Otitis Externa - Developing Anaesthesia
... Acute otitis externa may spread to the pinna, resulting in a chondritis, particularly in diabetics or patients with newly pierced ears. Clinical Features Diagnosis is usually obvious on clinical grounds. Purulent otitis media with perforation of the tympanic membrane and drainage may occasionally ma ...
... Acute otitis externa may spread to the pinna, resulting in a chondritis, particularly in diabetics or patients with newly pierced ears. Clinical Features Diagnosis is usually obvious on clinical grounds. Purulent otitis media with perforation of the tympanic membrane and drainage may occasionally ma ...
(GMO) Manual: Clinical Section
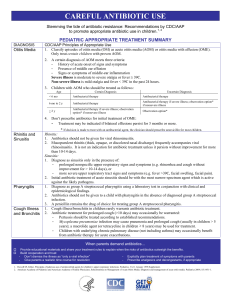
... Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphlococcus aureus. Amoxacillin, followed by Augmentin or Pediazole, are the first line drugs of choice. Second or third-line agents for persistent infection include second or third generation cephalosporins and the macrolides including Biaxin and Zithromax. Other effect ...
... Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphlococcus aureus. Amoxacillin, followed by Augmentin or Pediazole, are the first line drugs of choice. Second or third-line agents for persistent infection include second or third generation cephalosporins and the macrolides including Biaxin and Zithromax. Other effect ...
CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA
... the ambient air. The result is known as atelectasis, i.e. the tissues of the middle ear begin absorbing the air in the middle ear. Atelectasis leads to a displacement of the drum inward, i.e. a drum retraction. Following retraction, several kinds of fluid, know as effusion, can collect in the middle ...
... the ambient air. The result is known as atelectasis, i.e. the tissues of the middle ear begin absorbing the air in the middle ear. Atelectasis leads to a displacement of the drum inward, i.e. a drum retraction. Following retraction, several kinds of fluid, know as effusion, can collect in the middle ...
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)
... treatment of chronic OME may prevent middle ear complications, such as atelectatic tympanic membrane, permanent conductive hearing loss, cholesteatoma, etc. Medical treatment options for OME are generally ineffective. Antibiotics may hasten the resolution of OME in only 14 per cent of cases.1,2 Othe ...
... treatment of chronic OME may prevent middle ear complications, such as atelectatic tympanic membrane, permanent conductive hearing loss, cholesteatoma, etc. Medical treatment options for OME are generally ineffective. Antibiotics may hasten the resolution of OME in only 14 per cent of cases.1,2 Othe ...
Otitis Media – Fluid In The Ear What is Otitis Media? Otitis media is
... causing symptoms such as a plugged feeling, ear ringing/buzzing, slight hearing loss and pressure without infection. Acute otitis media (AOM) is fluid that is infected in the middle ear possibly causing symptoms of pain, discharge, inflammation, plugged feeling, ear ringing/buzzing, and slight heari ...
... causing symptoms such as a plugged feeling, ear ringing/buzzing, slight hearing loss and pressure without infection. Acute otitis media (AOM) is fluid that is infected in the middle ear possibly causing symptoms of pain, discharge, inflammation, plugged feeling, ear ringing/buzzing, and slight heari ...
Exam questions list in Oto-rhino
... Acute purulent otitis media. Acute otitis media in infectious diseases. Acute otitis media in infants and young children. Streptococcus Mucosus Otitis. Aerootitis. Facial nerve paralysis. Mastoiditis. Kinds. Gradenigo syndrome. Mastoidit with exteriorisation on the temporal bone. Chronic mastoiditis ...
... Acute purulent otitis media. Acute otitis media in infectious diseases. Acute otitis media in infants and young children. Streptococcus Mucosus Otitis. Aerootitis. Facial nerve paralysis. Mastoiditis. Kinds. Gradenigo syndrome. Mastoidit with exteriorisation on the temporal bone. Chronic mastoiditis ...
Blocked or Painful Ears. Wax and Otitis Media
... prompt treatment hearing loss or vertigo refer if canal occluded by Urgent referral debris or oedema Refer early if in any doubt. Perforation Do not blindly reassure the specialist referral patient, check (it usually heals) Canal wall bleeding bicarbonate drops follow up to ensure clot clears ...
... prompt treatment hearing loss or vertigo refer if canal occluded by Urgent referral debris or oedema Refer early if in any doubt. Perforation Do not blindly reassure the specialist referral patient, check (it usually heals) Canal wall bleeding bicarbonate drops follow up to ensure clot clears ...
Tonsillectomy or Grommet Insertion
... Child has speech or language problems or child has developmental problems or child has significant behavioural problems and her persistent bilateral otitis media with effusion Severe otalgia in otitis media requiring admission, and unresolved with conservative treatment over 3 days Review Date: Apri ...
... Child has speech or language problems or child has developmental problems or child has significant behavioural problems and her persistent bilateral otitis media with effusion Severe otalgia in otitis media requiring admission, and unresolved with conservative treatment over 3 days Review Date: Apri ...
Acute Otitis Media
... Lowered Resistance in malnutrition and anemia In early onset type: Short period breastfeeding and long time group child care Eustachian tube deformity, adenoid hypertrophy Septal deviation, cleft palate, sinusitis ...
... Lowered Resistance in malnutrition and anemia In early onset type: Short period breastfeeding and long time group child care Eustachian tube deformity, adenoid hypertrophy Septal deviation, cleft palate, sinusitis ...
Otitis media

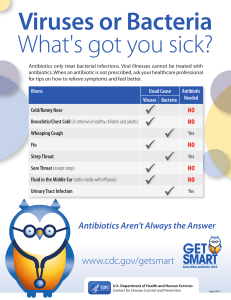
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of abrupt onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. OME is typically not associated with symptoms. Occasionally a feeling of fullness is described. It is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear for more than three months. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation of greater than two weeks that results in episodes of discharge from the ear. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three may be associated with hearing loss. The hearing loss in OME, due to its chronic nature, may affect a child's ability to learn.The cause of AOM is related to childhood anatomy and immune function. Either bacteria or viruses may be involved. Risk factors include: exposure to smoke, use of pacifiers, and attending daycare. It occurs more commonly in those who are Native American or who have Down syndrome. OME frequently occurs following AOM but may also be related to viral upper respiratory infections, irritants such as smoke, or allergies. Looking at the eardrum is important for making the correct diagnosis. Signs of AOM include bulging or a lack of movement of the tympanic membrane from a puff of air. New discharge not related to otitis externa also indicates the diagnosis.A number of measures decrease the risk of otitis media including: pneumococcal and influenza vaccination, exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, and avoiding tobacco smoke. In those with otitis media with effusion antibiotics do not generally speed recovery. The use of pain medications for AOM is important. This may include: paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, benzocaine ear drops, or opioids. In AOM, antibiotics may speed recovery but may result in side effects. Antibiotics are often recommended in those with severe disease or under two years old. In those with less severe disease they may only be recommended in those who do not improve after two or three days. The initial antibiotic of choice is typically amoxicillin. In those with frequent infections tympanostomy tubes may decrease recurrence.Worldwide AOM affect about 11% of people a year (about 710 million cases). Half the cases involve children less than five years of age and it is more common among males. Of those affected about 4.8% or 31 million develop chronic suppurative otitis media. Before the age of ten OME affects about 80% of children at some point in time. Otitis media resulted in 2,400 deaths in 2013 – down from 4,900 deaths in 1990.