Text (Open Access) - Reading`s CentAUR
... alleles for selfishness can reach frequencies around 50%. We evaluate quantitative estimates of b, c and r from field studies in the light of these predictions, but the values do not fall in the regions where genetic polymorphisms are expected. Nevertheless, it will be interesting to see as genes fo ...
... alleles for selfishness can reach frequencies around 50%. We evaluate quantitative estimates of b, c and r from field studies in the light of these predictions, but the values do not fall in the regions where genetic polymorphisms are expected. Nevertheless, it will be interesting to see as genes fo ...
Vorms final version + images
... The early history of classical genetics provides us with a fascinating case of interdisciplinary research. The laying and consolidation of its essential components, in the 1910’s and 1920’s, resulted to a large extent from the integration of two modes of analysis, corresponding to two different disc ...
... The early history of classical genetics provides us with a fascinating case of interdisciplinary research. The laying and consolidation of its essential components, in the 1910’s and 1920’s, resulted to a large extent from the integration of two modes of analysis, corresponding to two different disc ...
Department of Biomedical Informatics
... The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) [pronounced "snip"] is the most common form of genetic variation. As the name suggests, each SNP is a difference in a single nucleotide (A,T,C,or G) of an individual's DNA sequence, such as having AAGG instead of ATGG. There may be from 1 to 10 million SNPs i ...
... The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) [pronounced "snip"] is the most common form of genetic variation. As the name suggests, each SNP is a difference in a single nucleotide (A,T,C,or G) of an individual's DNA sequence, such as having AAGG instead of ATGG. There may be from 1 to 10 million SNPs i ...
tutorial in biostatistics genetic mapping of complex traits
... sets of 23 chromosomes, one maternal and one paternal in origin. One of the 23 pairs of chromosomes are the sex chromosomes, and we shall concern ourselves with the remaining 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes in this tutorial. Each chromosome consists of a long strand of DNA, a linear molecule with ...
... sets of 23 chromosomes, one maternal and one paternal in origin. One of the 23 pairs of chromosomes are the sex chromosomes, and we shall concern ourselves with the remaining 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes in this tutorial. Each chromosome consists of a long strand of DNA, a linear molecule with ...
To clone or not to clone plant QTLs
... the consequence of mating behaviour and others. However, within such models polygenes are usually dealt with as a whole, whereas the actual genes remain in what has been defined as a ‘statistical fog’ [2]. Within this framework, the problem of understanding the molecular nature of quantitative trait ...
... the consequence of mating behaviour and others. However, within such models polygenes are usually dealt with as a whole, whereas the actual genes remain in what has been defined as a ‘statistical fog’ [2]. Within this framework, the problem of understanding the molecular nature of quantitative trait ...
2001_butterfield_THE SUGARCANE GENOME
... is further evidence that the chromosome complement of S. officinarum does not consist of eight equal sets of ten homologous linkage groups, and may in fact differ between clones. Ming et al. (1998) suggested that the preferential pairing of S. robustum and S. officinarum, and a monoploid number of 1 ...
... is further evidence that the chromosome complement of S. officinarum does not consist of eight equal sets of ten homologous linkage groups, and may in fact differ between clones. Ming et al. (1998) suggested that the preferential pairing of S. robustum and S. officinarum, and a monoploid number of 1 ...
Chapter 3
... • Actual approaches for detecting aggregation depend on the nature of the phenotype, but the common factor in existing approaches is that they are taken without any specific genetic model in mind. • The basic design of familial aggregation studies typically involves sampling families • In most place ...
... • Actual approaches for detecting aggregation depend on the nature of the phenotype, but the common factor in existing approaches is that they are taken without any specific genetic model in mind. • The basic design of familial aggregation studies typically involves sampling families • In most place ...
Brooker Chapter 4
... Heterozygosity at a locus creates a phenotype that is more beneficial or more deterimental than homozygosity of either locus with any allele ...
... Heterozygosity at a locus creates a phenotype that is more beneficial or more deterimental than homozygosity of either locus with any allele ...
NATURAL POPULATIONS OF DROSOPHZLA PSEUDOOBSCURAl
... is q.sl = (2 7/2)/(8 7 -4- 1) = .55. Such a method can give only a very crude estimate of the frequency of alleles in the original sample brought into the laboratory, except for Strawberry Canyon where the sample was examined in the F, and F, generations from the wild. Since these original samples w ...
... is q.sl = (2 7/2)/(8 7 -4- 1) = .55. Such a method can give only a very crude estimate of the frequency of alleles in the original sample brought into the laboratory, except for Strawberry Canyon where the sample was examined in the F, and F, generations from the wild. Since these original samples w ...
