is entirely genetic - can estimate by studies, including of twins ...
... - H2 = 0 means genetics does not contribute - H2 = 1 means trait is entirely genetic - can estimate by studies, including of twins ...
MOLECULAR MARKERS APPLICATION FOR GENETIC RESOURCES CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFERENT PLANT SPECIES
... identification and verification of old and new collected genotypes; detection of duplicates; genetic purity analysis; genetic diversity analysis; construction of „core collection“ and selection of interesting, gene resources; monitoring of viability and health and genetic changes due to long-term st ...
... identification and verification of old and new collected genotypes; detection of duplicates; genetic purity analysis; genetic diversity analysis; construction of „core collection“ and selection of interesting, gene resources; monitoring of viability and health and genetic changes due to long-term st ...
Informed consent.
... genetic alteration to explain the disease and there is still a medical indication, it may be possible to extend the study to include additional genes or even the complete exome (WES), if patient agrees. In those cases that do not show any specific diagnosis, the application of WES could be directly ...
... genetic alteration to explain the disease and there is still a medical indication, it may be possible to extend the study to include additional genes or even the complete exome (WES), if patient agrees. In those cases that do not show any specific diagnosis, the application of WES could be directly ...
Study Guide:
... Incomplete Dominance Sex Determination Carrier Pedigree Blood Types DNA fingerprinting Ethics ...
... Incomplete Dominance Sex Determination Carrier Pedigree Blood Types DNA fingerprinting Ethics ...
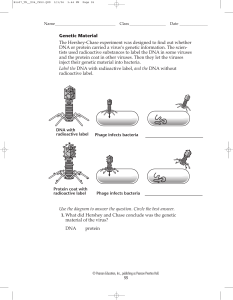
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to find out whether DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic mater ...
... Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to find out whether DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic mater ...
UNIT I: INTRODUCTION
... transmission of characters from parents to offspring. The term genetics was coined by Bateson in 1906. It has been derived from the Greek word ‘gene’. (gene= ‘to become’) ...
... transmission of characters from parents to offspring. The term genetics was coined by Bateson in 1906. It has been derived from the Greek word ‘gene’. (gene= ‘to become’) ...
Genetic Diseases & Disorders
... Tay-Sachs disease— Recessive disorder more common in among Jewish, causes a build up of lipids in the brain cells ...
... Tay-Sachs disease— Recessive disorder more common in among Jewish, causes a build up of lipids in the brain cells ...
Mendelian Genetics
... • evaluate the possible impact of biotechnology on the individual, society, and the environment, including medical and ethical issues, such as: ...
... • evaluate the possible impact of biotechnology on the individual, society, and the environment, including medical and ethical issues, such as: ...
PROCESS OF EVOLUTION I Evolution in a Genetic Context
... 5. No selection (all genotypes are equally important) If these conditions are met there will be no evolution The last two are the main causes of evolution ...
... 5. No selection (all genotypes are equally important) If these conditions are met there will be no evolution The last two are the main causes of evolution ...
Lesson 7: Genetic Disorders & Gene Therapy
... • Should blood relatives be warned? • Should our genetics be part of our records? • Should employers be allowed to consider genetically based diseases in hiring employees? • Will eugenics (manipulation of the hereditary qualities of a race) be practiced? ...
... • Should blood relatives be warned? • Should our genetics be part of our records? • Should employers be allowed to consider genetically based diseases in hiring employees? • Will eugenics (manipulation of the hereditary qualities of a race) be practiced? ...
Genetically Modified Organisms in Our Food and on Our Farms
... the natural order of things? Darwin’s understanding of Natural Selection, Mendel’s crossing sweet peas to produce predictable results, and now scientists creating genetic modification by transferring genesfrom one species to another have all led to protests from outside and sometimes within the scie ...
... the natural order of things? Darwin’s understanding of Natural Selection, Mendel’s crossing sweet peas to produce predictable results, and now scientists creating genetic modification by transferring genesfrom one species to another have all led to protests from outside and sometimes within the scie ...
Genetic Modification - Christians in Science
... adding a small number of genes (often just one) to the chromosomes of that organism. In more recent developments it can also mean changing the ways in which genes are controlled, for example by altering their ‘on-off’ switches or by knocking individual genes Animal GM followed within a few years. ou ...
... adding a small number of genes (often just one) to the chromosomes of that organism. In more recent developments it can also mean changing the ways in which genes are controlled, for example by altering their ‘on-off’ switches or by knocking individual genes Animal GM followed within a few years. ou ...
the title overview
... HS-LS3-2. Make and defend a claim based on evidence that inheritable genetic variations may result from: (1) new genetic combinations through meiosis, (2) viable errors occurring during replication, and/or (3) mutations caused by environmental factors. HS-LS3-3. Apply concepts of statistics and prob ...
... HS-LS3-2. Make and defend a claim based on evidence that inheritable genetic variations may result from: (1) new genetic combinations through meiosis, (2) viable errors occurring during replication, and/or (3) mutations caused by environmental factors. HS-LS3-3. Apply concepts of statistics and prob ...
Genetics of Complex Disease - Association for Molecular Pathology
... general, the higher the value, the stronger the genetic component. • Values can be used to estimate the number of genes under different genetic models. • Note that the magnitude of the estimate is very dependent on the frequency in the population. For example, a common disorder may have frequency es ...
... general, the higher the value, the stronger the genetic component. • Values can be used to estimate the number of genes under different genetic models. • Note that the magnitude of the estimate is very dependent on the frequency in the population. For example, a common disorder may have frequency es ...
Genetic Algorithm
... evaluate the starting position and store it as best repeat generate a new random position evaluate the new position if the new position is better than the best found so far – store the new position as the best ...
... evaluate the starting position and store it as best repeat generate a new random position evaluate the new position if the new position is better than the best found so far – store the new position as the best ...
Genetic Algorithm
... evaluate the starting position and store it as best repeat generate a new random position evaluate the new position if the new position is better than the best found so far – store the new position as the best ...
... evaluate the starting position and store it as best repeat generate a new random position evaluate the new position if the new position is better than the best found so far – store the new position as the best ...
Document
... Definition: two different organisms’ DNA put together in the same DNA strand. Example – Human DNA is cut by a restriction enzyme. Bacteria DNA is inserted into the cut. This makes a transgenic organism. ...
... Definition: two different organisms’ DNA put together in the same DNA strand. Example – Human DNA is cut by a restriction enzyme. Bacteria DNA is inserted into the cut. This makes a transgenic organism. ...
PPT
... cff DNA can be detected in plasma of pregnant woman cff DNA only makes up about 5% of total cell free DNA extracted most common from the mother cff DNA derived from the placenta Can be detected as early as 5 weeks of gestation Rapidly cleared after delivery Cell free fetal RNA (cff RNA) ...
... cff DNA can be detected in plasma of pregnant woman cff DNA only makes up about 5% of total cell free DNA extracted most common from the mother cff DNA derived from the placenta Can be detected as early as 5 weeks of gestation Rapidly cleared after delivery Cell free fetal RNA (cff RNA) ...
Changing Allele Frequencies
... – Founded by 2 individuals in the 1930’s – 50% of all fumarate deficiency Mental retardation, seizures, coma ...
... – Founded by 2 individuals in the 1930’s – 50% of all fumarate deficiency Mental retardation, seizures, coma ...