Inheritance 1 - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... (iii) Using the Punnett square, calculate the probability that individuals C and D could have a child with haemophilia. ...
... (iii) Using the Punnett square, calculate the probability that individuals C and D could have a child with haemophilia. ...
Mapping Complex Genetic Traits in Humans: New Methods Using A Complete RFLP Linkage Map.
... protein complex by mutation in the structural gene for any subunit, although other possibilities (including regulatory genes, posttranslational modifications, etc.) are not hard to imagine. For example, hereditary methemoglobinemia, once thought to be a homogeneous clinical entity, can be produced b ...
... protein complex by mutation in the structural gene for any subunit, although other possibilities (including regulatory genes, posttranslational modifications, etc.) are not hard to imagine. For example, hereditary methemoglobinemia, once thought to be a homogeneous clinical entity, can be produced b ...
Genetics and Heredity
... It was discovered that Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes during sexual life cycles. ...
... It was discovered that Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes during sexual life cycles. ...
Genetics Disorder Grading Rubric
... How the disorder is inherited Is it sex-linked? Is there a particular chromosome it is located on? Is it recessive or dominant? How the disorder is treated Medications? Gene therapy? How the disorder is diagnosed What tests are done? Is genetic counseling an option? How many and what type ...
... How the disorder is inherited Is it sex-linked? Is there a particular chromosome it is located on? Is it recessive or dominant? How the disorder is treated Medications? Gene therapy? How the disorder is diagnosed What tests are done? Is genetic counseling an option? How many and what type ...
Laws of Inheritance EnBio
... traits are connected to the diploid genotypes of the plants in the P, F1 , and F2 generations. We will use a second trait that Mendel investigated, seed color, as an example. Seed color is governed by a single gene with two alleles. The yellow-seed allele is dominant and the green-seed allele is rec ...
... traits are connected to the diploid genotypes of the plants in the P, F1 , and F2 generations. We will use a second trait that Mendel investigated, seed color, as an example. Seed color is governed by a single gene with two alleles. The yellow-seed allele is dominant and the green-seed allele is rec ...
Convergent grey and white matter evidence of
... Inventory scores alone. These findings were corroborated by other studies (Kertesz and Munoz, 1998; Bozeat et al., 2000), indicating that disinhibition can be an efficient discriminator of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and patients with FTD, whereas other behavioural symptoms can overlap between ...
... Inventory scores alone. These findings were corroborated by other studies (Kertesz and Munoz, 1998; Bozeat et al., 2000), indicating that disinhibition can be an efficient discriminator of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and patients with FTD, whereas other behavioural symptoms can overlap between ...
CommercialOutbreds07..
... and the inbreeding coefficient rose from 3 to more than 30. We discovered that due to infection the colony had been reformed from a small number of rederived founders, thereby introducing a severe population bottleneck and explaining the changes in genetic architecture. However such drastic changes ...
... and the inbreeding coefficient rose from 3 to more than 30. We discovered that due to infection the colony had been reformed from a small number of rederived founders, thereby introducing a severe population bottleneck and explaining the changes in genetic architecture. However such drastic changes ...
Genetic Testing for Marfan Syndrome, Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms
... Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a systemic connective tissue disorder (CTD) that may have a high degree of clinical variability and phenotypes overlapping with other syndromes and disorders. The diagnosis of most suspected CTDs can be made based on clinical findings and family history. Some of these disord ...
... Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a systemic connective tissue disorder (CTD) that may have a high degree of clinical variability and phenotypes overlapping with other syndromes and disorders. The diagnosis of most suspected CTDs can be made based on clinical findings and family history. Some of these disord ...
Kangaroo Genetics: Impacts of Harvesting (PDF
... hunting and poaching, both of which target elephants with large tusks. Another example is the phenotypic selection on some fish species by gillnetting, which catches larger fish and has changed the phenotype towards early maturity (Law 2000). There is concern also that the selection imposed by harve ...
... hunting and poaching, both of which target elephants with large tusks. Another example is the phenotypic selection on some fish species by gillnetting, which catches larger fish and has changed the phenotype towards early maturity (Law 2000). There is concern also that the selection imposed by harve ...
Laboratory #4: Segregation of Traits According to Mendel
... From this we have that 25% of the progeny have the ‘SS’ genotype and are hence round (homozygous), 50% have the ‘Ss’ genotype and are also round (heterozygous), and 25% of the progeny have the ‘ss’ genotype and are hence wrinkled. Pulling like phenotypes together we have that 75% (25% + 50%) of the ...