Lessons from Founder Populations - Digital Commons @ RU
... genome reference sequence in 2004 (The Human Genome Project, 2004). Another landmark achievement was the release, in 2005, by the HapMap Consortium, of the first phase of an international effort to discover and expand the catalogue of human single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). As a result, by Aug ...
... genome reference sequence in 2004 (The Human Genome Project, 2004). Another landmark achievement was the release, in 2005, by the HapMap Consortium, of the first phase of an international effort to discover and expand the catalogue of human single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). As a result, by Aug ...
Mendel`s Work - the science center
... generation, were purebred because they always produced offspring with the same trait as the parent. In all of Mendel’s crosses, only one form of the trait appeared in the F1 generation. However, in the F2 generation, the “lost” form of the trait always reappeared in about one fourth of the plants. F ...
... generation, were purebred because they always produced offspring with the same trait as the parent. In all of Mendel’s crosses, only one form of the trait appeared in the F1 generation. However, in the F2 generation, the “lost” form of the trait always reappeared in about one fourth of the plants. F ...
Bio 111 Handout for Genetics 1 Bio 111 iClicker Question #1
... In lecture, I talked about “counting unrelated carriers” - finding out how many people had to bring in a disease allele to explain a particular pedigree. This was useful in the case where more than one mode of inheritance was possible but you were asked to determine which was more likely. There are ...
... In lecture, I talked about “counting unrelated carriers” - finding out how many people had to bring in a disease allele to explain a particular pedigree. This was useful in the case where more than one mode of inheritance was possible but you were asked to determine which was more likely. There are ...
Does genetic diversity limit disease spread in natural host
... Does genetic diversity limit disease spread in natural host populations? KC King1 and CM Lively2 It is a commonly held view that genetically homogenous host populations are more vulnerable to infection than genetically diverse populations. The underlying idea, known as the ‘monoculture effect,’ is w ...
... Does genetic diversity limit disease spread in natural host populations? KC King1 and CM Lively2 It is a commonly held view that genetically homogenous host populations are more vulnerable to infection than genetically diverse populations. The underlying idea, known as the ‘monoculture effect,’ is w ...
Introduction to Genetics
... X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated X-inactivation occurs so that the female, with two X chromosomes, does not have twice as many X chromosome gene products as the male, which only posse ...
... X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated X-inactivation occurs so that the female, with two X chromosomes, does not have twice as many X chromosome gene products as the male, which only posse ...
Mendel`s Laws: Human Inheritance of Single Gene Traits
... genotypes: RR, Rr, and rr. 1. The probability of receiving R from both parents (RR genotype) is p x p, or p2. 2. The probability of receiving r from both parents (rr genotype) is q x q, or q2. 3. Receiving the Rr combination is described by 2pq since it is possible for the R or r allele to come from ...
... genotypes: RR, Rr, and rr. 1. The probability of receiving R from both parents (RR genotype) is p x p, or p2. 2. The probability of receiving r from both parents (rr genotype) is q x q, or q2. 3. Receiving the Rr combination is described by 2pq since it is possible for the R or r allele to come from ...
Subset-Based Ant Colony Optimisation for the Discovery of Gene
... 1.1 Previous Research Keywords ...
... 1.1 Previous Research Keywords ...
GAs
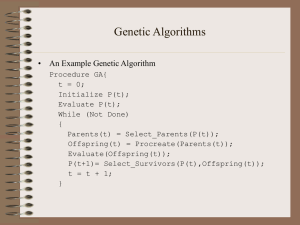
... Parent Selection Methods • GA researchers have used a number of parent selection methods. Some of the more popular methods are: – Proportionate Selection – Linear Rank Selection – Tournament Selection ...
... Parent Selection Methods • GA researchers have used a number of parent selection methods. Some of the more popular methods are: – Proportionate Selection – Linear Rank Selection – Tournament Selection ...
Medical genetic studies in the Amish: Historical perspective
... In the more than 40 years since this research has started, there have been notable changes among the Amish as well. to reach an Amish farmer on his cell phone. In addition, the pressure of encroaching suburbs is slowly eroding the farmland of Lancaster County, causing families to disperse to settlem ...
... In the more than 40 years since this research has started, there have been notable changes among the Amish as well. to reach an Amish farmer on his cell phone. In addition, the pressure of encroaching suburbs is slowly eroding the farmland of Lancaster County, causing families to disperse to settlem ...
