Unit 2: Using Algebra and Graphs to Describe Relationships
... Learning Goal 2.3 • The domain and range of a function may be continuous or discrete depending on the situation. – If a variable can take all values within some interval it is called a continuous variable. • For example, distance traveled as a function of time is a continuous function since there w ...
... Learning Goal 2.3 • The domain and range of a function may be continuous or discrete depending on the situation. – If a variable can take all values within some interval it is called a continuous variable. • For example, distance traveled as a function of time is a continuous function since there w ...
MATH103
... The x-coordinate indicates the point’s distance to the right of, left of, or on the y-axis. Similarly, the y-coordinate of a point indicates its distance above, below, or on the x-axis. The signs of the x- and ycoordinates are shown in the figure for each quadrant. We refer to the point correspondin ...
... The x-coordinate indicates the point’s distance to the right of, left of, or on the y-axis. Similarly, the y-coordinate of a point indicates its distance above, below, or on the x-axis. The signs of the x- and ycoordinates are shown in the figure for each quadrant. We refer to the point correspondin ...
Specifying Domain and Range
... Specifying Domain and Range Domain and Range Describing the domain and range of a function is a common task and an important part of mathematical vocabulary. As you study various functions and examine various graphs and their symbolic representations you will be expected to give the domain and range ...
... Specifying Domain and Range Domain and Range Describing the domain and range of a function is a common task and an important part of mathematical vocabulary. As you study various functions and examine various graphs and their symbolic representations you will be expected to give the domain and range ...
Math 2415 – Calculus III Calculus
... Alternate Edition with EWA, James Stewart Brooks Cole; 8th edition; ISBN-13: 978-1285741550 ...
... Alternate Edition with EWA, James Stewart Brooks Cole; 8th edition; ISBN-13: 978-1285741550 ...
4.6: Formalizing Relations and Functions
... represented as a set of ordered pairs (x, y). In this case, the domain is the set of x-values and the range is the set of y-values. ...
... represented as a set of ordered pairs (x, y). In this case, the domain is the set of x-values and the range is the set of y-values. ...
12-14-15-Intro to Relations-domain
... Name the Domain and Range The following set of ordered pairs has a limited number of points. ...
... Name the Domain and Range The following set of ordered pairs has a limited number of points. ...
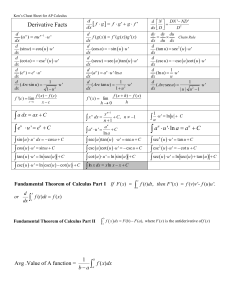
Ken`s Cheat Sheet 2014 Version 11 by 17
... For a limit to exist, the left and right hand limits must agree (be equal) V R r dx ...
... For a limit to exist, the left and right hand limits must agree (be equal) V R r dx ...
Chapter 1
... Use the Intermediate Value Theorem to show that the polynomial function f (x) = x 3 + 2x -1 has a zero in the interval [0, 1]. First Note that f is continuous on the closed interval [0, 1]. Then plug in the endpoints into the function. Since the function goes from negative to positive, ZERO has to e ...
... Use the Intermediate Value Theorem to show that the polynomial function f (x) = x 3 + 2x -1 has a zero in the interval [0, 1]. First Note that f is continuous on the closed interval [0, 1]. Then plug in the endpoints into the function. Since the function goes from negative to positive, ZERO has to e ...
Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts and Calculus Review
... When confronted with a computation that cannot be done exactly, we often replace that relevant function with something simpler that approximates it, and carry out the computation exactly on the simple approximation. ...
... When confronted with a computation that cannot be done exactly, we often replace that relevant function with something simpler that approximates it, and carry out the computation exactly on the simple approximation. ...