... From this we have that 25% of the progeny have the ‘SS’ genotype and are hence round (homozygous), 50% have the ‘Ss’ genotype and are also round (heterozygous), and 25% of the progeny have the ‘ss’ genotype and are hence wrinkled. Pulling like phenotypes together we have that 75% (25% + 50%) of the ...
COMPARING ENVIRONMENTAL AND GENETIC VARIANCE AS
... where they might be more common than previously thought. In multicellular organisms, there are only few well-supported examples for discrete phenotypic distributions due to bet-hedging and these examples almost exclusively deal with occurrence of some type of resting stage (Hopper 1999; Evans and De ...
... where they might be more common than previously thought. In multicellular organisms, there are only few well-supported examples for discrete phenotypic distributions due to bet-hedging and these examples almost exclusively deal with occurrence of some type of resting stage (Hopper 1999; Evans and De ...
Lecture 8
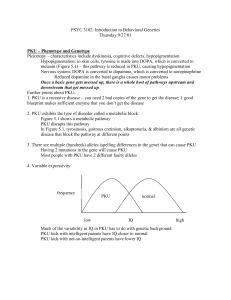
... Test blood for phenylalanine, and if positive, do further tests Impetus behind the testing is that PKU is preventable Issue of mandatory genetic testing: there is a recommendation against genetic testing at birth for disorders that cannot be fixed; if something can be done, as in PKU, then mandatory ...
... Test blood for phenylalanine, and if positive, do further tests Impetus behind the testing is that PKU is preventable Issue of mandatory genetic testing: there is a recommendation against genetic testing at birth for disorders that cannot be fixed; if something can be done, as in PKU, then mandatory ...
Genetic conflict, kin and the origins of novel genetic systems
... a transmission advantage for maternal alleles at the expense of paternal alleles, essentially viewing haplodiploidy as an outcome of maternal-allele victory in a conflict with paternal alleles over transmission by males [3,15,23–28]. Usually, asymmetric genetic systems are those in which the role of ...
... a transmission advantage for maternal alleles at the expense of paternal alleles, essentially viewing haplodiploidy as an outcome of maternal-allele victory in a conflict with paternal alleles over transmission by males [3,15,23–28]. Usually, asymmetric genetic systems are those in which the role of ...
Modelling genotype–phenotype relationships and human disease
... However there are many other classes of interactions that can occur between genes, and approaches have also been devised to begin to identify these interactions systematically (Collins et al., 2006; Drees et al., 2005; Hartman and Tippery, 2004; Schuldiner et al., 2005). For example, Schuldiner et a ...
... However there are many other classes of interactions that can occur between genes, and approaches have also been devised to begin to identify these interactions systematically (Collins et al., 2006; Drees et al., 2005; Hartman and Tippery, 2004; Schuldiner et al., 2005). For example, Schuldiner et a ...
GENES AND SPECIATION
... ‘weak effect–strong interaction’ — that is, each individual gene has little effect on its own, but in combination, these genes cause reproductive incompatibility10. Functional studies of one of these interacting genes (OdsH; see below) have indeed shown that it has an extremely weak effect. Despite ...
... ‘weak effect–strong interaction’ — that is, each individual gene has little effect on its own, but in combination, these genes cause reproductive incompatibility10. Functional studies of one of these interacting genes (OdsH; see below) have indeed shown that it has an extremely weak effect. Despite ...
Polygenic Traits
... Another exception to Mendel’s rules is polygenic inheritance, which occurs when a trait is controlled by more than one gene. This means that each dominant allele "adds" to the expression of the next dominant allele. Usually, traits are polygenic when there is wide variation in the trait. For example ...
... Another exception to Mendel’s rules is polygenic inheritance, which occurs when a trait is controlled by more than one gene. This means that each dominant allele "adds" to the expression of the next dominant allele. Usually, traits are polygenic when there is wide variation in the trait. For example ...
1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 C2: 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0
... asexual or single-child crossover as well. (2) Mutation: changing gene value(s) –lets offspring evolve in new directions; otherwise, population traits may become fixed ; introduces a certain amount of randomness to the search. (3) Replication: copy an individual without alteration ...
... asexual or single-child crossover as well. (2) Mutation: changing gene value(s) –lets offspring evolve in new directions; otherwise, population traits may become fixed ; introduces a certain amount of randomness to the search. (3) Replication: copy an individual without alteration ...