Genetic Algorithms
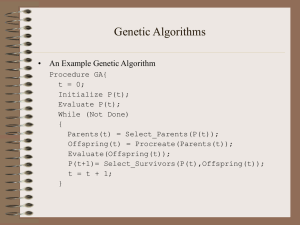
... Parent Selection Methods • GA researchers have used a number of parent selection methods. Some of the more popular methods are: – Proportionate Selection – Linear Rank Selection – Tournament Selection ...
... Parent Selection Methods • GA researchers have used a number of parent selection methods. Some of the more popular methods are: – Proportionate Selection – Linear Rank Selection – Tournament Selection ...
Key Points on Allele Dominance
... b. If either of an organism’s alleles is the ______________ allele, the trait given by this allele will be seen in the organism’s ______________. c. The trait given by the recessive allele will only be seen in the organism’s phenotype if the other allele is also the ______________ ______________. 4. ...
... b. If either of an organism’s alleles is the ______________ allele, the trait given by this allele will be seen in the organism’s ______________. c. The trait given by the recessive allele will only be seen in the organism’s phenotype if the other allele is also the ______________ ______________. 4. ...
Here - Personal Genome Project Study Guide
... caused by mutations in the DMD gene. The DMD gene codes for a protein called dystrophin that is necessary for muscle cells to maintain their shape. When this protein is missing, muscle cells literally burst as material from outside the cell membrane leaks in, raising cell pressure. Mutations in the ...
... caused by mutations in the DMD gene. The DMD gene codes for a protein called dystrophin that is necessary for muscle cells to maintain their shape. When this protein is missing, muscle cells literally burst as material from outside the cell membrane leaks in, raising cell pressure. Mutations in the ...
controversy and its implications Genetic hitchhiking versus
... et al. 2003) and several plant species such as wild tomatoes (Stephan & Langley 1998; Roselius et al. 2005)), it has provoked extensive modelling and analysis efforts. The development of methods for distinguishing BGS and hitchhiking was a major activity in those years (until about 2000). An importa ...
... et al. 2003) and several plant species such as wild tomatoes (Stephan & Langley 1998; Roselius et al. 2005)), it has provoked extensive modelling and analysis efforts. The development of methods for distinguishing BGS and hitchhiking was a major activity in those years (until about 2000). An importa ...
controversy and its implications Genetic hitchhiking versus
... et al. 2003) and several plant species such as wild tomatoes (Stephan & Langley 1998; Roselius et al. 2005)), it has provoked extensive modelling and analysis efforts. The development of methods for distinguishing BGS and hitchhiking was a major activity in those years (until about 2000). An importa ...
... et al. 2003) and several plant species such as wild tomatoes (Stephan & Langley 1998; Roselius et al. 2005)), it has provoked extensive modelling and analysis efforts. The development of methods for distinguishing BGS and hitchhiking was a major activity in those years (until about 2000). An importa ...
Complex” inheritance - CSC's mainpage — CSC
... each other, colonize a previously uninhabited island. Assume that the alleles at different loci in each populations are in linkage equilibrium, and that a rare “Mendelian” trait, with causative allele(s) “D”, is only present in one of the two populations. If one sampled case and control individuals ...
... each other, colonize a previously uninhabited island. Assume that the alleles at different loci in each populations are in linkage equilibrium, and that a rare “Mendelian” trait, with causative allele(s) “D”, is only present in one of the two populations. If one sampled case and control individuals ...
What is individual quality? An evolutionary
... describe environmentally-induced heterogeneity in life history traits which, as has long been recognised, can complicate and potentially bias the measurement of ecologically and evolutionary important processes [4,24,29,30]. For example, cohort and maternal effects can have important and long lastin ...
... describe environmentally-induced heterogeneity in life history traits which, as has long been recognised, can complicate and potentially bias the measurement of ecologically and evolutionary important processes [4,24,29,30]. For example, cohort and maternal effects can have important and long lastin ...
Behavioural genetics

Behavioural genetics, also commonly referred to as behaviour genetics, is the field of study that examines the role of genetic and environmental influences on animal (including human) behaviour. Often associated with the ""nature versus nurture"" debate, behavioural genetics is highly interdisciplinary, involving contributions from biology, neuroscience, genetics, epigenetics, ethology, psychology, and statistics. Behavioural geneticists study the inheritance of behavioural traits. In humans, this information is often gathered through the use of the twin study or adoption study. In animal studies, breeding, transgenesis, and gene knockout techniques are common. Psychiatric genetics is a closely related field.