When Christian Faith and Genetics Meet
... Here are some examples of recent developments in Canada. An international team of scientists from Canada, China, Japan, the U.K. and the U.S. has been collaborating since 2002 on what is known as the HapMap Project. Research published in 2007 allows scientists to detect minute fractions of genetic m ...
... Here are some examples of recent developments in Canada. An international team of scientists from Canada, China, Japan, the U.K. and the U.S. has been collaborating since 2002 on what is known as the HapMap Project. Research published in 2007 allows scientists to detect minute fractions of genetic m ...
Deleterious mutations can reduce differentiation in small, subdivided
... Effects of deleterious mutations are examined with fixed values of s = h = 0.1. Background selection reduces somewhat the heterozygosity at the linked neutral locus when we assume one population of size N = 100. The same holds for a subdivided population. The total heterozygosity in a subdivided pop ...
... Effects of deleterious mutations are examined with fixed values of s = h = 0.1. Background selection reduces somewhat the heterozygosity at the linked neutral locus when we assume one population of size N = 100. The same holds for a subdivided population. The total heterozygosity in a subdivided pop ...
Evolution of Phenotypic Robustness
... Within adaptive robustness, two main types may be distinguished, marking the endpoints of a scale. The first, mechanistic type corresponds to the classic view of canalization. Here, the trait and its buffering mechanism are genetically independent. Since the selective advantage of buffering depends ...
... Within adaptive robustness, two main types may be distinguished, marking the endpoints of a scale. The first, mechanistic type corresponds to the classic view of canalization. Here, the trait and its buffering mechanism are genetically independent. Since the selective advantage of buffering depends ...
High-resolution haplotype structure in the human genome
... because the higher mutation rate at such sites8,9 might introduce recurrent mutation and thereby confound the analysis. Of the 16 high frequency CpG SNPs genotyped, 13 had alleles that aligned perfectly with the haplotype patterns in Fig. 1 and only one added significantly to the overall heterozygos ...
... because the higher mutation rate at such sites8,9 might introduce recurrent mutation and thereby confound the analysis. Of the 16 high frequency CpG SNPs genotyped, 13 had alleles that aligned perfectly with the haplotype patterns in Fig. 1 and only one added significantly to the overall heterozygos ...
PSYB1 Biopsychology Short Qs JM09 December
... 29. Outline what is meant by adoption studies and explain why they are used by psychologists. (5 marks) Jan 04 AO1 Maximum of two marks for a description of adoption studies, eg involves comparing a characteristic or trait between adopted children and children of their biological parents. Reference ...
... 29. Outline what is meant by adoption studies and explain why they are used by psychologists. (5 marks) Jan 04 AO1 Maximum of two marks for a description of adoption studies, eg involves comparing a characteristic or trait between adopted children and children of their biological parents. Reference ...
Polygenic Traits
... Polygenic inheritance often results in a bell shaped curve when you analyze the population ( Figure 1.1). That means that most people fall in the middle of the phenotypic range, such as average height, while very few people are at the extremes, such as very tall or very short. At one end of the curv ...
... Polygenic inheritance often results in a bell shaped curve when you analyze the population ( Figure 1.1). That means that most people fall in the middle of the phenotypic range, such as average height, while very few people are at the extremes, such as very tall or very short. At one end of the curv ...
Generation Means Analysis of the Twin
... S2 progenies were self-pollinated to the S7 generation. Twin-ear expression of the S7 generation was 16%, but progenies ranged from 0-42.1%. Expression of twin-ear in S8 progenies was 37.9%, with a range among progenies from 0-85%. Additional evaluations of twin-ear for estimates of penetrance were ...
... S2 progenies were self-pollinated to the S7 generation. Twin-ear expression of the S7 generation was 16%, but progenies ranged from 0-42.1%. Expression of twin-ear in S8 progenies was 37.9%, with a range among progenies from 0-85%. Additional evaluations of twin-ear for estimates of penetrance were ...
Behavioural genetics

Behavioural genetics, also commonly referred to as behaviour genetics, is the field of study that examines the role of genetic and environmental influences on animal (including human) behaviour. Often associated with the ""nature versus nurture"" debate, behavioural genetics is highly interdisciplinary, involving contributions from biology, neuroscience, genetics, epigenetics, ethology, psychology, and statistics. Behavioural geneticists study the inheritance of behavioural traits. In humans, this information is often gathered through the use of the twin study or adoption study. In animal studies, breeding, transgenesis, and gene knockout techniques are common. Psychiatric genetics is a closely related field.